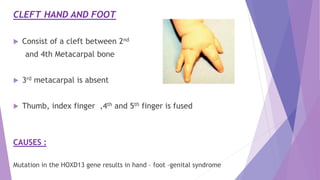
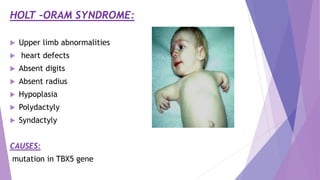
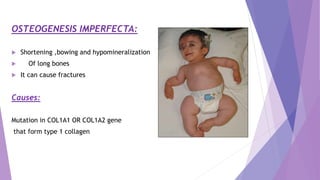
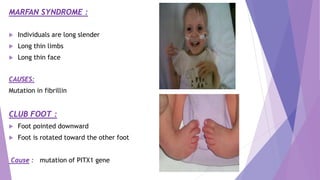
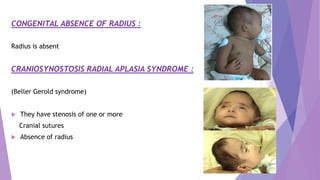
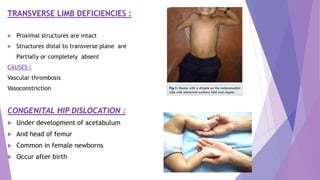
This document discusses various congenital limb defects including:
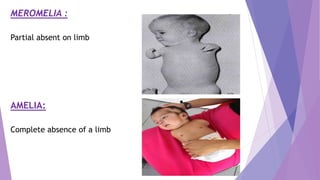
- Meromelia which is the partial absence of a limb
- Amelia which is the complete absence of a limb
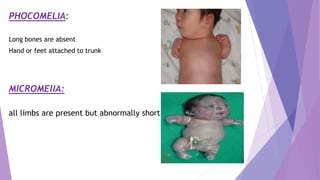
- Phocomelia where the long bones are absent and the hands/feet are attached to the trunk
- Micomelia where all limbs are present but abnormally short
The causes of many limb defects are genetic mutations affecting genes like HOXD13, TBX5, COL1A1, COL1A2, and fibrillin. Environmental factors like vascular problems in utero can also lead to transverse limb deficiencies.