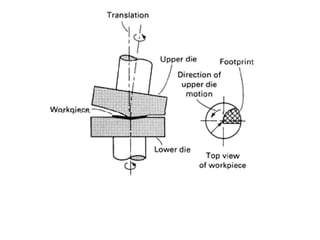
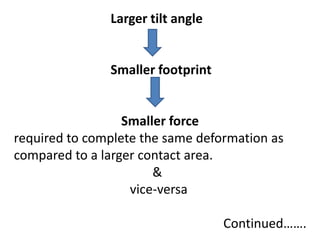
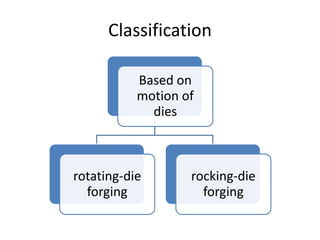
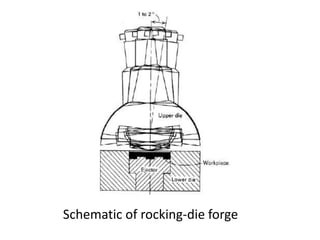
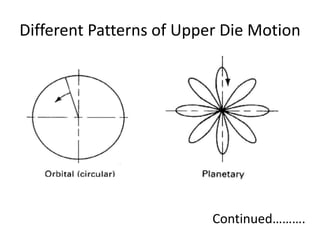
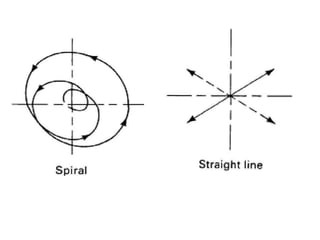
Orbital forging, also known as rotary forging, is a forging process where one die rotates relative to the other, gradually deforming the workpiece into the final shape. The tilt angle between the dies determines the amount of forging force applied. While orbital forging requires less force than conventional forging, the process is limited to symmetrical parts due to complex die motions required for asymmetrical shapes. Common applications include gears, hubs, and thin disks. Advantages include lower forces, accuracy, and tooling costs compared to conventional forging.