This chapter discusses key concepts in public speaking including:
1) The power of public speaking and how it has allowed many to spread ideas throughout history.
2) Similarities and differences between public speaking and conversation, noting public speaking requires more structure and formal language.
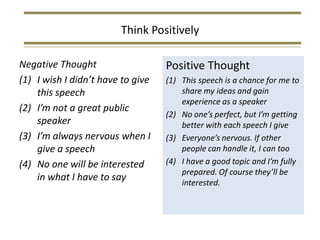
3) Developing confidence in public speaking and transforming nervousness into "positive nervousness" through preparation and experience.
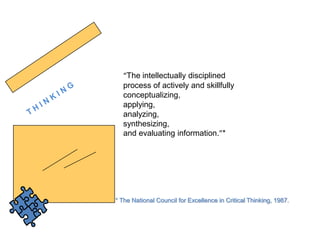
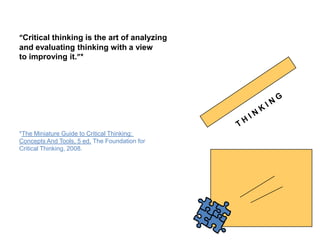
4) The importance of critical thinking in public speaking and its role in developing traits like intellectual humility, autonomy, and fairness.