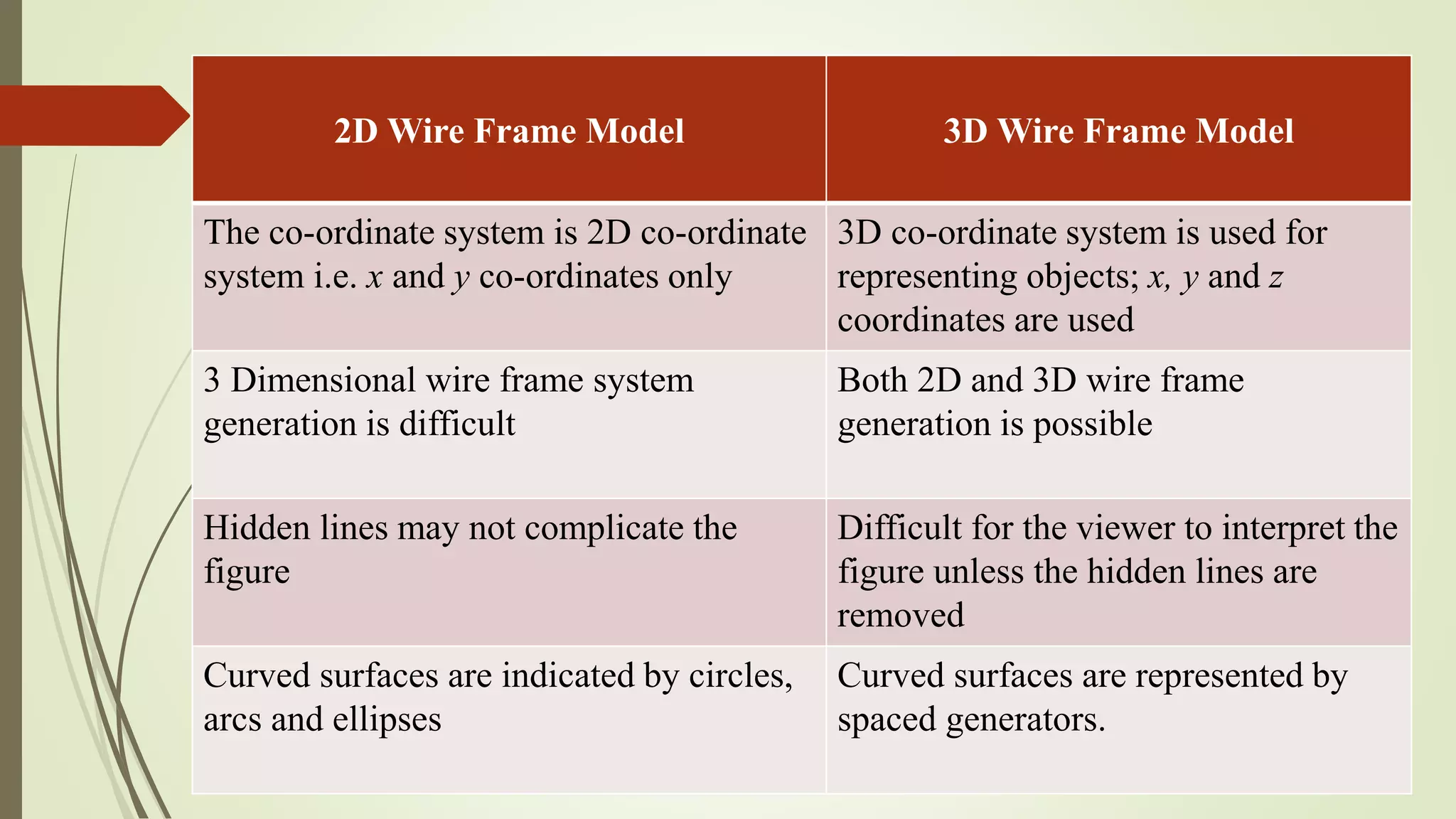
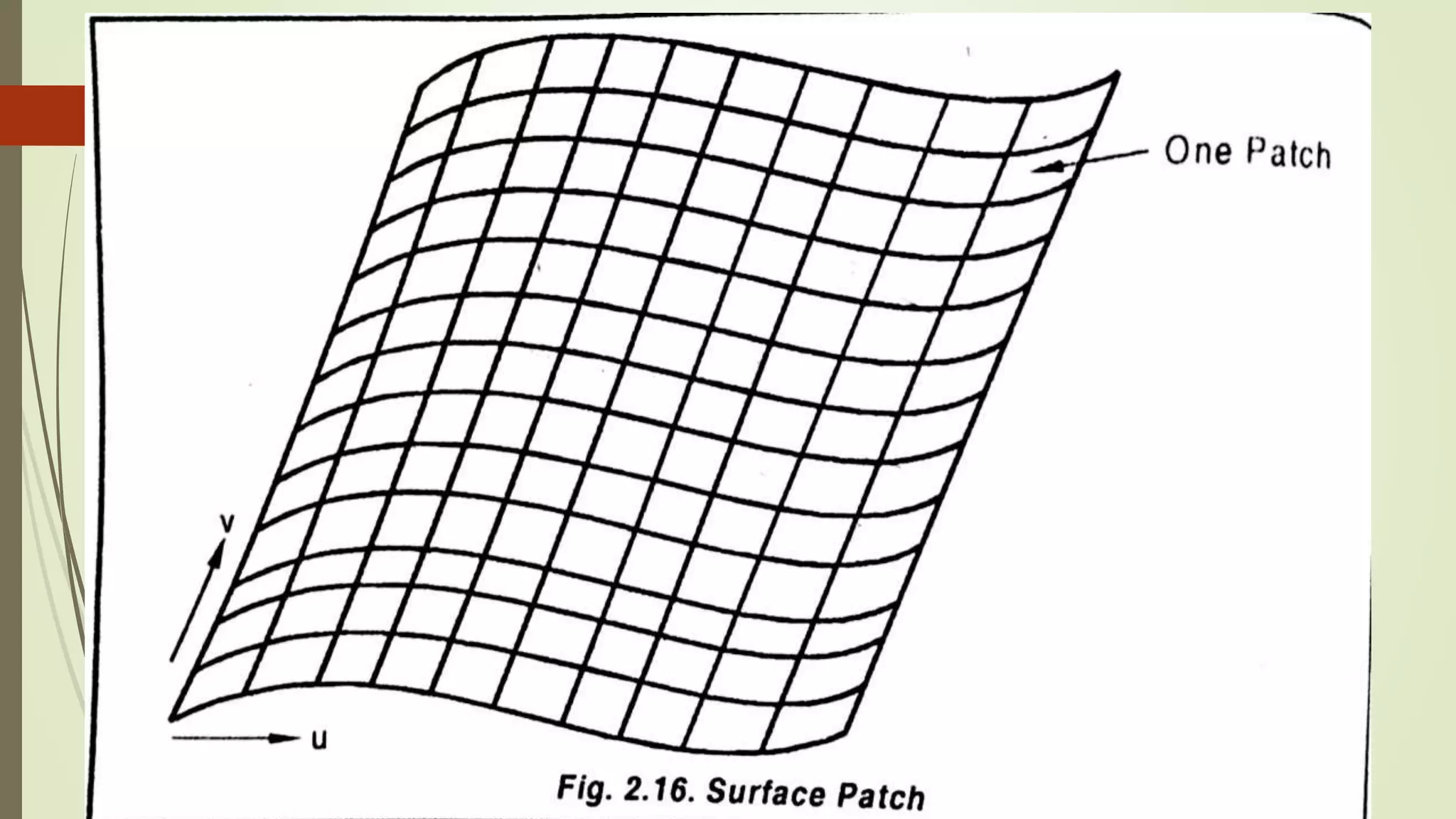
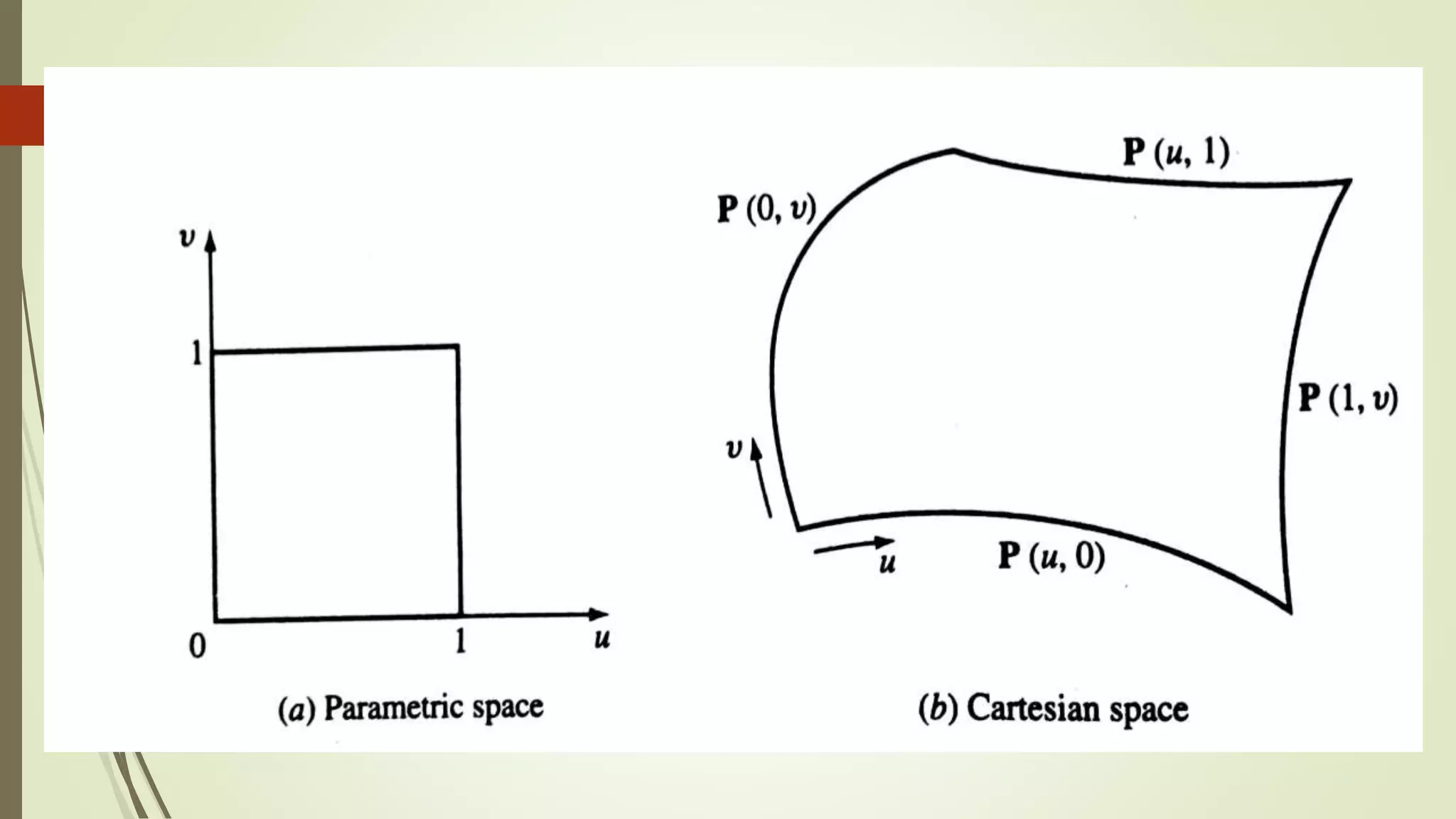
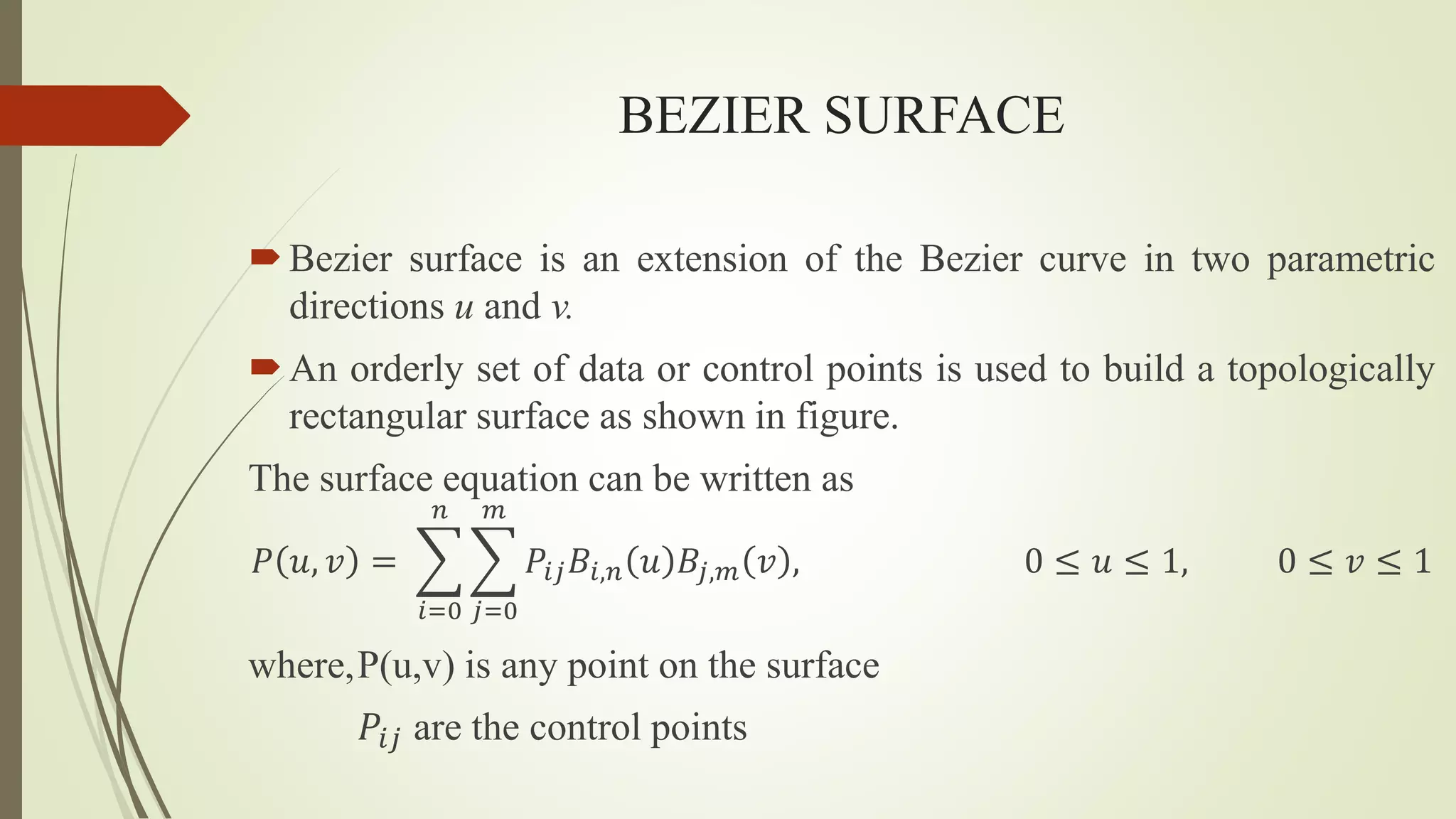
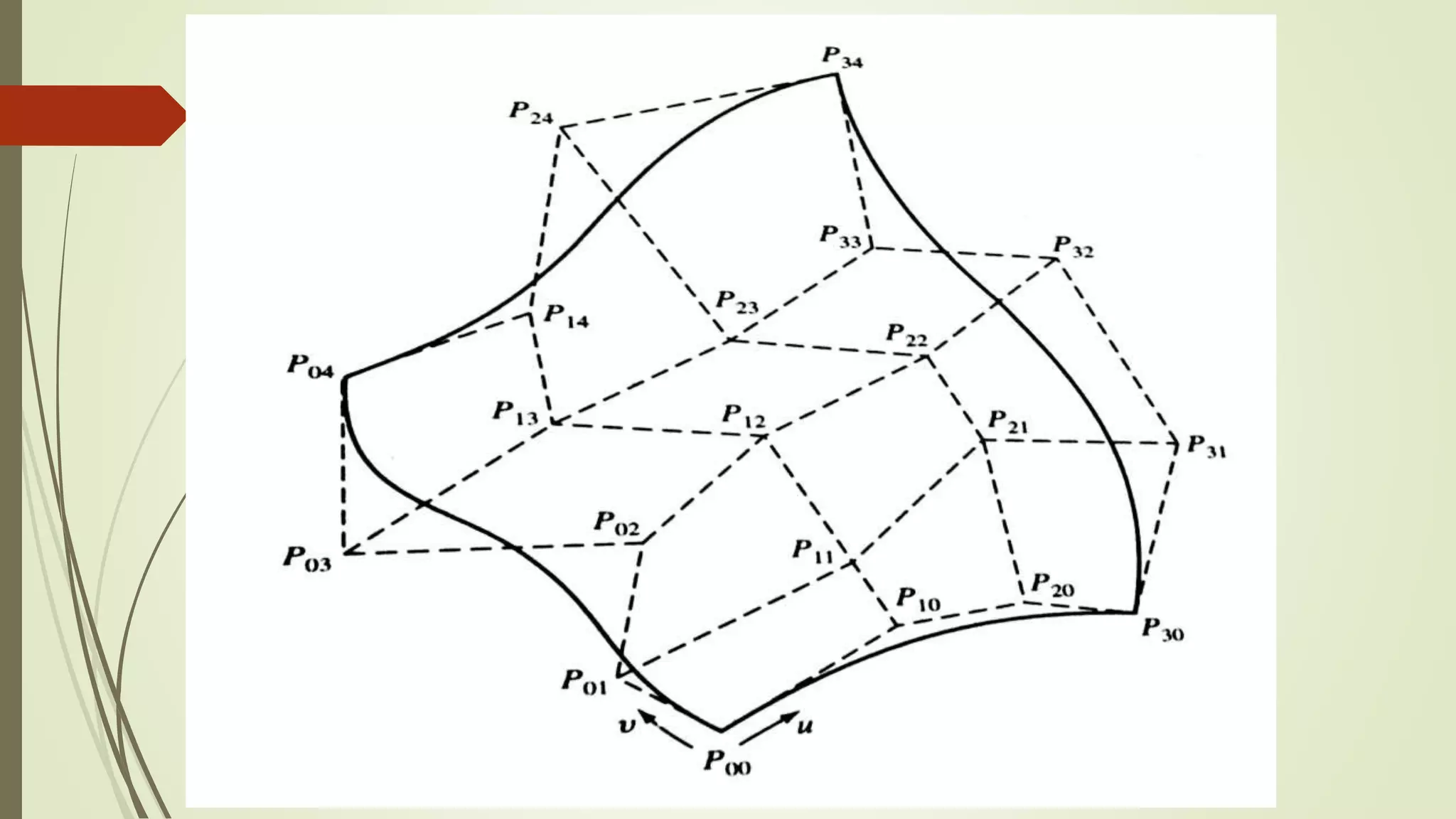
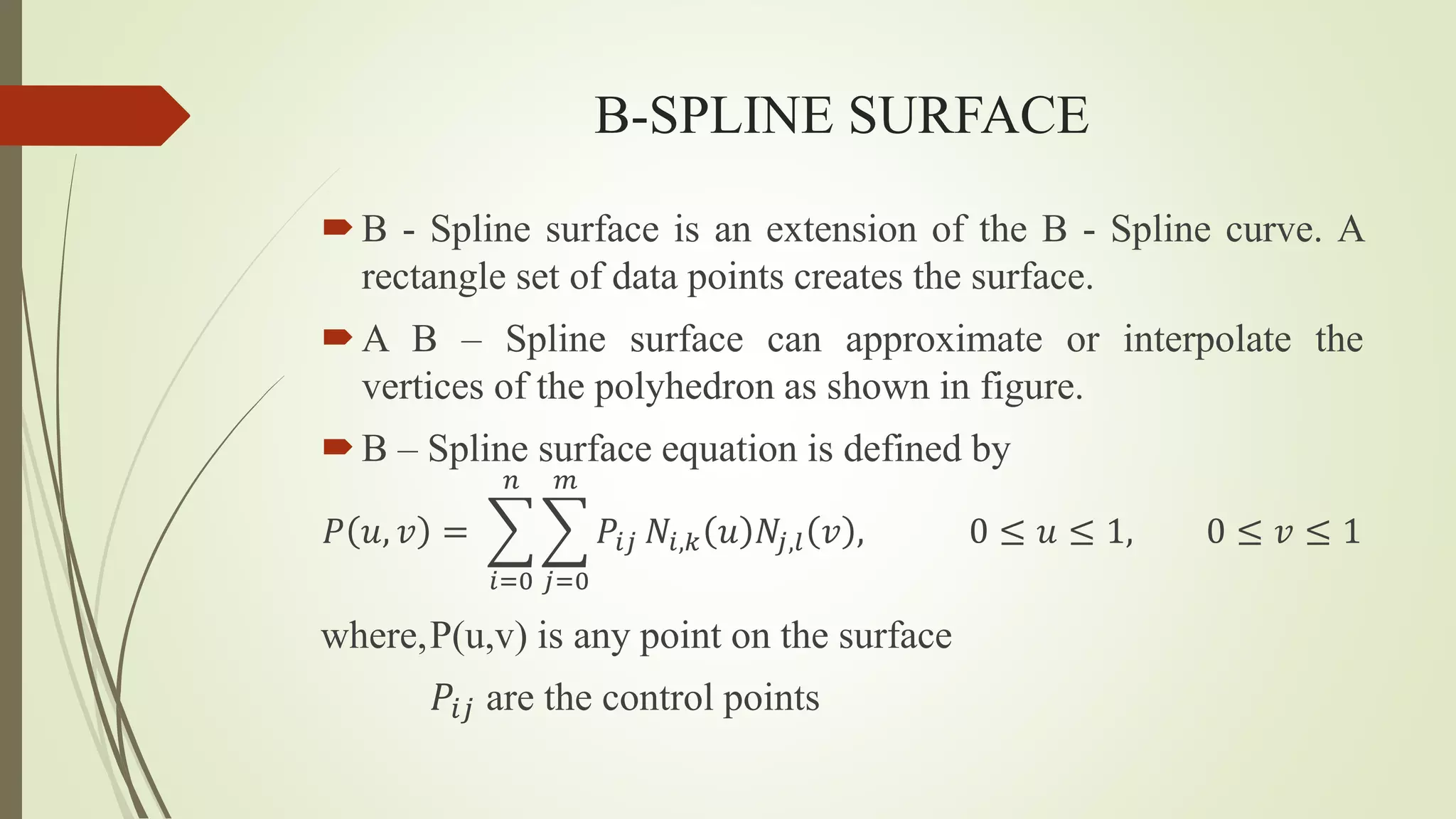
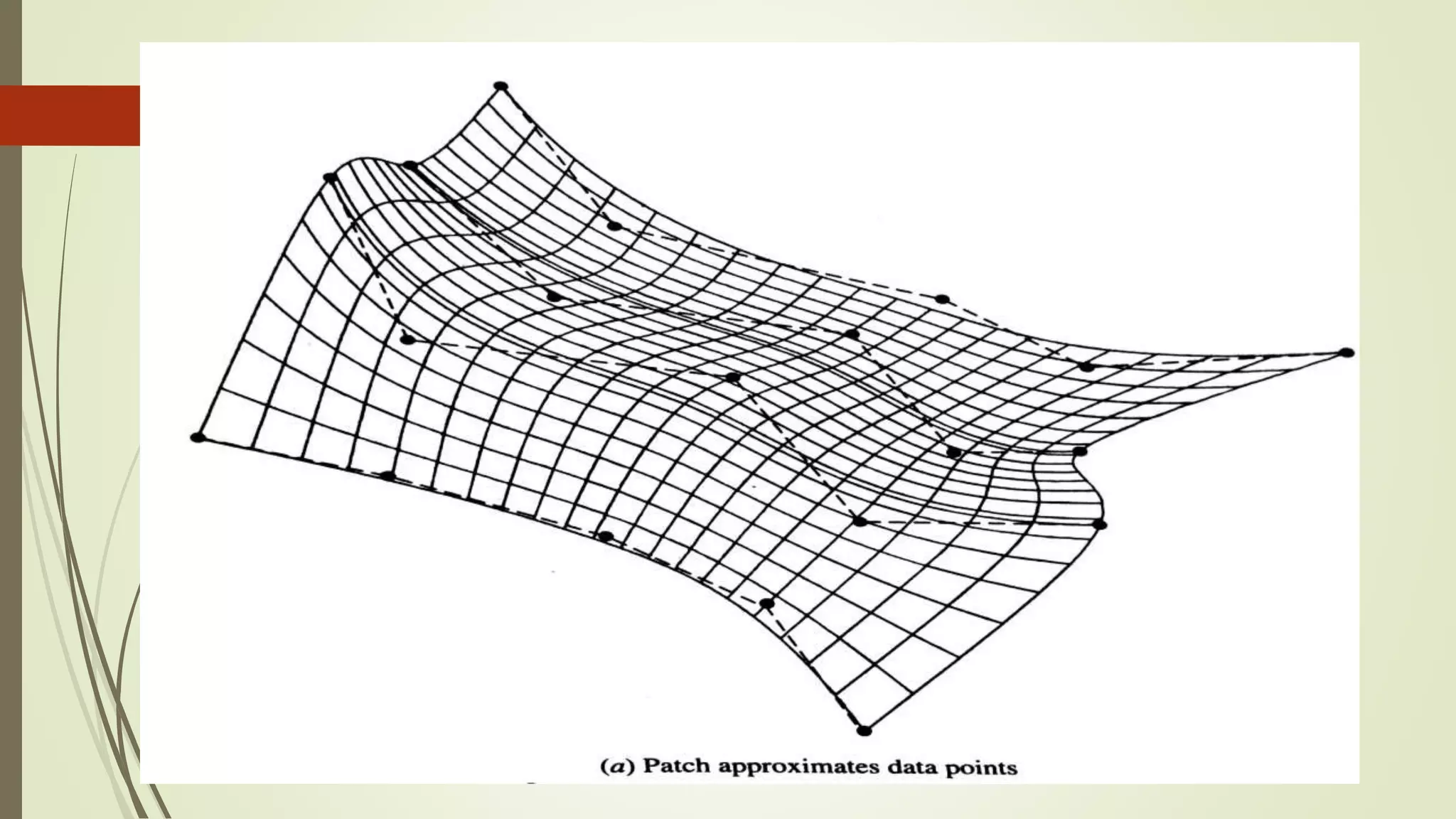
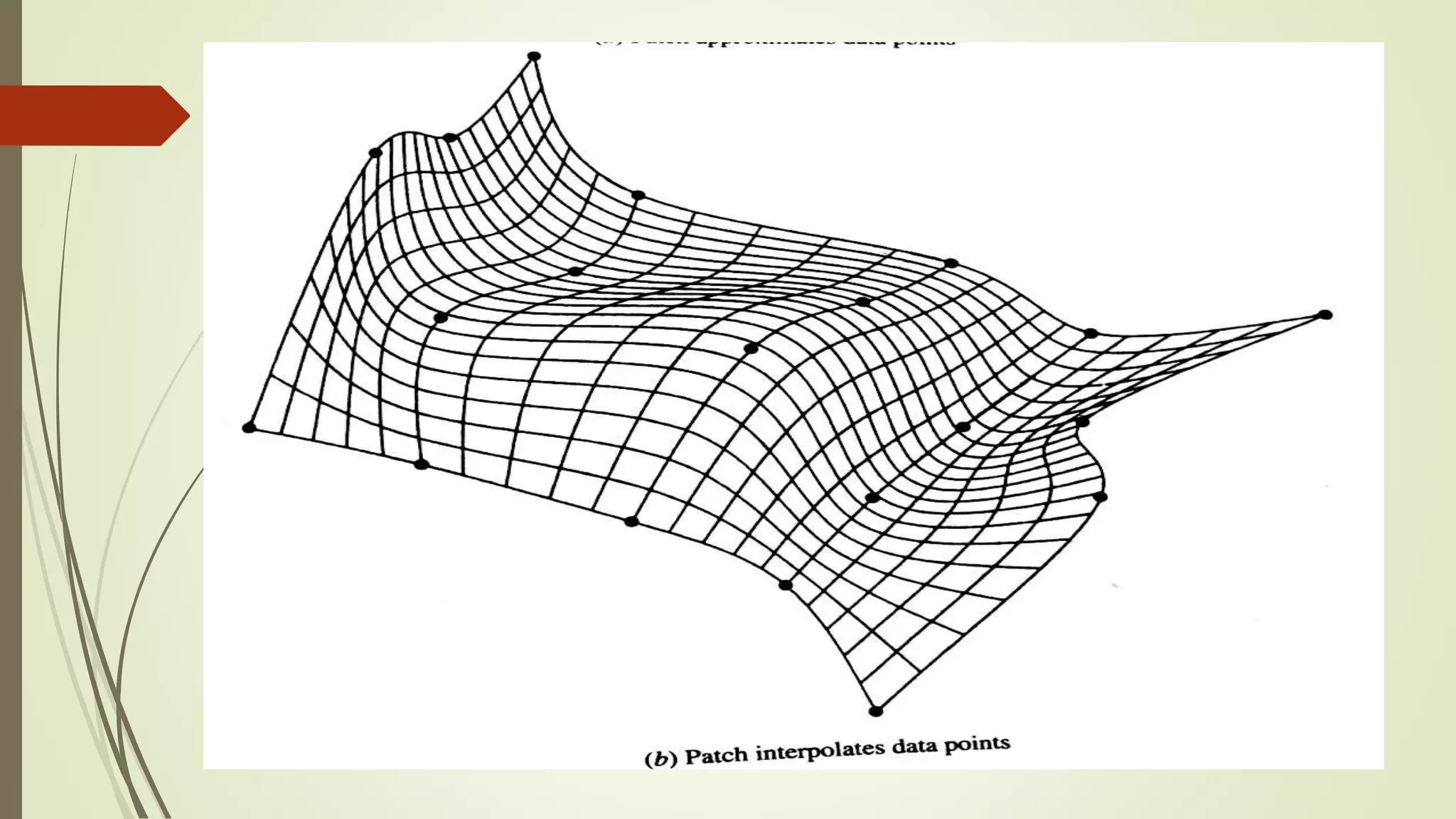
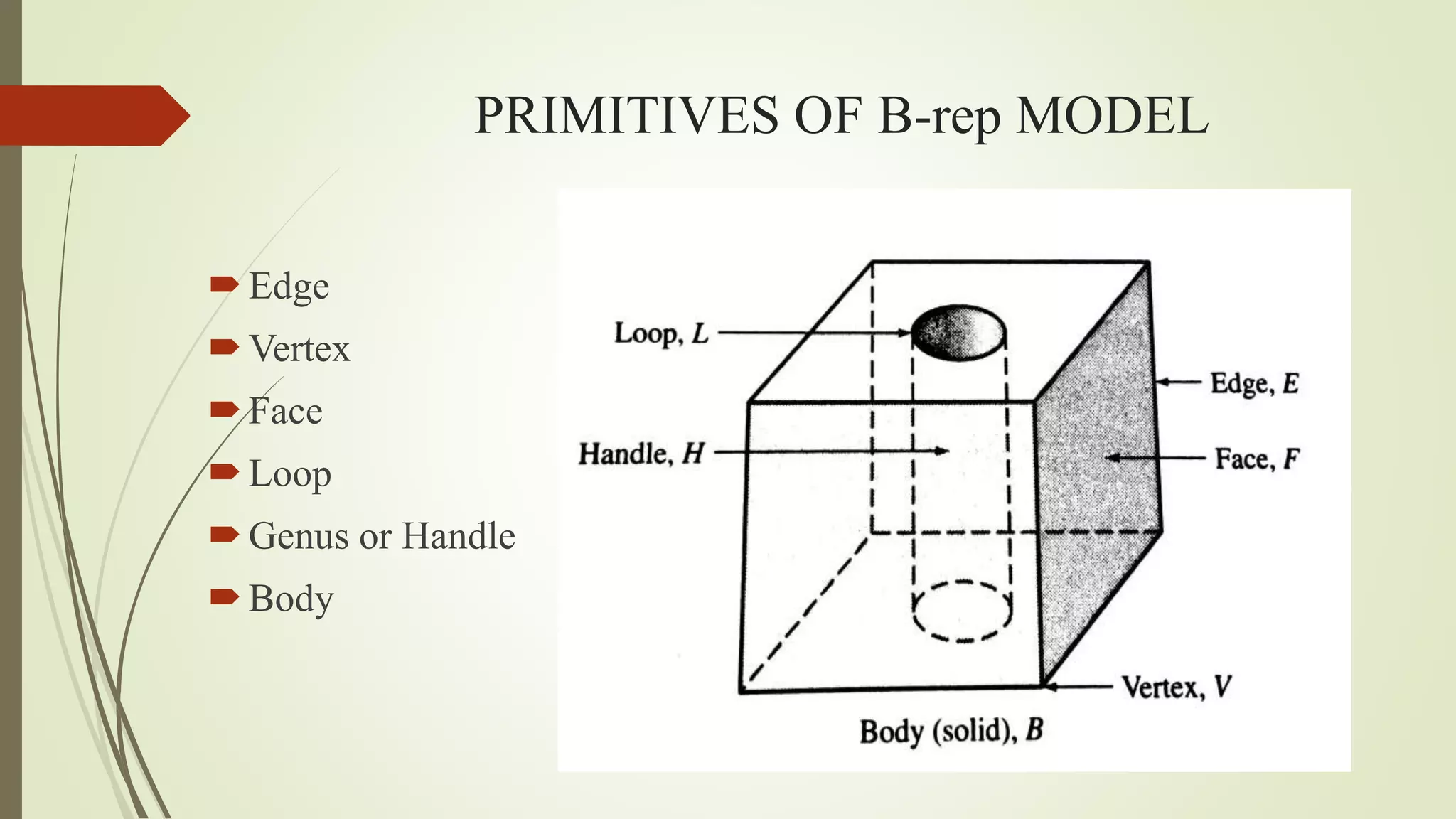
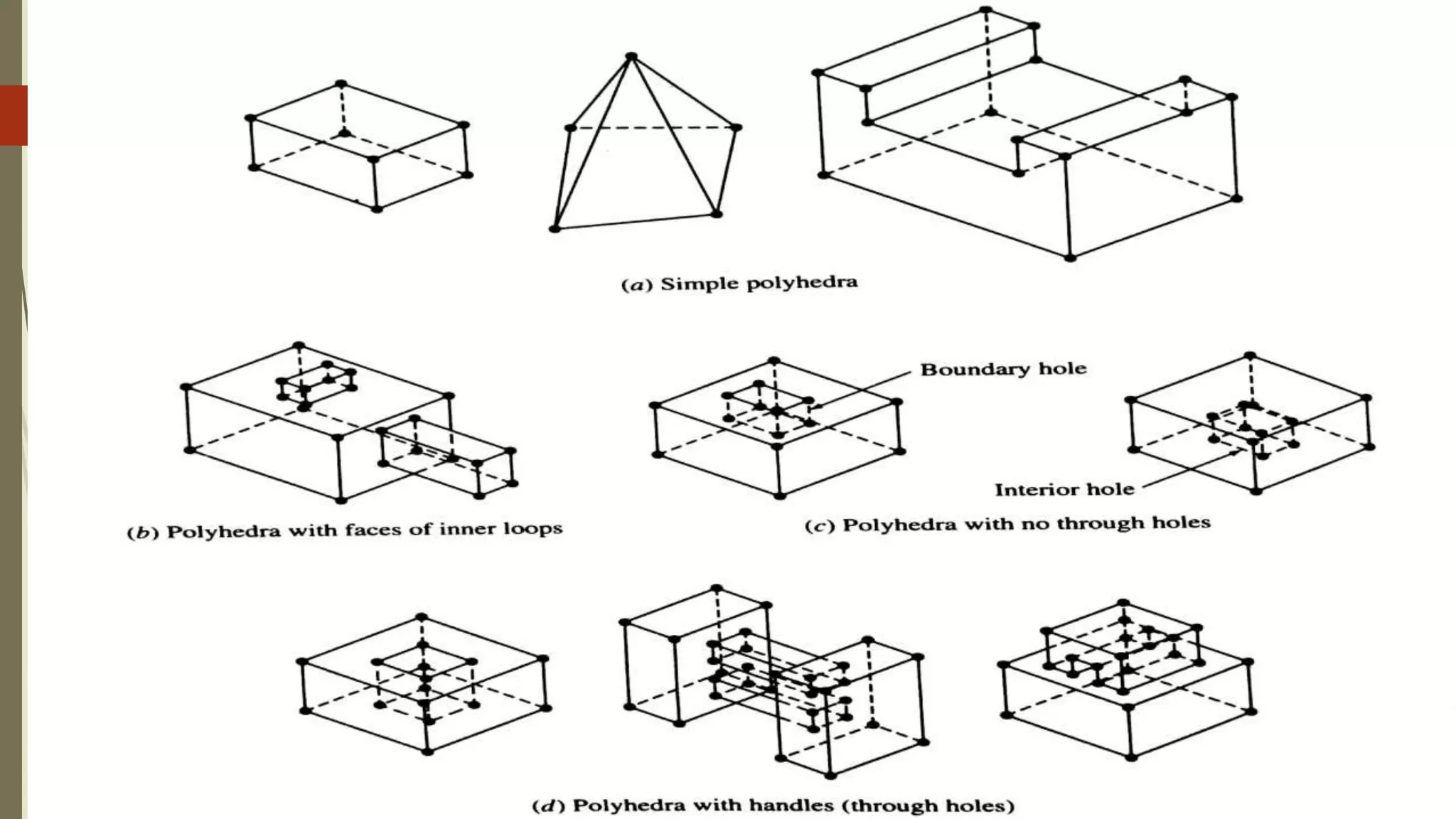
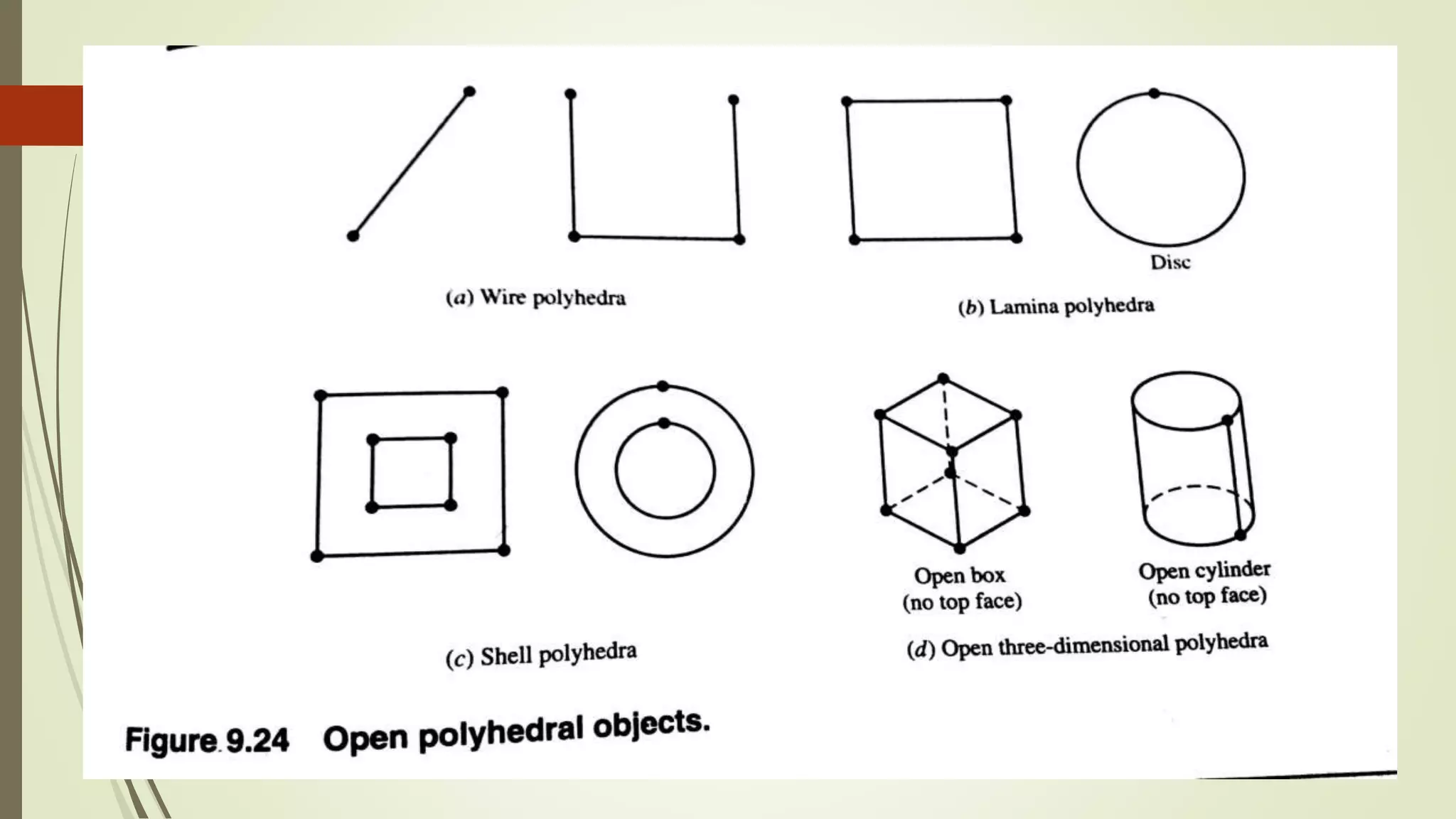
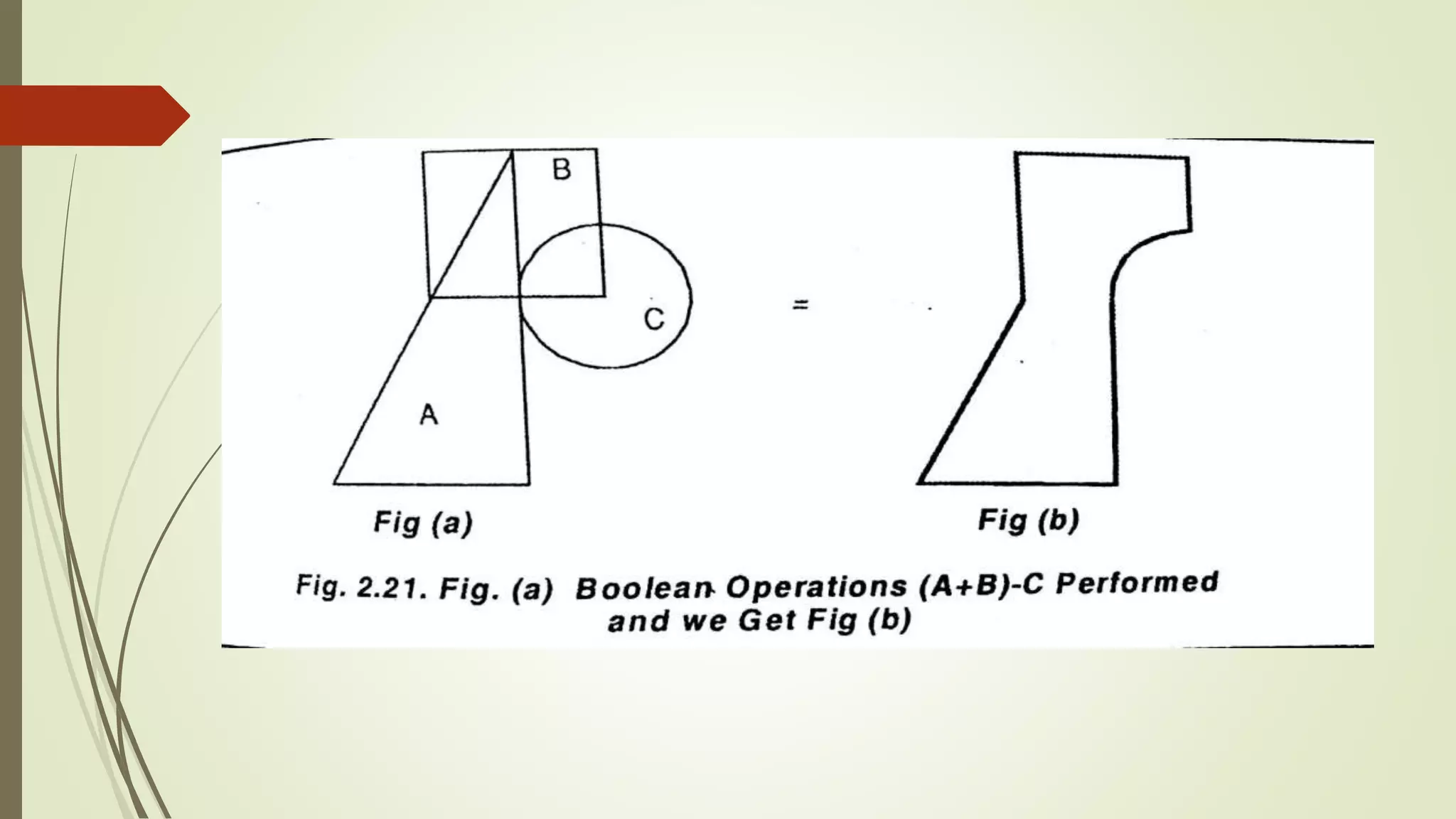
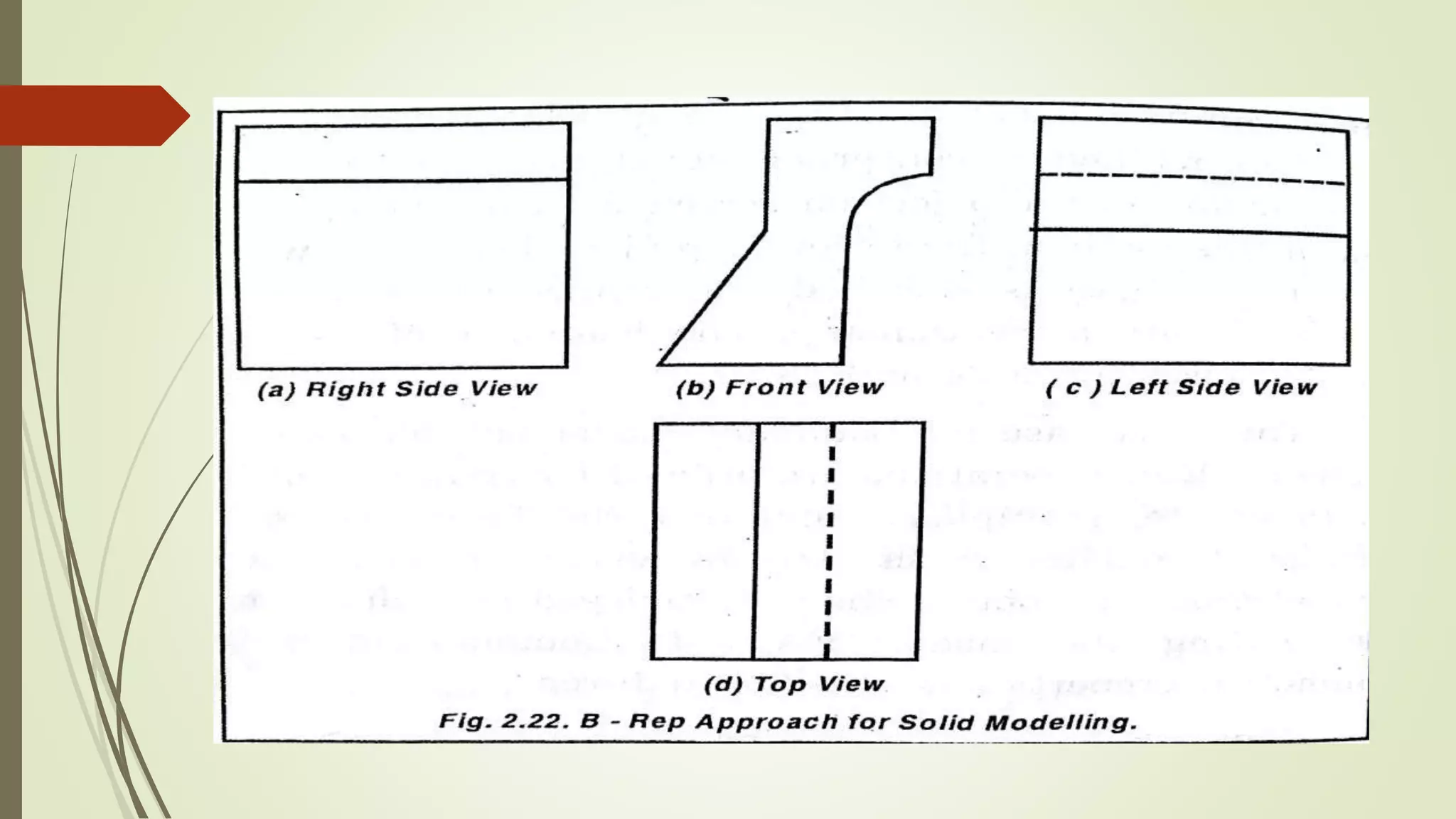
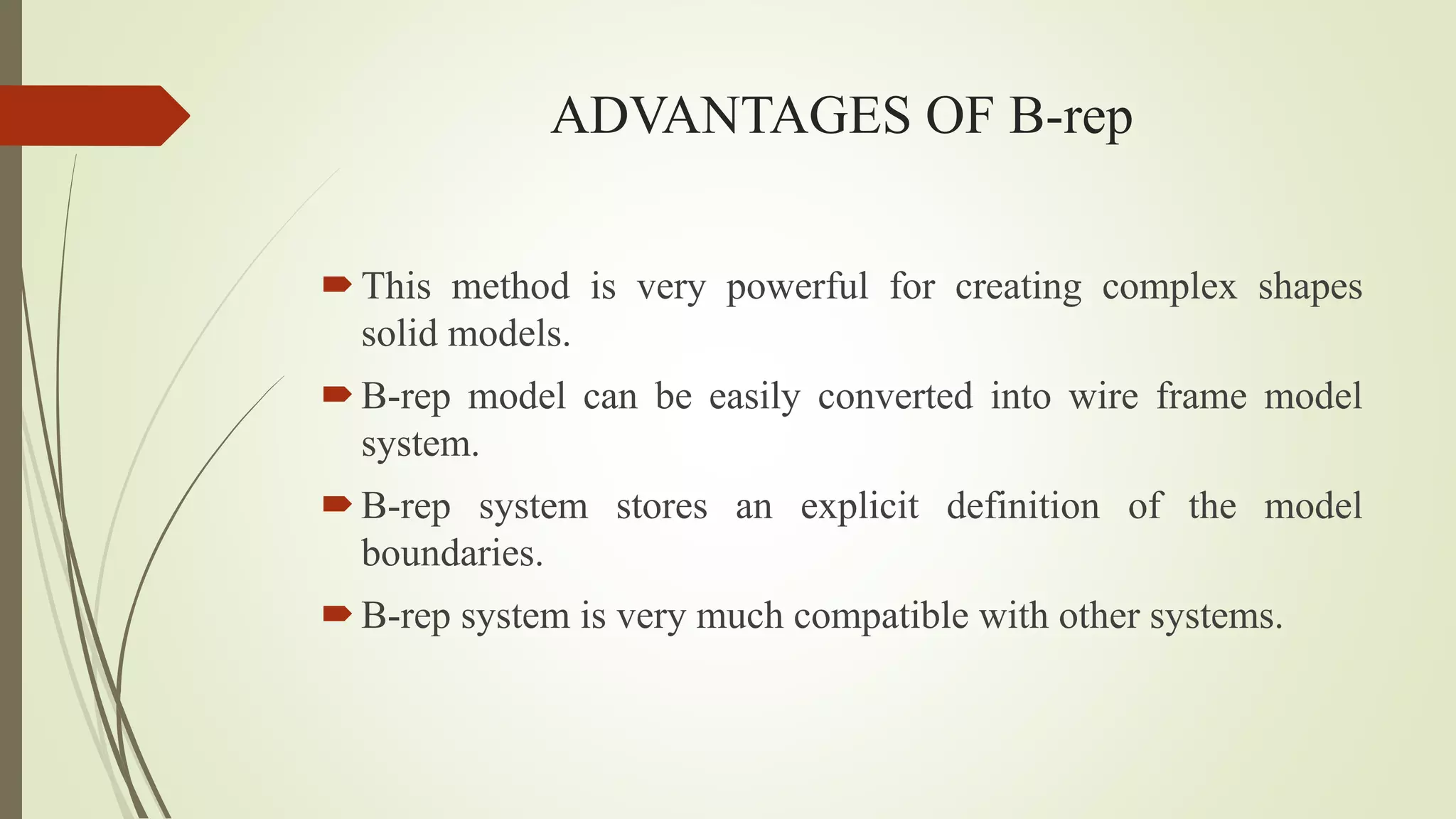
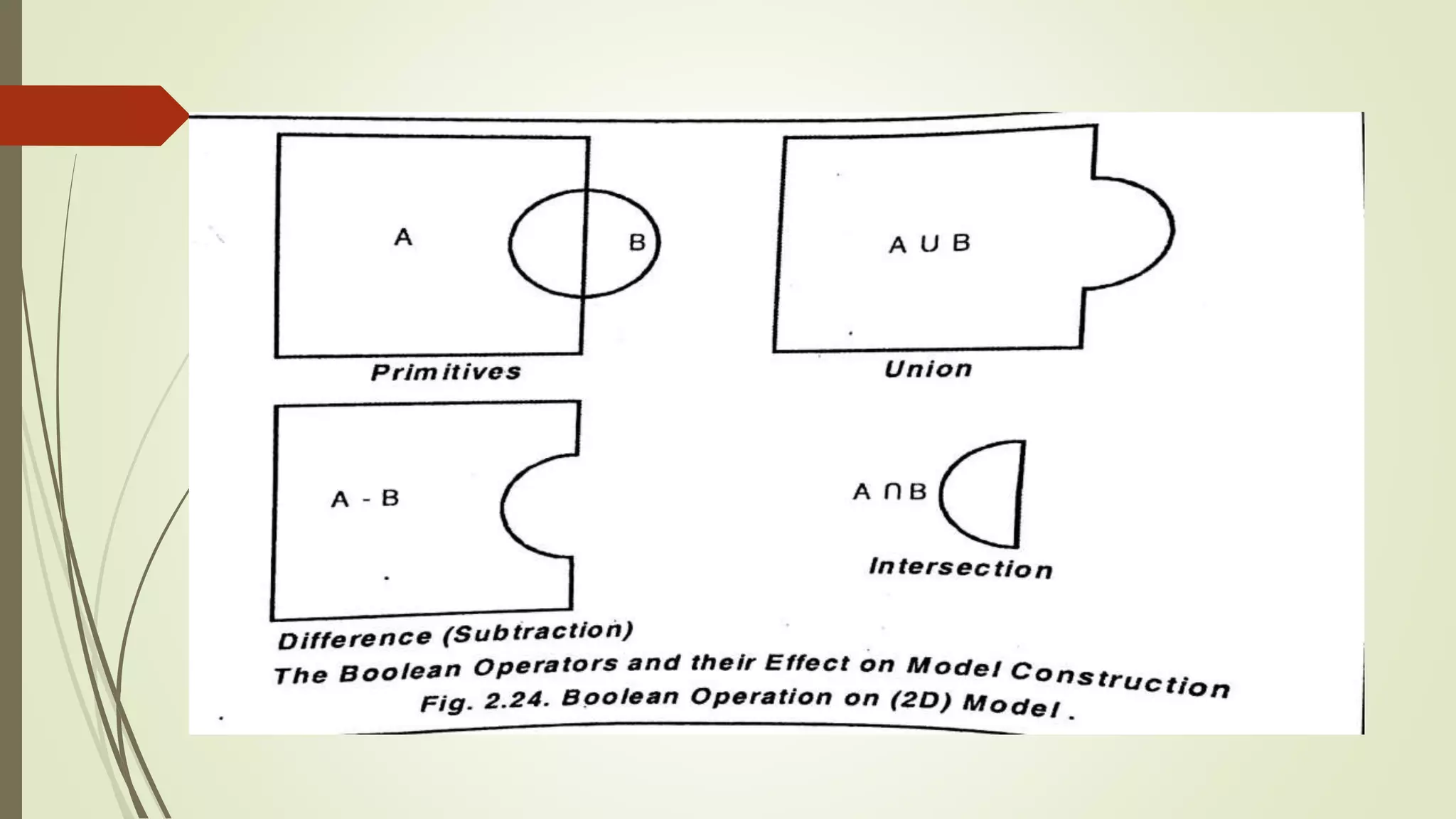
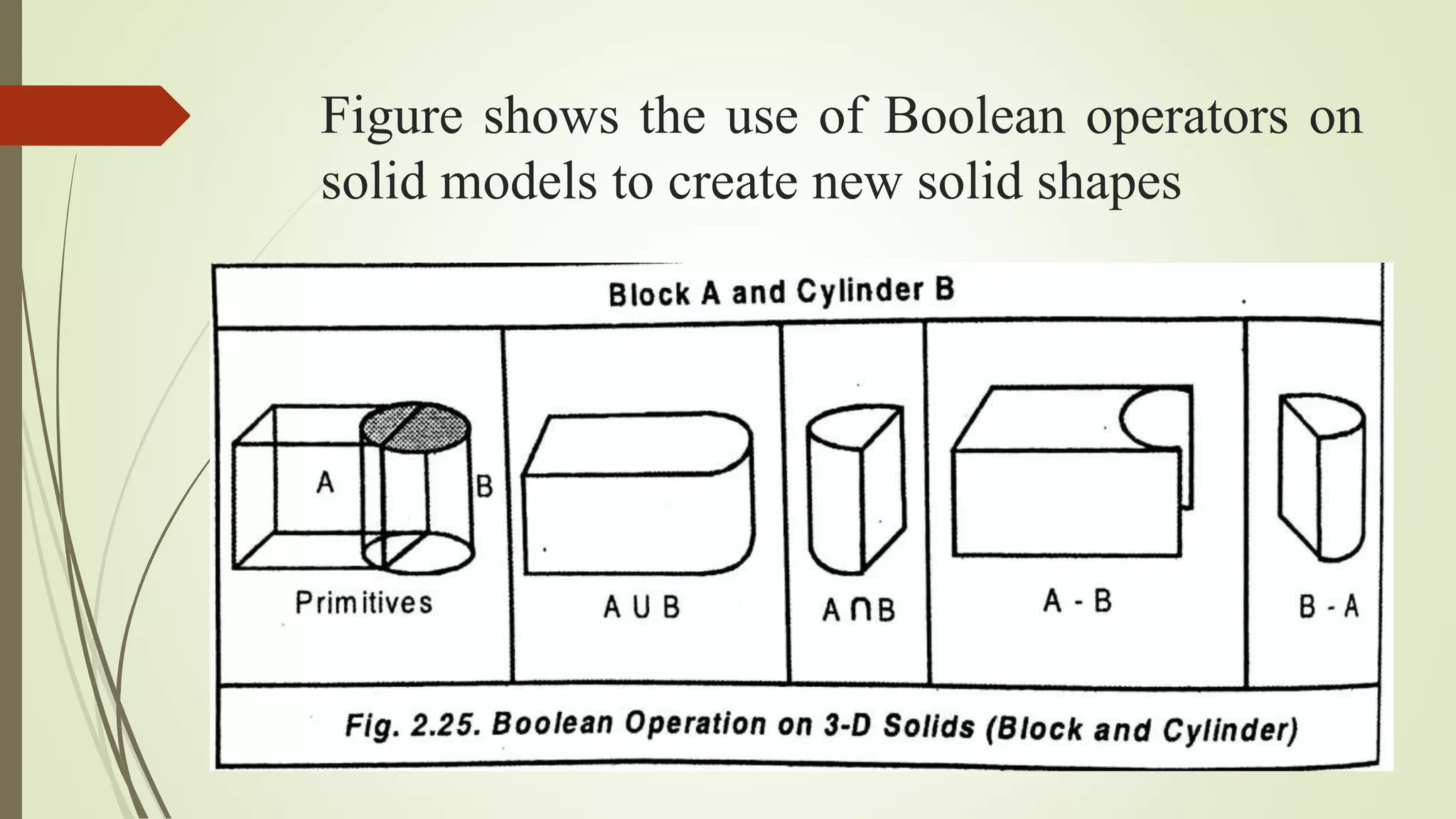
Geometric modeling uses software to mathematically describe an object's geometry. There are three main methods: wireframe modeling represents edges as lines; surface modeling depicts objects' surfaces clearly but provides no interior data; and solid modeling displays whole solids realistically without misinterpretation risk. Boundary representation is a popular solid modeling technique where views are sketched and connected via lines. Constructive solid geometry also constructs solids using primitives combined through Boolean operations.