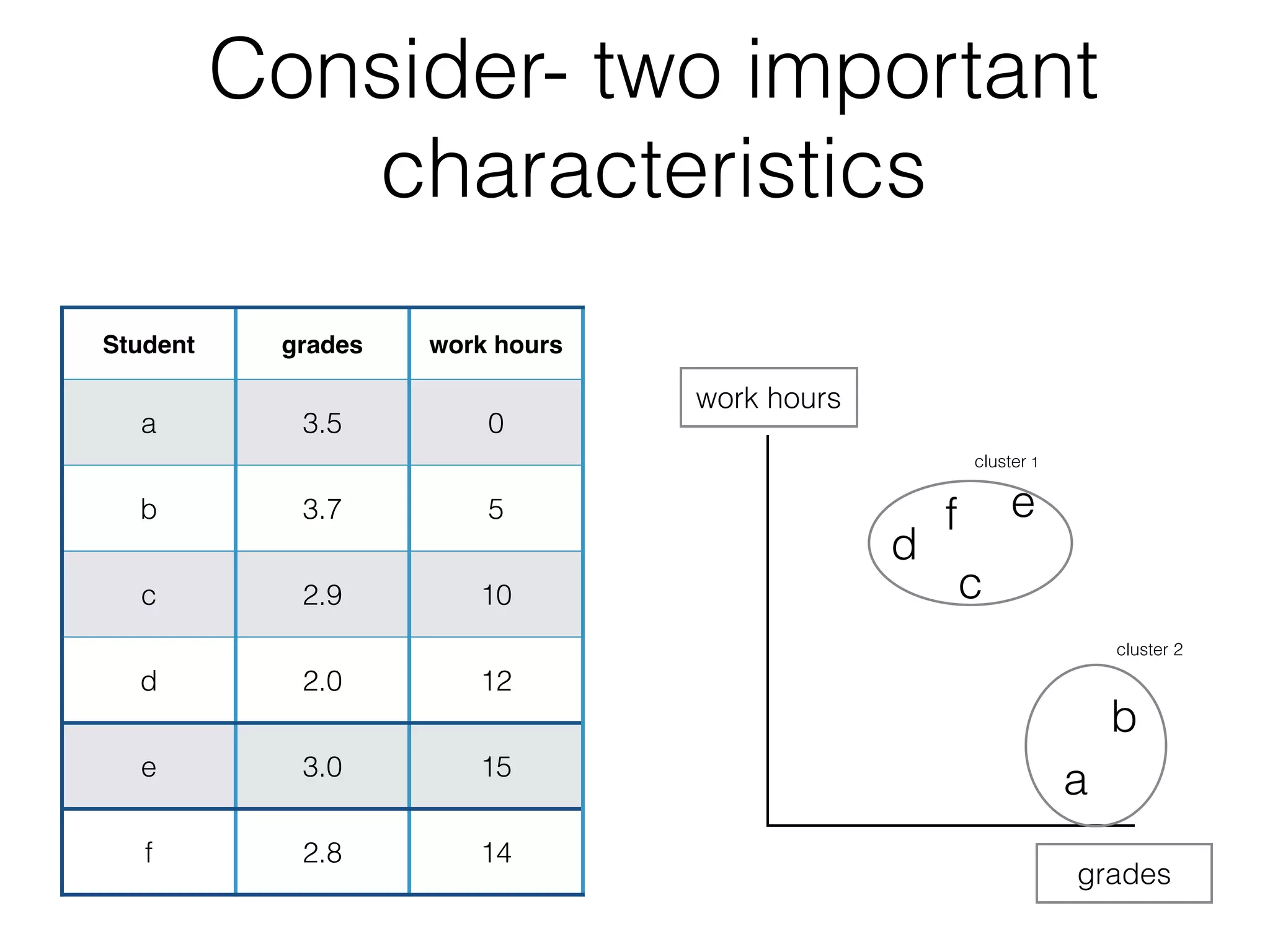
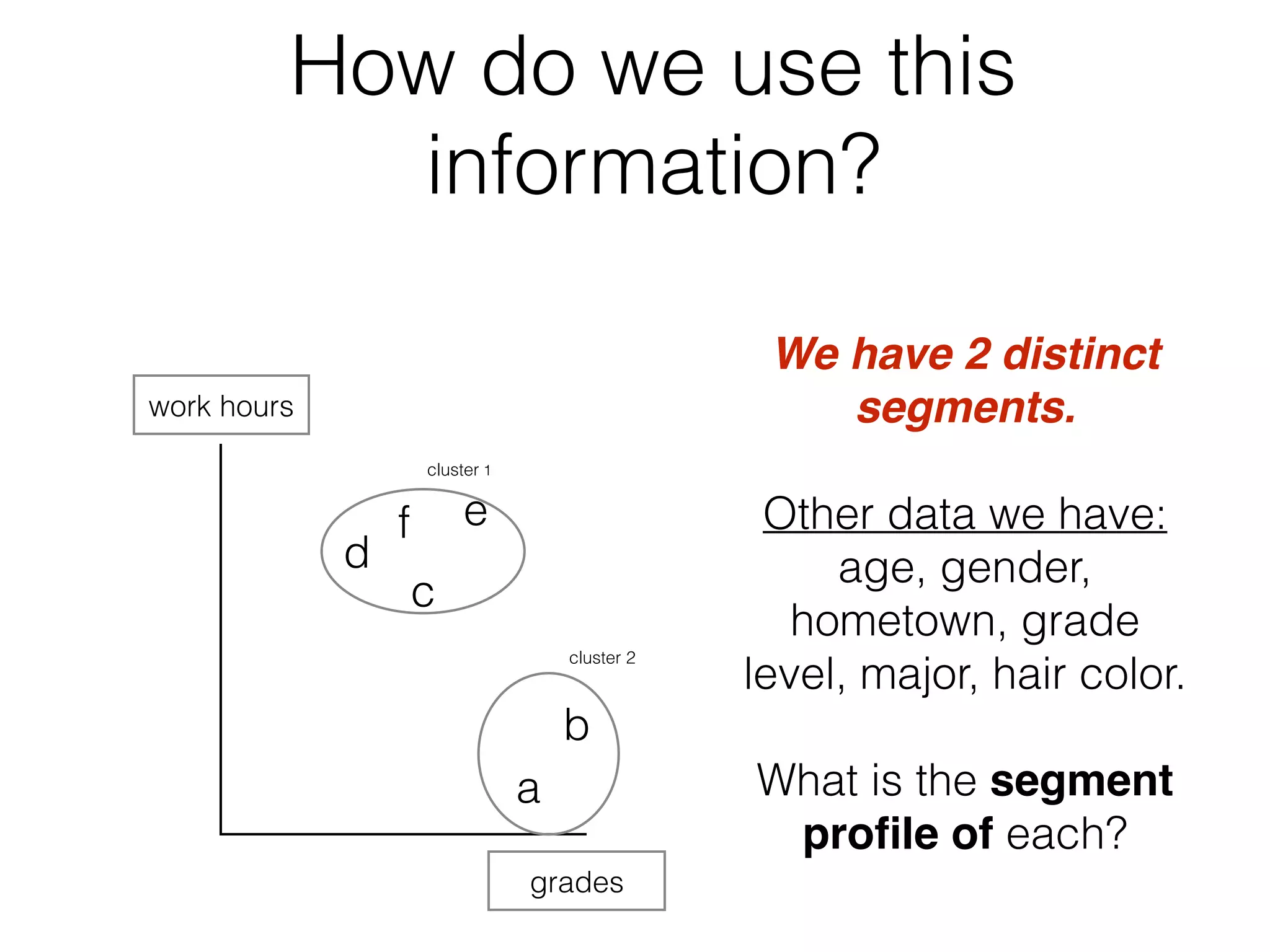
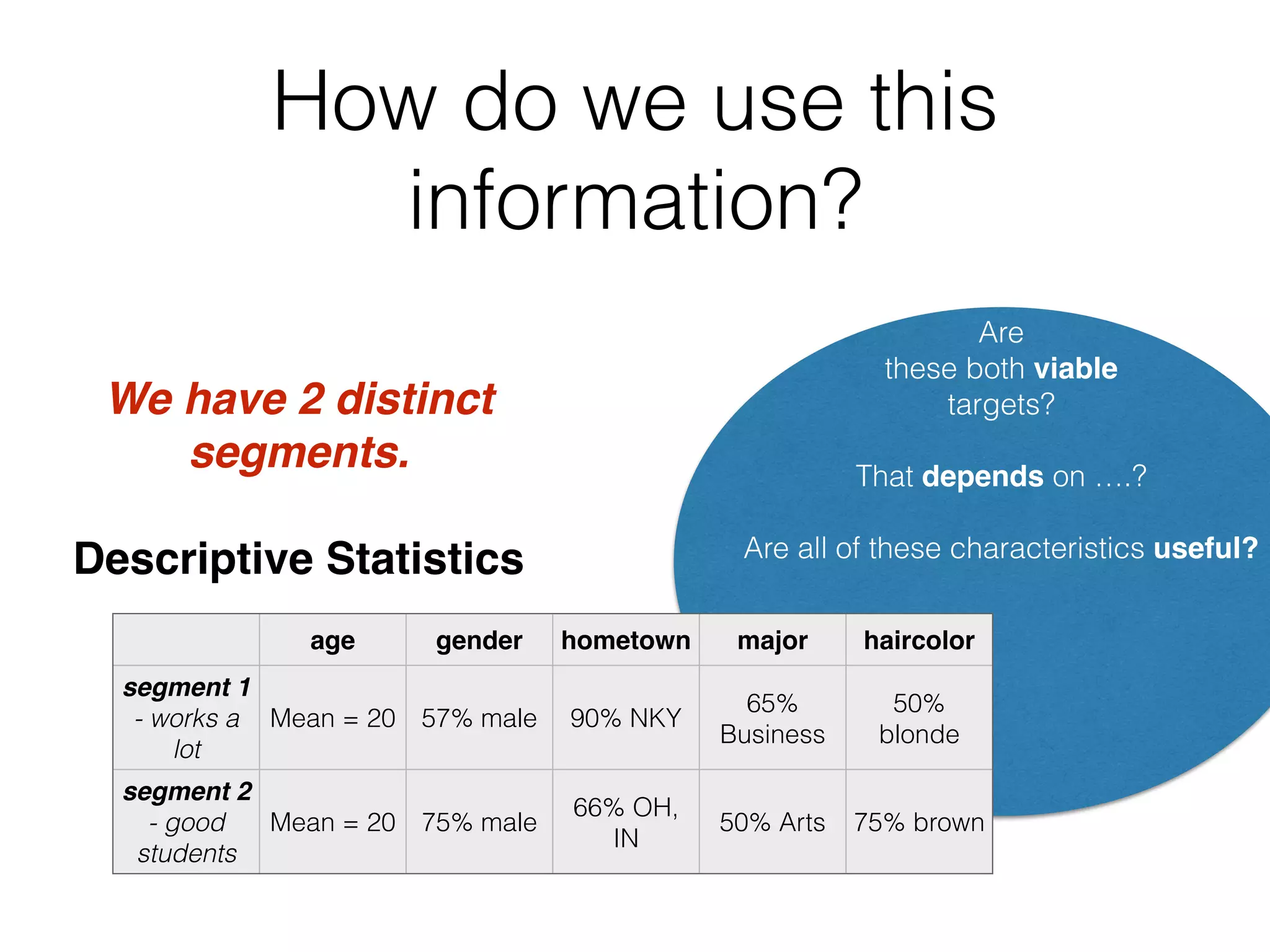
This document discusses cluster analysis, which is the process of grouping a set of data into clusters. Cluster analysis is used to discover distinct groups or segments in data like customer bases. It groups observations so that observations within each cluster are similar to each other but dissimilar to observations in other clusters. Cluster analysis is used in marketing to develop targeted programs for different customer segments. Insurance companies also use it to group drivers into risk levels and set premiums accordingly. The document provides steps for performing cluster analysis using SPSS, including warnings about variables to avoid and ideal numbers of clusters.