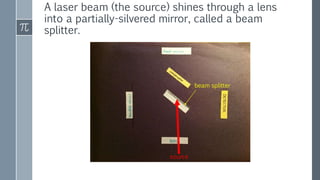
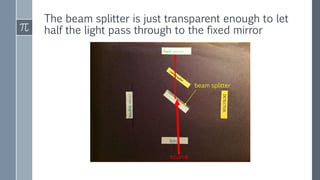
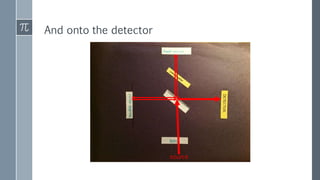
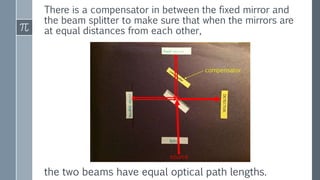
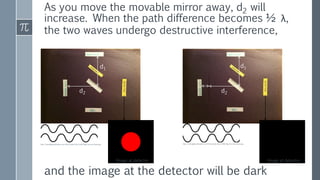
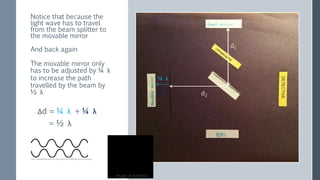
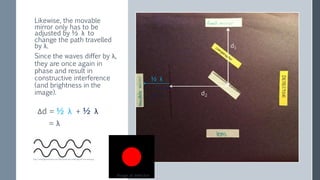
The Michelson interferometer uses a laser beam that is split by a partially-silvered mirror (beam splitter) into two beams that travel different paths and are reflected by mirrors. When the beams recombine at the detector, their interference creates bright or dark bands depending on the difference between their path lengths (path difference). Initially with equal path lengths, the center is bright, but as one mirror moves further, increasing the path difference by half wavelengths, the center alternates between dark and bright as the path difference causes first destructive then constructive interference.