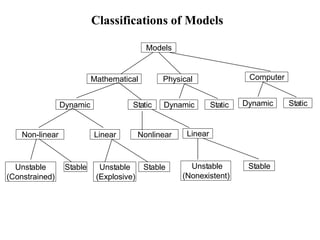
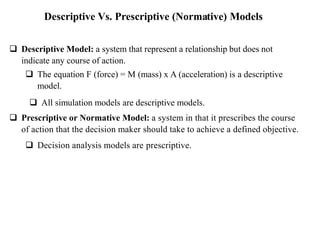
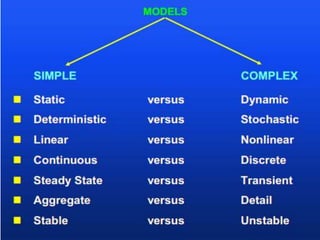
This document discusses different types of models used in computer science and engineering. It defines models as representations and abstractions of real or proposed systems. Models are classified as mathematical, physical, static, dynamic, linear, nonlinear, stable, unstable, analytical, numerical, descriptive, and prescriptive. Examples are provided for each type to illustrate the distinctions between mathematical, physical, static, dynamic, linear, nonlinear, stable, unstable, analytical, numerical, descriptive, and prescriptive models. Distributed-lag and autoregressive models are also introduced as special cases of regression models.