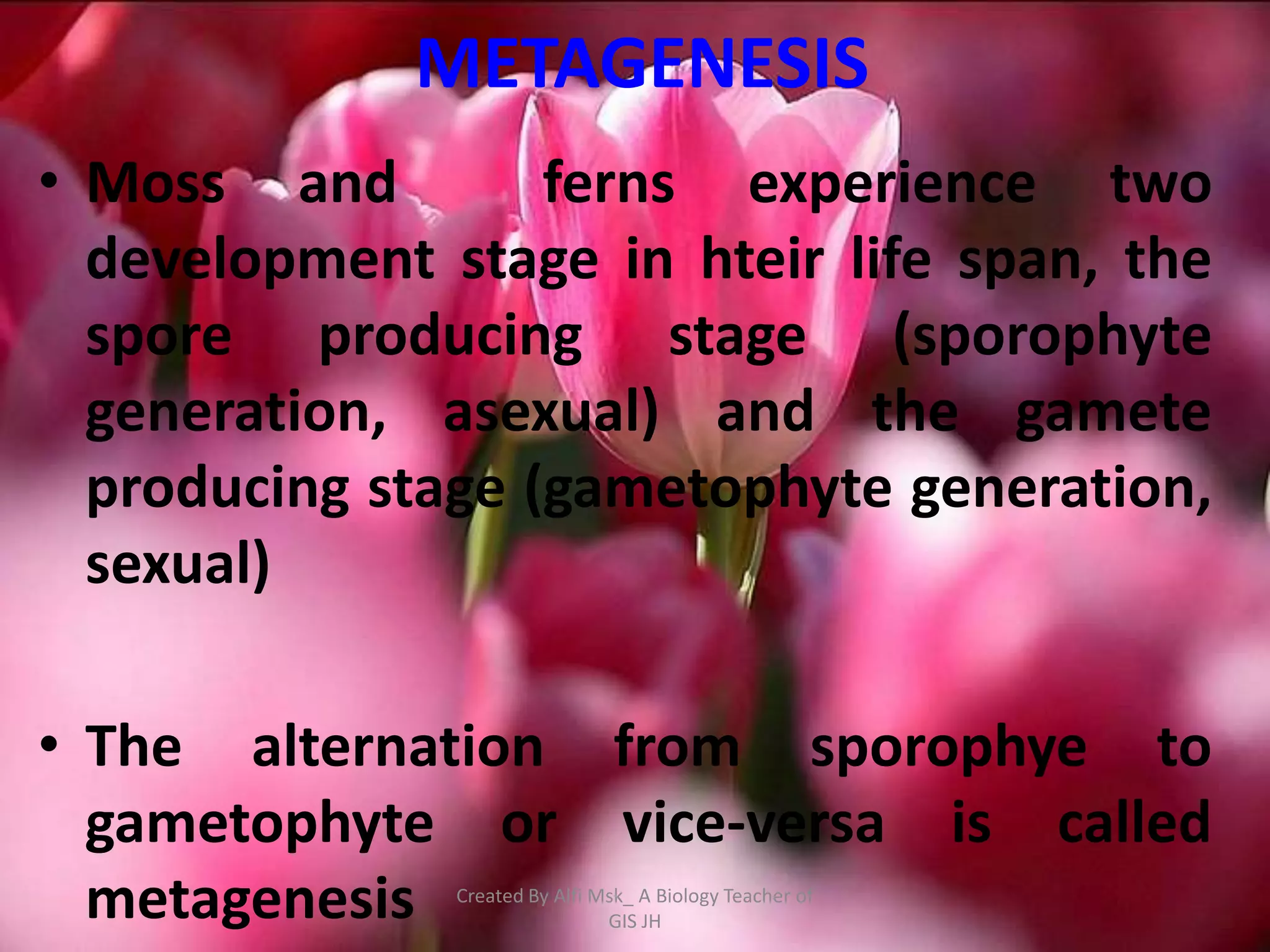
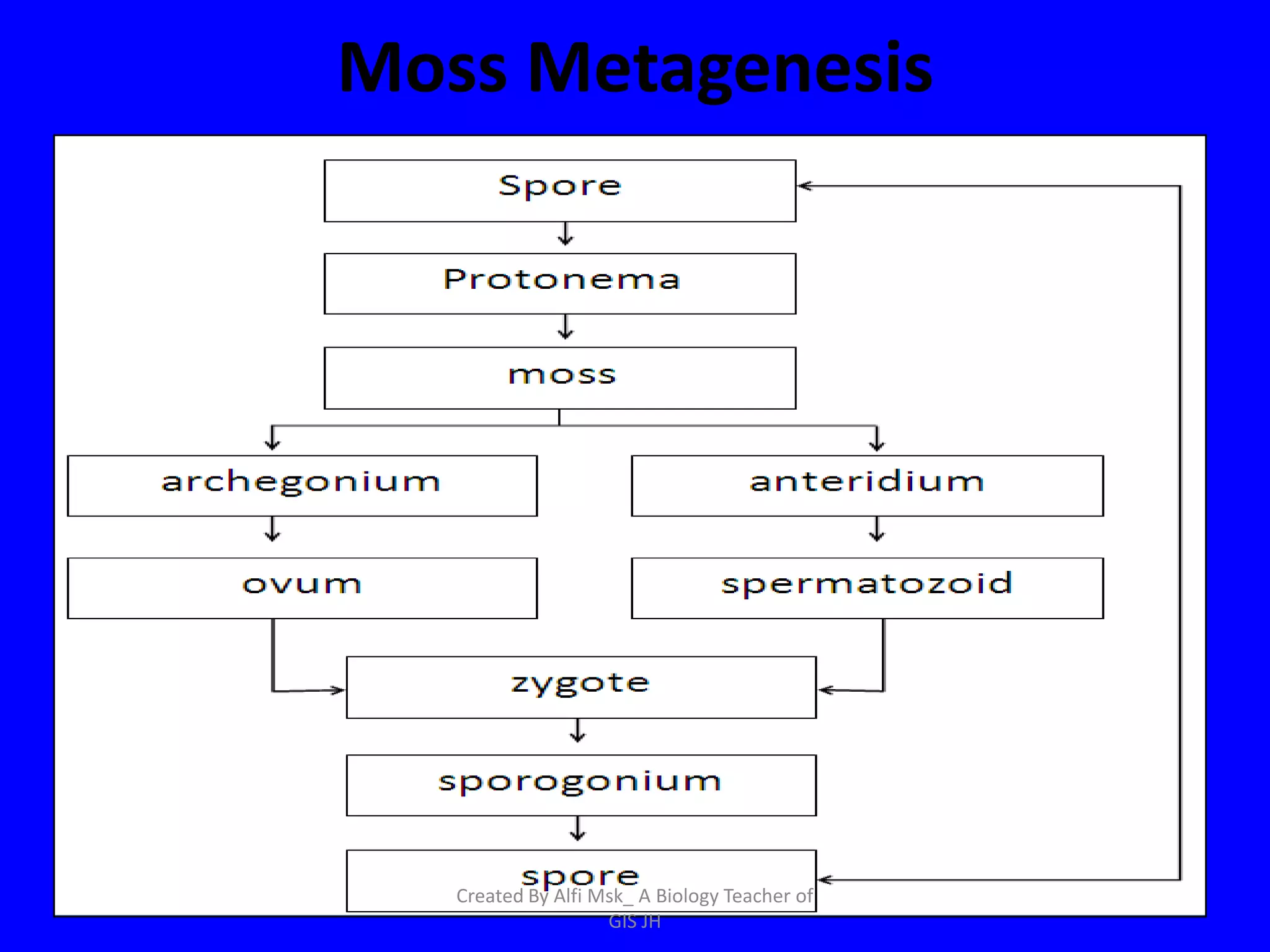
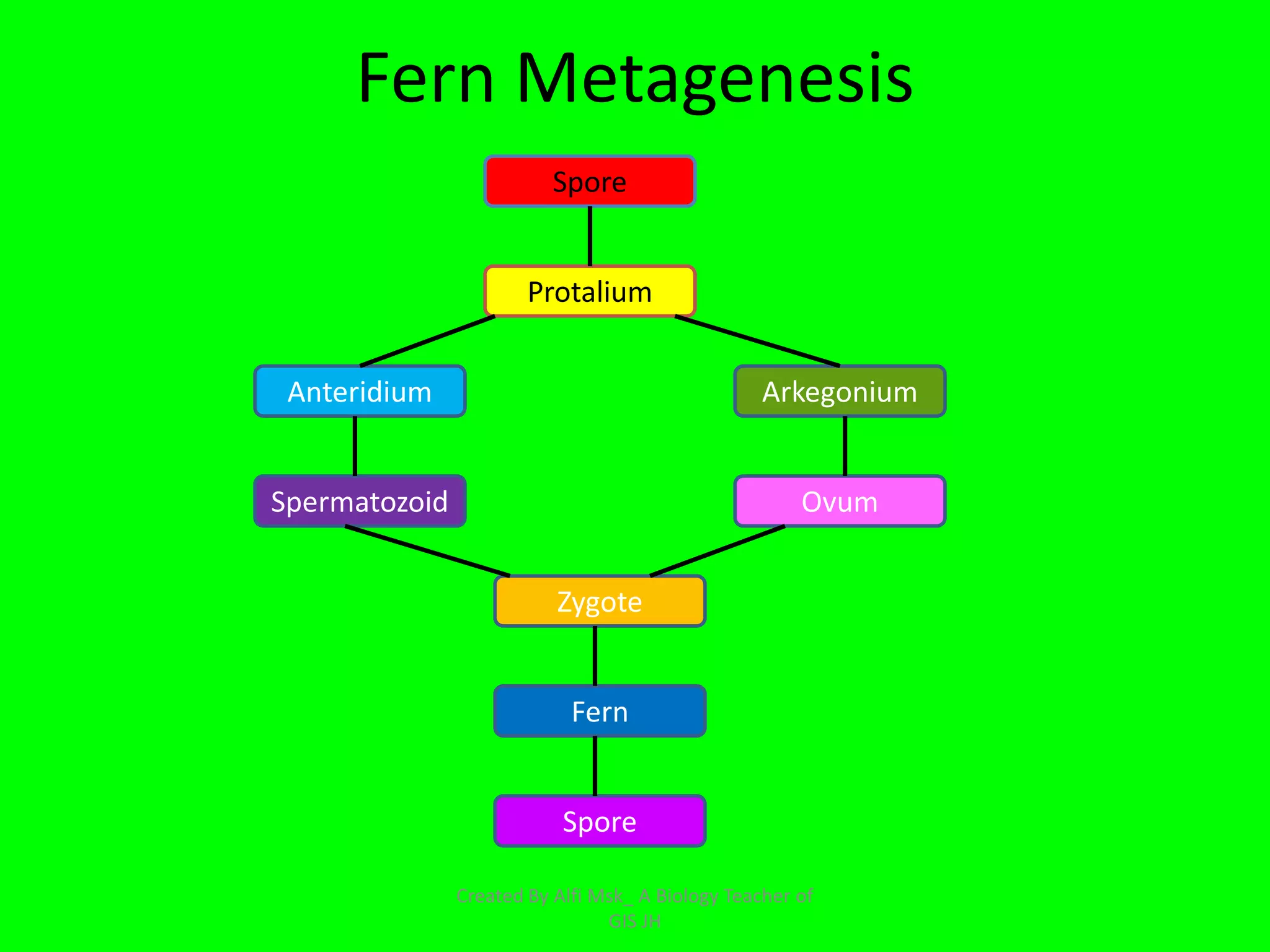
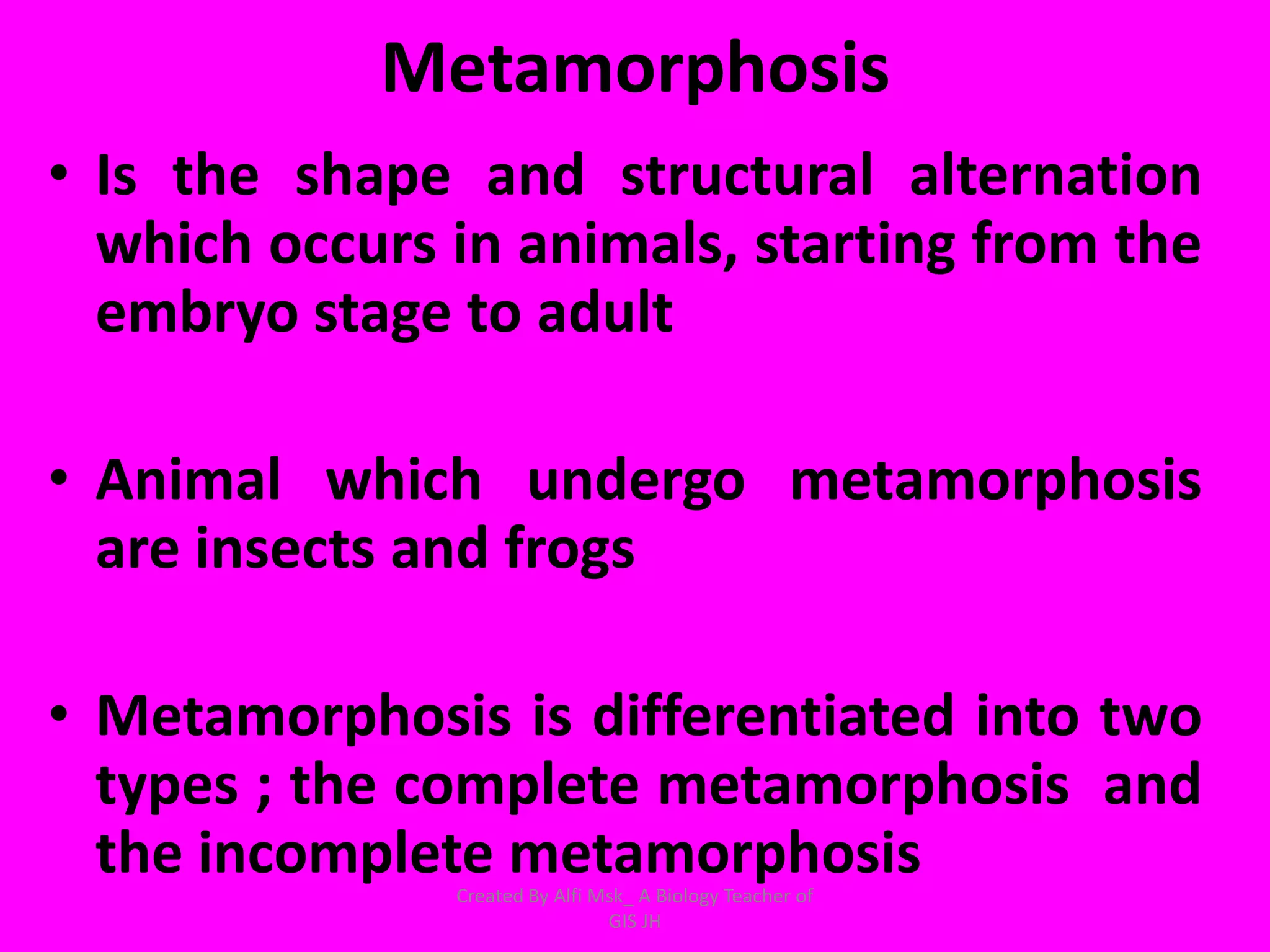
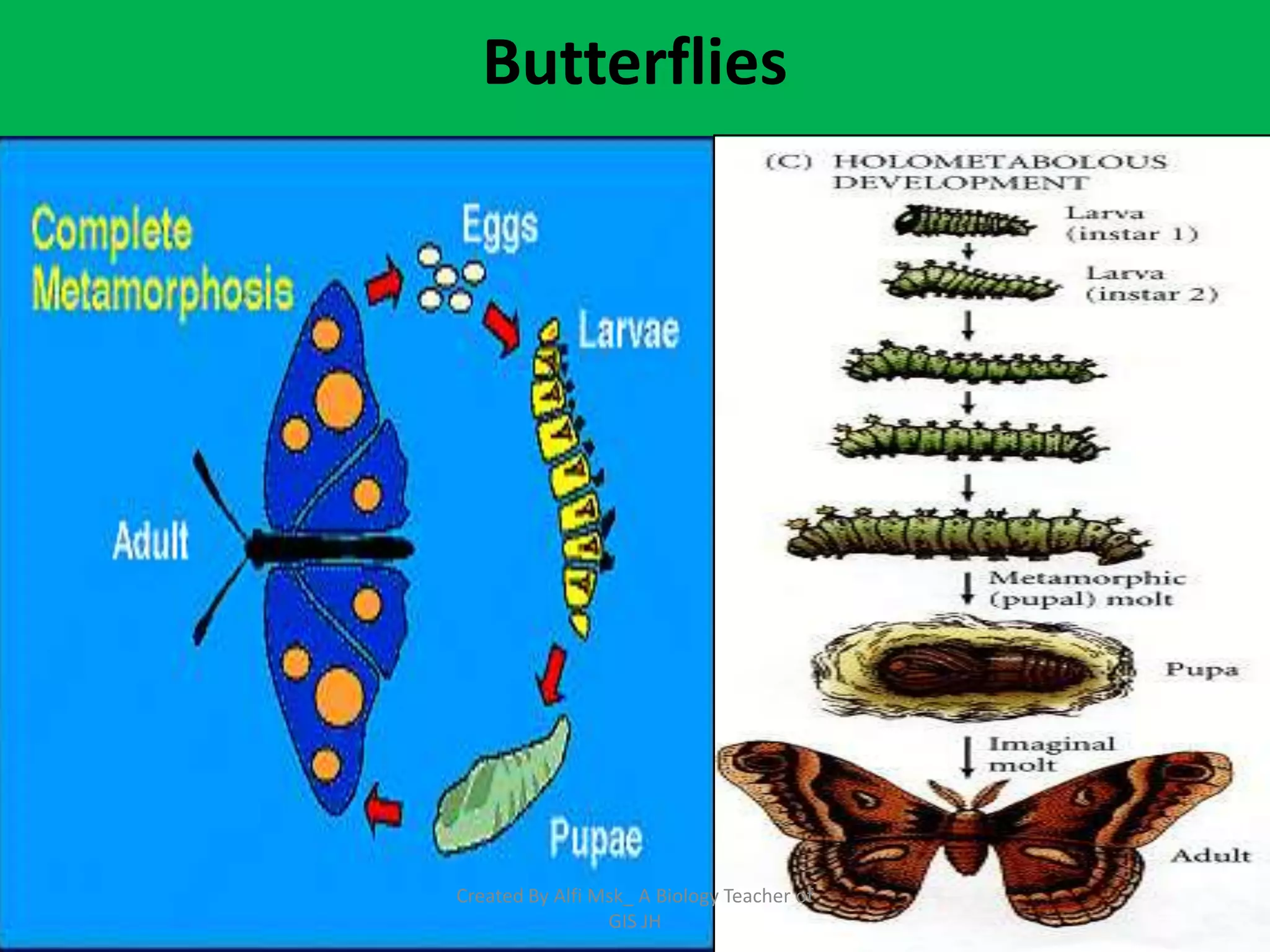
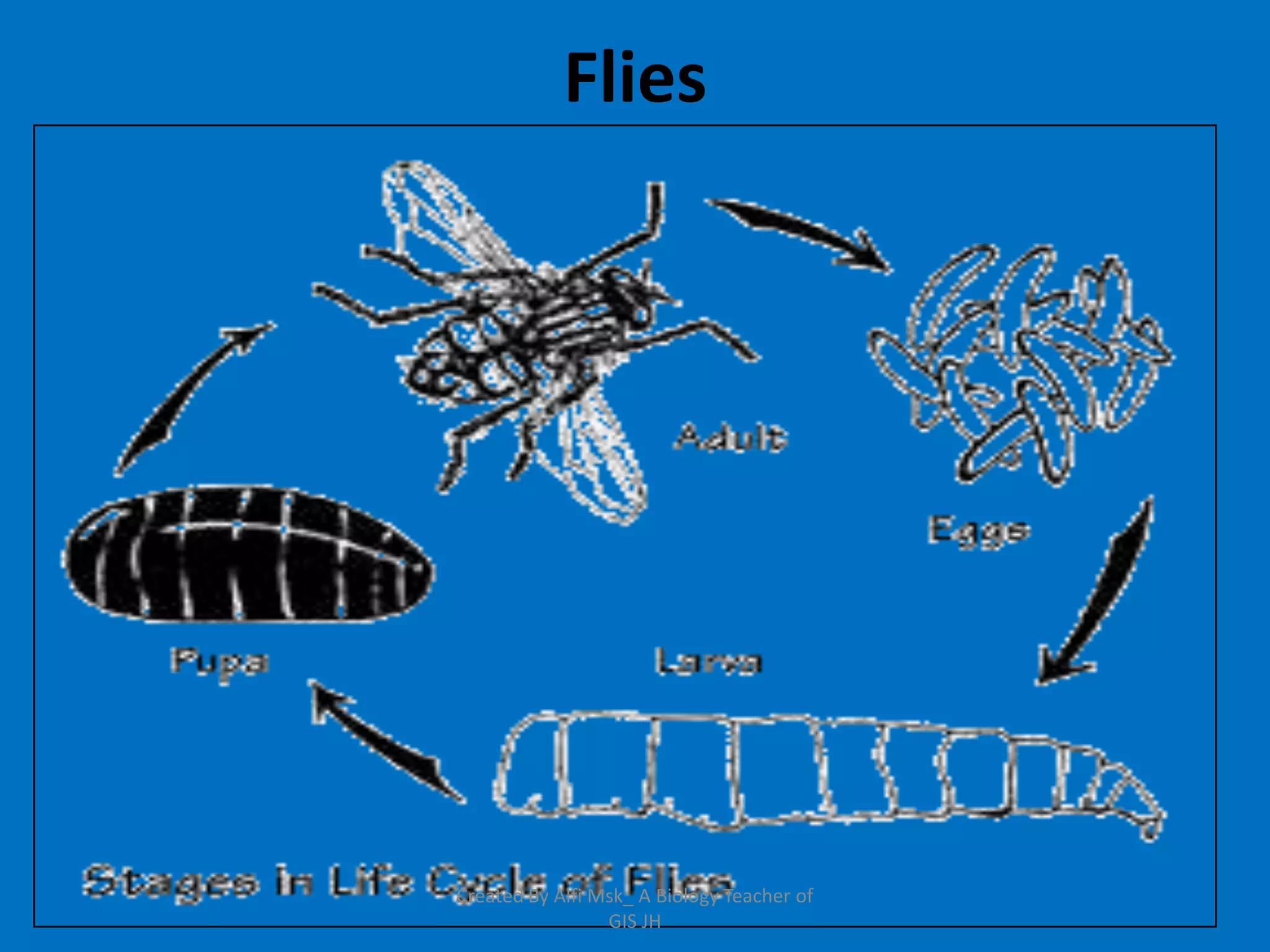
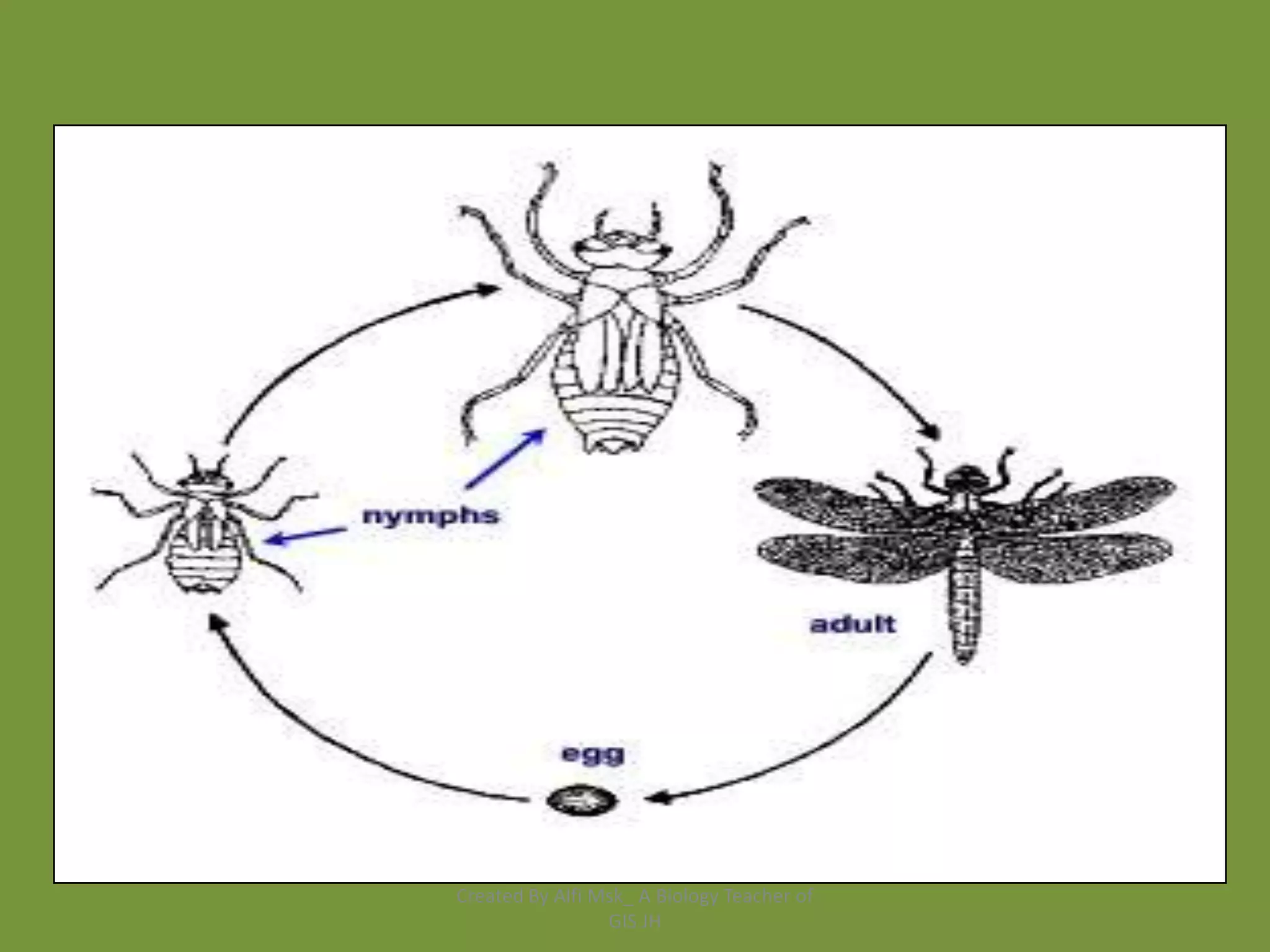
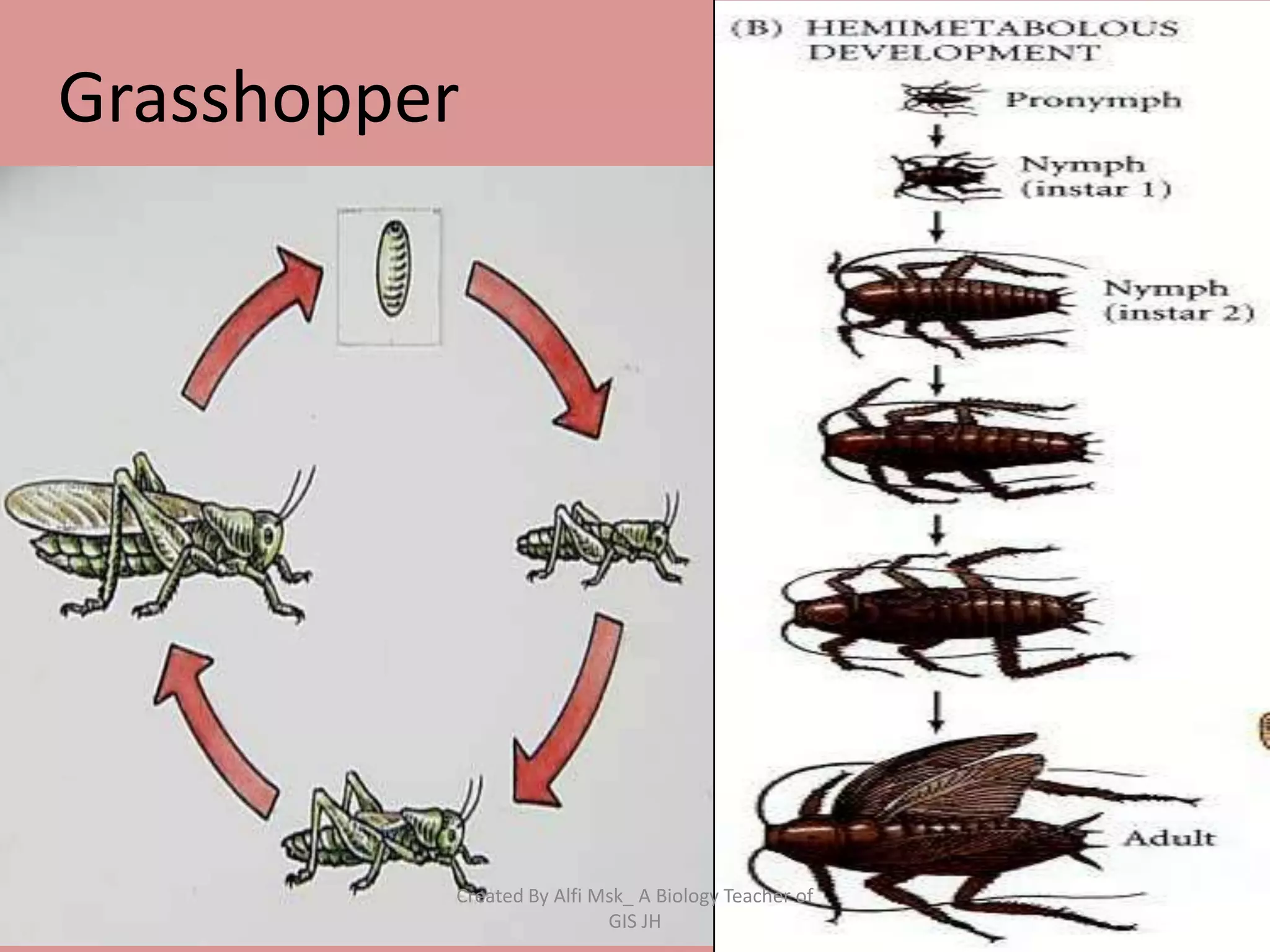
1. The document defines growth as an increase in size that is quantitative and irreversible, while development is a process towards maturity that is qualitative.
2. In plants, growth occurs through cell division and enlargement, primarily in root tips, stem tips, and secondary growth in woody stems. Development begins as a zygote and progresses to an embryo, then a plant with organs.
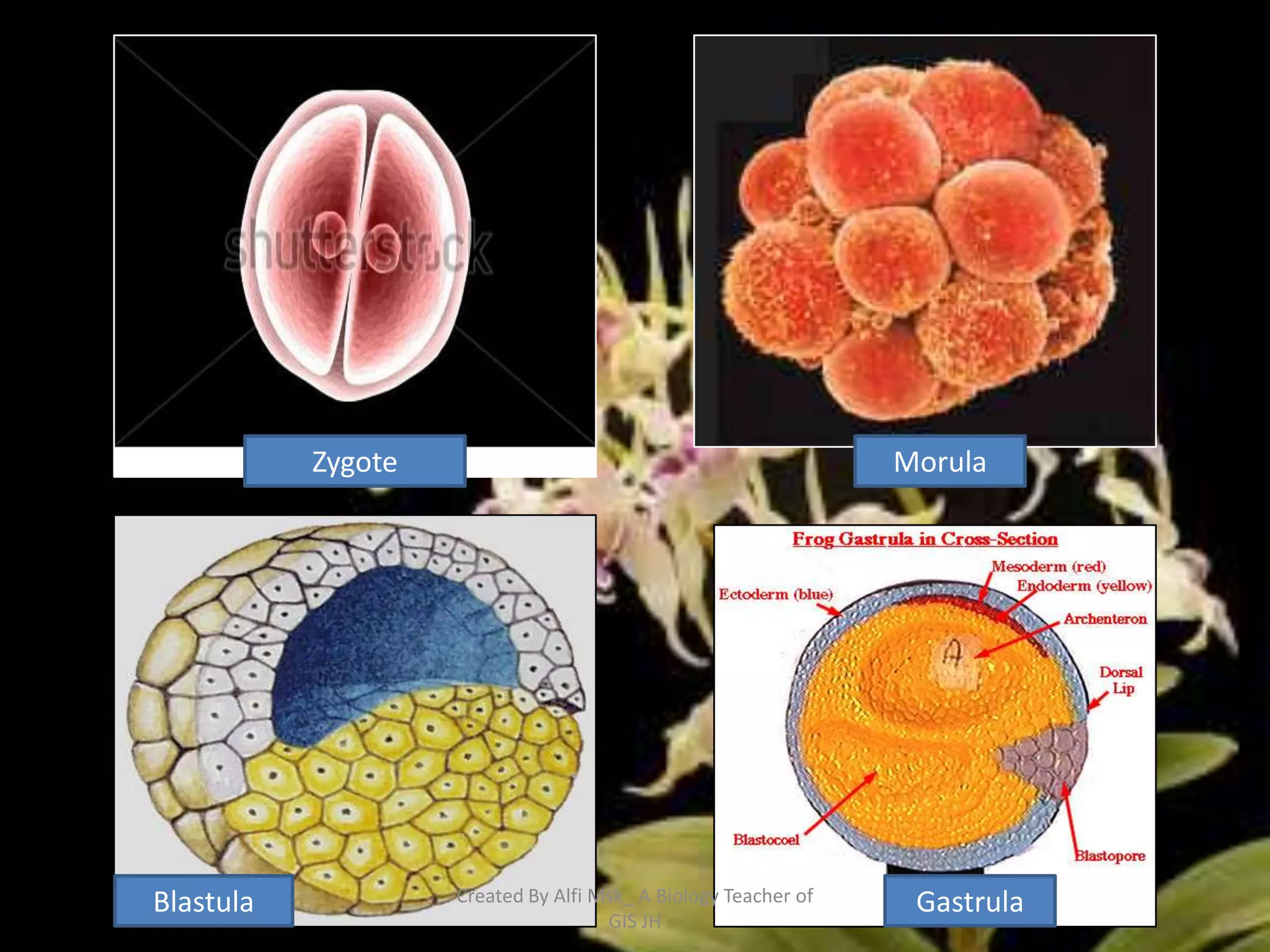
3. In animals and humans, growth and development begin as a zygote and progress through embryonic and post-embryonic phases as an embryo forms and the individual matures.