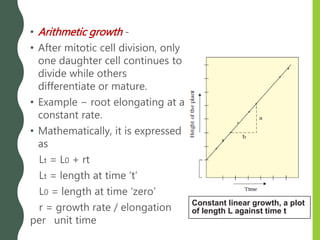
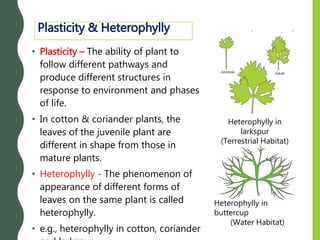
All cells of a plant develop from the zygote. The zygote produces more cells through growth and differentiation to form tissues, organs, and the full plant body. Growth is defined as a permanent increase in size through cellular processes. There are two types of growth rates - arithmetic and geometric. Plant development includes growth and differentiation guided by plant hormones and responses to environmental cues like photoperiodism and vernalization.