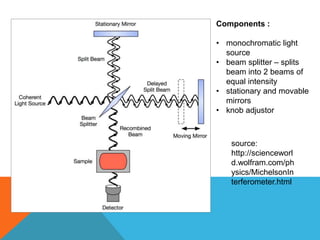
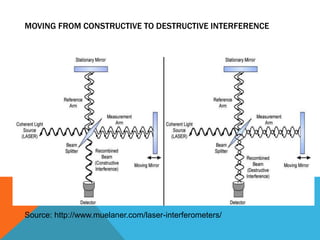
The Michelson interferometer splits a beam of monochromatic light into two beams using a beam splitter. One beam reflects off a stationary mirror while the other reflects off a movable mirror before recombining at the beam splitter. As the movable mirror is adjusted, the interference pattern of light and dark projected changes, allowing the number of alterations between constructive and destructive interference to be counted. By tracking this change over a known distance, the wavelength of the light can be calculated.