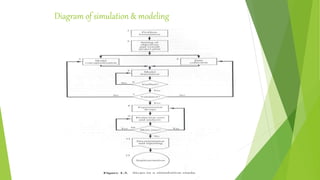
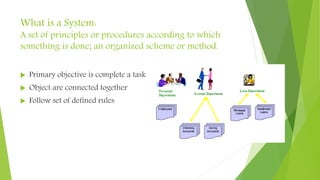
The document discusses the significance of simulation and system modeling in engineering, highlighting the process of creating digital prototypes to predict real-world performance of physical models. It outlines the workflow of simulation modeling, the conditions under which simulation is necessary, and the advantages and disadvantages of using such models. Additionally, it explains types of models, the concept of a system, and key components essential for effective simulation.