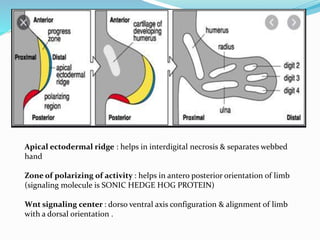
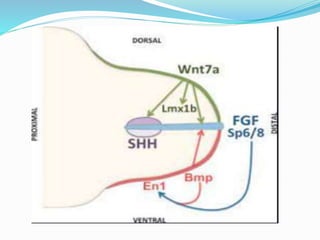
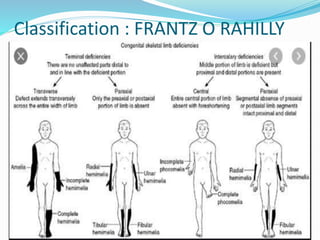
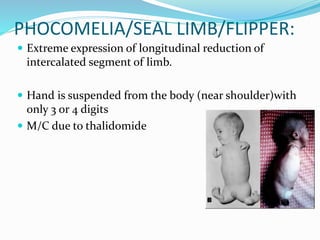
The document discusses congenital anomalies related to limb development, highlighting critical signaling centers involved in embryogenesis. It classifies various types of congenital defects such as hemimelia, phocomelia, and radial dysplasia, detailing their characteristics and classifications. Treatment approaches, ranging from conservative methods to surgical interventions, are also outlined for these conditions.