1. Growth and development are processes that occur simultaneously in organisms. Growth involves an increase in size through cell division and expansion, while development involves qualitative changes that lead to maturity.
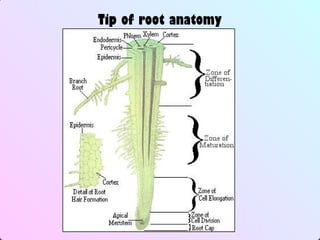
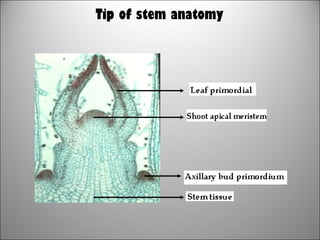
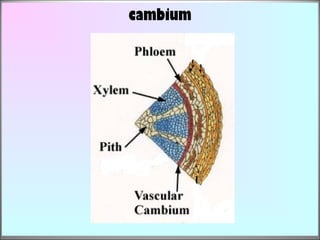
2. In plants, growth occurs in meristematic regions through primary growth in length and secondary growth in thickness. Plant growth and development are influenced by internal factors like genes and hormones, and external factors like nutrients, water, light, temperature, and oxygen.
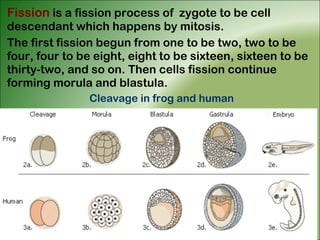
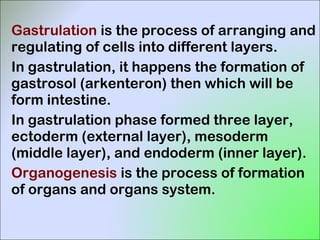
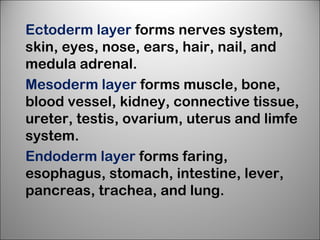
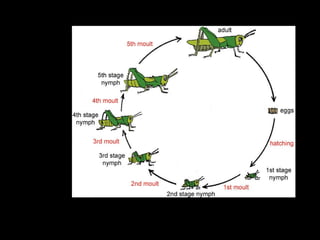
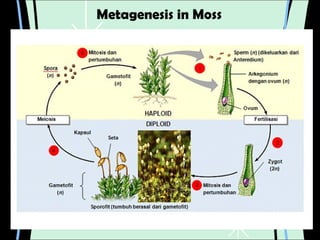
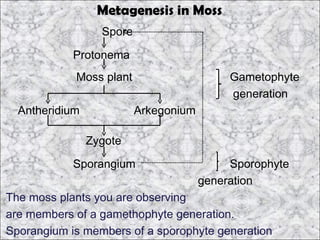
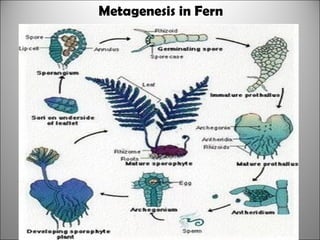
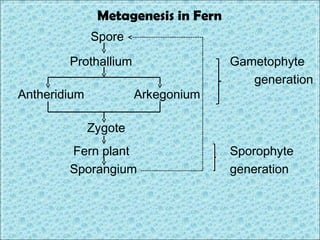
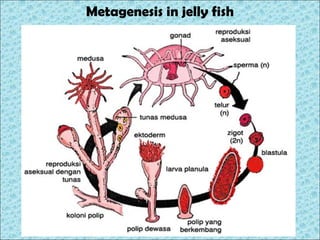
3. Animal growth and development occur through cell division, gastrulation, and organogenesis. It is influenced by internal hormones and external nutrients, water, light, temperature, and oxygen. Some animals undergo metamorphosis or metagenesis between life stages.