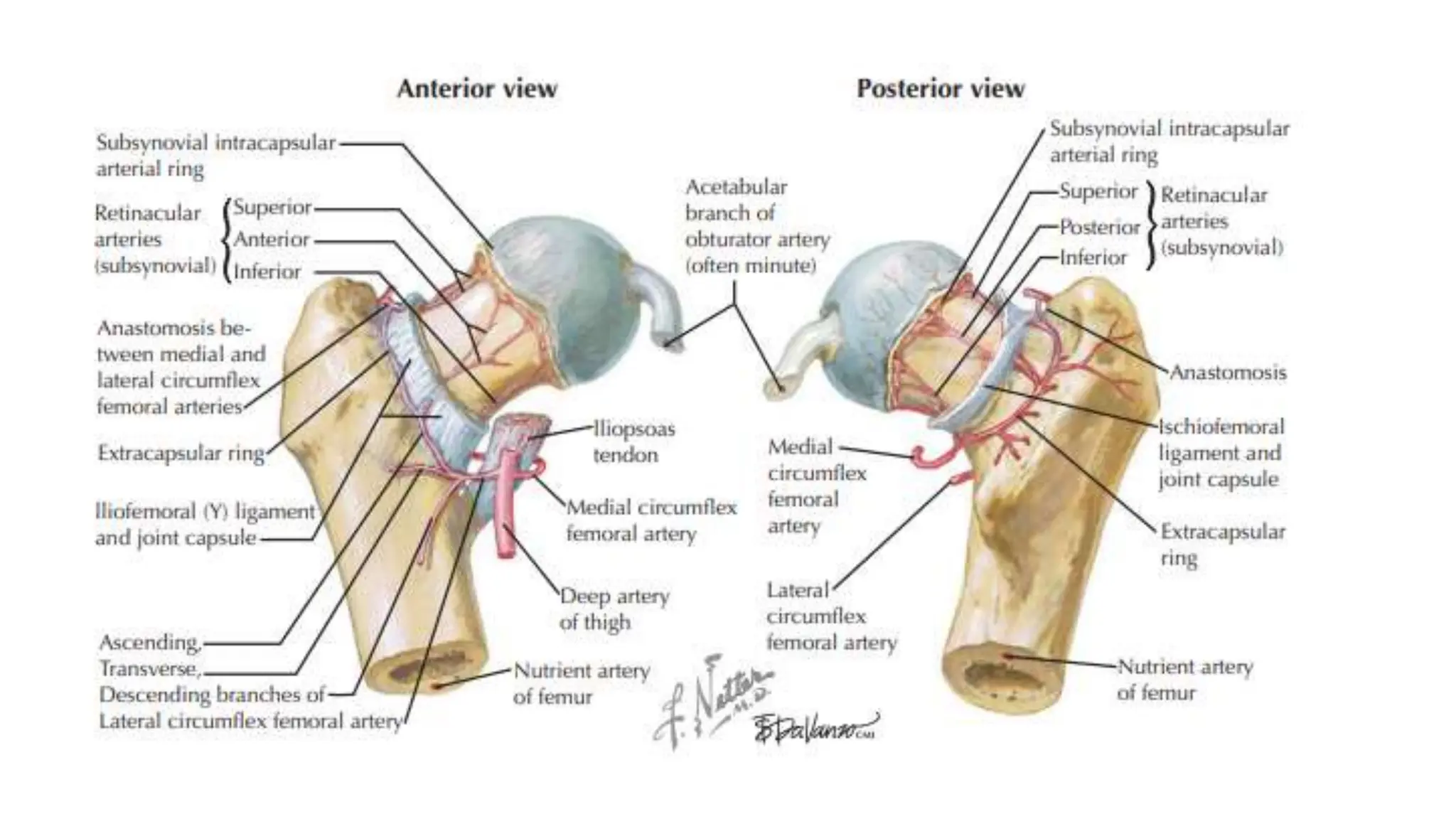
The medial and lateral femoral circumflex arteries are the primary blood suppliers to the adult femoral head. The medial femoral circumflex artery courses behind the femoral neck and gives rise to the extracapsular arterial ring at the base of the neck. The lateral femoral circumflex artery courses along the anterior femoral neck. In children, the ligamentum teres artery also contributes significantly to femoral head blood supply, but its importance decreases with age as the medial femoral circumflex artery becomes the predominant supplier by age 8.