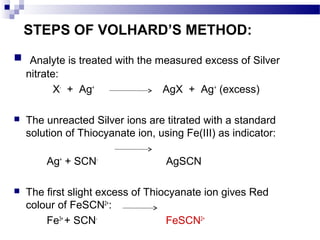
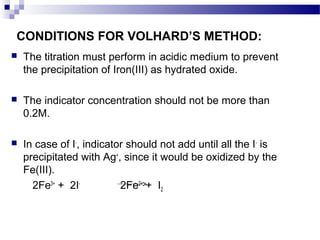
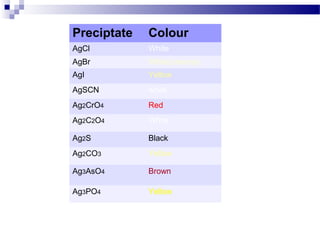
Volhard's method is an indirect argentometric titration procedure used to determine anions that precipitate with silver ions. It involves adding excess silver nitrate to the analyte to form a silver salt precipitate. The unreacted silver ions are then back titrated with a standard thiocyanate solution using an iron(III) indicator to detect the endpoint color change from red to bright lemon yellow. Volhard's method is useful for determining halides and other anions like phosphate, arsenate, and chromate, especially in acidic conditions where carbonate and oxalate do not interfere.