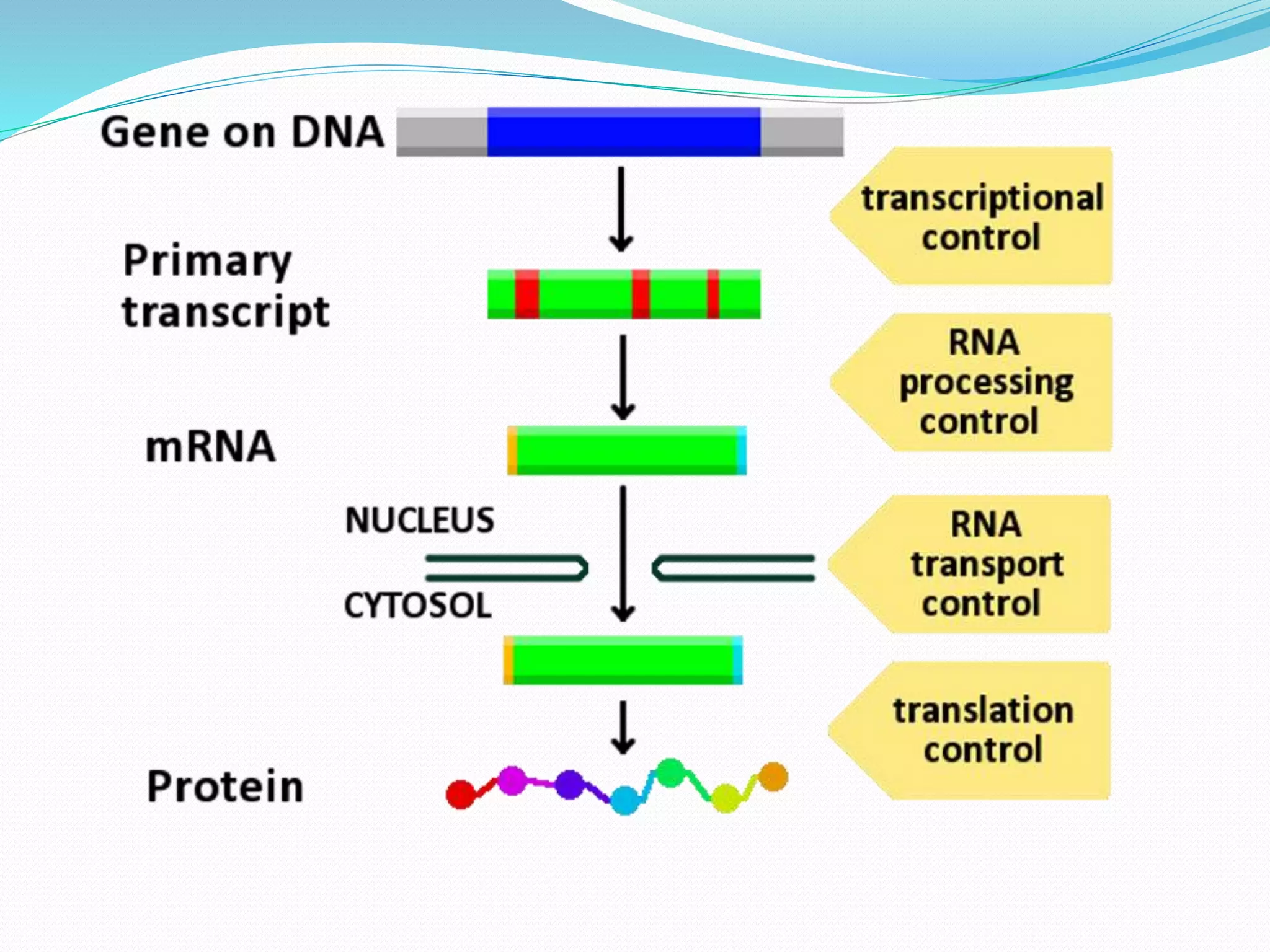
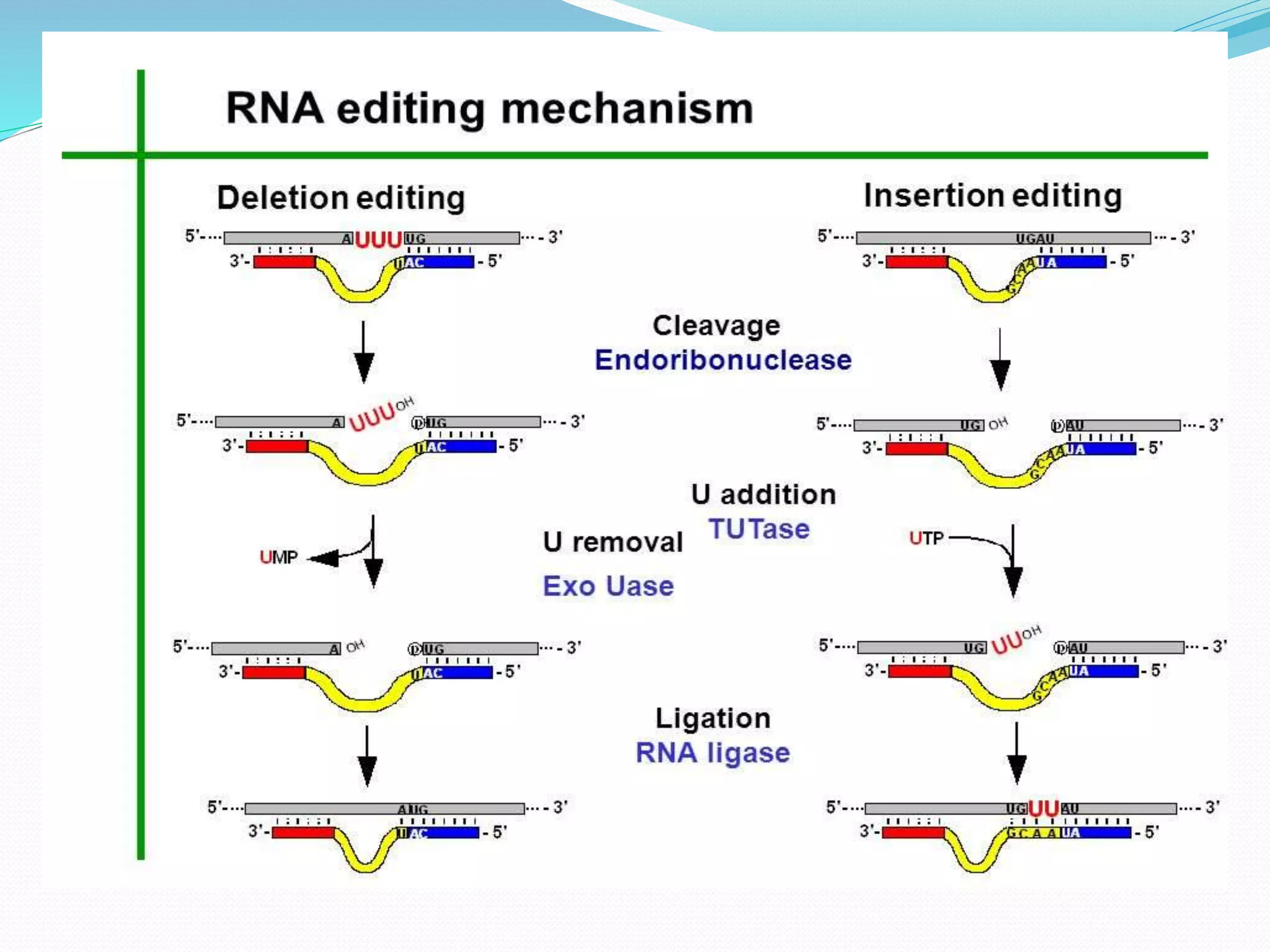
RNA editing is a post-transcriptional process that makes discrete changes to RNA sequences. There are three main types of RNA editing: cytosine to uracil deamination, adenine to inosine deamination, and guide RNA-mediated insertion/deletion of uridine bases. Cytidine deamination is site-specific and involves enzymes like cytidine deaminase. Adenine deamination occurs in RNA secondary structures and involves enzymes like ADAR. Guide RNA editing involves hybridization of RNA to guide RNA, cleavage by an endonuclease, addition of uridine by TuTase, and ligation. RNA editing increases protein diversity and is essential for organelle development in eukaryotes.