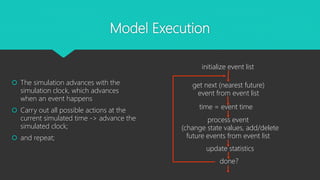
This presentation introduces discrete-event simulation software. It discusses what discrete-event simulation is, how it models systems as sequences of events over time. It covers the basic constructs like entities, resources, control elements and operations. It explains how simulation execution advances by processing the next event. It discusses entity states like active, ready, time-delayed and conditional-delayed. It also summarizes different implementations in discrete-event modeling languages and tools like Arena and AutoMod.










![Group Members
Rawnat Jahan Anika [183 019 042]
Subho Mrong [163 019 042]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/discrete-event-simulation-190410063238/85/Discrete-event-simulation-13-320.jpg)
