Parathyroid gland and The pituitary and Hypothalamus
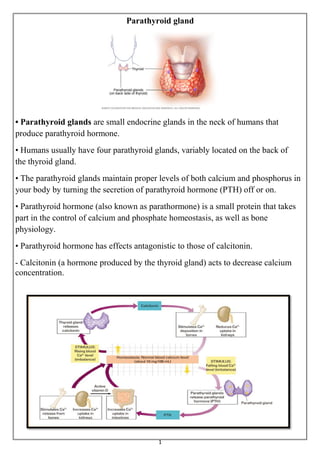
- 1. 1 Parathyroid gland • Parathyroid glands are small endocrine glands in the neck of humans that produce parathyroid hormone. • Humans usually have four parathyroid glands, variably located on the back of the thyroid gland. • The parathyroid glands maintain proper levels of both calcium and phosphorus in your body by turning the secretion of parathyroid hormone (PTH) off or on. • Parathyroid hormone (also known as parathormone) is a small protein that takes part in the control of calcium and phosphate homeostasis, as well as bone physiology. • Parathyroid hormone has effects antagonistic to those of calcitonin. - Calcitonin (a hormone produced by the thyroid gland) acts to decrease calcium concentration.
- 2. 2 ♦ Calcium: • PTH increases blood calcium levels by:- - directly stimulating osteoblasts and thereby indirectly stimulating osteoclasts (to break down bone and release calcium. (Efflux of calcium from bone) - PTH increases gastrointestinal calcium absorption by activating vitamin D, and promotes calcium conservation (reabsorption) by the kidneys (Decrease loss of calcium in urine). PTH action in Calcium regulation
- 3. 3 ♦ Vitamin D and Calcium : (المحاضرة في منو كبير جسء شرحت الدكتوره ولكن االنترنت من زياده) • The body needs vitamin D to absorb calcium. • Without enough vitamin D, one can’t form enough of the hormone calcitriol (known as the “active vitamin D”). • This in turn leads to insufficient calcium absorption from the diet. • In this situation, the body must take calcium from its stores in the skeleton, which weakens existing bone and prevents the formation of strong, new bone. • You can get vitamin D in three ways: through the skin, from the diet, and from supplements. • Vitamin D-rich foods such as egg yolks, saltwater fish, liver, and fortified milk, Mushroom, Orange juice. ♦ Vitamin D Deficiency: • Vitamin D deficiency has been associated with rickets, a disease in which the bone tissue doesn't properly mineralize, leading to soft bones and skeletal deformities. • These are common risk factors for vitamin D deficiency: Having dark skin. Being elderly. Being overweight or obese. Not eating much fish or milk. Living far from the equator where there is little sun year-round. Always using sunscreen when going out. Staying indoors.
- 4. 4 Phosphate: - PTH is the major regulator of serum phosphate concentrations via actions on the kidney. - It is an inhibitor of proximal tubular reabsorption of phosphorus (Increase excretion of phosphate on renal tubules). - Through activation of vitamin D the absorption (intestinal) of Phosphate is increased. Watch on YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EEM0iRJNhU8 Hyperparathyroidism • Hyperparathyroidism is an excess of parathyroid hormone in the bloodstream due to overactivity of one or more of the body's four parathyroid glands. • These glands are about the size of a grain of rice and are located in your neck. • The parathyroid glands produce parathyroid hormone, which helps maintain an appropriate balance of calcium in the bloodstream and in tissues that depend on calcium for proper functioning. • Two types of hyperparathyroidism exist: - In primary hyperparathyroidism, an enlargement of one or more of the parathyroid glands causes overproduction of the hormone, resulting in high levels of calcium in the blood (hypercalcemia), which can cause a variety of health problems. - Secondary hyperparathyroidism occurs as a result of another disease that initially causes low levels of calcium in the body and over time, increased parathyroid hormone levels occur.
- 5. 5 ♦ Symptoms may be so mild and nonspecific that they don't seem at all related to parathyroid function, or they may be severe. The range of signs and symptoms include: Fragile bones that easily fracture (osteoporosis) Kidney stones Excessive urination Abdominal pain Tiring easily or weakness Depression or forgetfulness Bone and joint pain Frequent complaints of illness with no apparent cause Nausea, vomiting or loss of appetite • The parathyroid glands maintain proper levels of both calcium and phosphorus in your body by turning the secretion of parathyroid hormone (PTH) off or on • Vitamin D also is involved in regulating the amount of calcium in your blood. • Normally, this balancing act works well. • When calcium levels in your blood fall too low, your parathyroid glands secrete enough PTH to restore the balance. - PTH raises calcium levels by releasing calcium from your bones and increasing the amount of calcium absorbed from your small intestine. • When blood-calcium levels are too high, the parathyroid glands produce less PTH. - But sometimes one or more of these glands produce too much hormone, leading to abnormally high levels of calcium (hypercalcemia) and low levels of phosphorus in your blood.
- 6. 6 Primary hyperparathyroidism • Primary hyperparathyroidism occurs because of some problem with one or more of the four parathyroid glands: • A noncancerous growth (adenoma) on a gland is the most common cause. • Enlargement (hyperplasia) of two or more parathyroid glands accounts for most other cases. • A cancerous (malignant) tumor is a rare cause of primary hyperparathyroidism. • Primary hyperparathyroidism usually occurs randomly, but some people inherit a gene that causes the disorder. Secondary hyperparathyroidism • Secondary hyperparathyroidism is the result of another condition that lowers calcium levels. • Therefore, your parathyroid glands overwork to compensate for the loss of calcium. ♦ Factors that may contribute to secondary hyperparathyroidism include: • Severe calcium deficiency: Your body may not get enough calcium from your diet, often because your digestive system doesn't absorb the calcium from it. • Severe vitamin D deficiency: Vitamin D helps maintain appropriate levels of calcium in the blood, and it helps your digestive system absorb calcium from your food. • Your body produces vitamin D when your skin is exposed to sunlight, and you consume some vitamin D in food - If you don't get enough vitamin D, then calcium levels may drop. • Chronic kidney failure: Your kidneys convert vitamin D into a form that your body can use. - If your kidneys function poorly, usable vitamin D may decline and calcium levels drop. - Chronic kidney failure is the most common cause of secondary hyperparathyroidism.
- 7. 7 Complications • Complications of hyperparathyroidism are primarily related to the long-term effect of too little calcium in your bones and too much calcium circulating in your bloodstream. • Common complications include: • Osteoporosis. - The loss of calcium often results in weak, brittle bones that fracture easily (osteoporosis). • Kidney stones. - The excess of calcium in your blood may lead to excess calcium in your urine, which can cause small, hard deposits of calcium and other substances to form in your kidneys. - A kidney stone usually causes significant pain as it passes through the urinary tract. • Cardiovascular disease. - Although the exact cause-and-effect link is unclear, high calcium levels are associated with cardiovascular conditions, such as high blood pressure (hypertension) and certain types of heart disease. • Neonatal hypoparathyroidism. - Severe, untreated hyperparathyroidism in pregnant women may cause dangerously low levels of calcium in newborns. Degradation of parathormone (Parathyroid hormone) • Half-life of PTH is approximately 10 minutes. • Most of the newly synthesized PTH is degraded immediately after its synthesis and only a minority enters the bloodstream. • Peripheral degradation of PTH takes place mainly in liver and kidneys. • Inside the liver Kupffer cells, PTH undergoes proteolysis to carboxy- and amino-fragments. • Amino-fragments are quickly degraded, but carboxy-fragments remain in the circulation and leave the body through kidneys.
- 8. 8 Calcitonin • Calcitonin is a hormone that the C-cells in the thyroid gland produce and release. • It opposes the action of the parathyroid hormone, helping to regulate the blood’s calcium and phosphate levels. • Calcitonin works to control calcium and potassium levels. • It does this by inhibiting the activity of the osteoclasts, the cells that break down bone. - Osteoclast: a type of bone cell that breaks down bone tissue. - Osteoblast: are the cells that form new bone. ♦ Calcitonin: - Decreases blood calcium levels by causing its deposition on bone. - Antagonistic to parathyroid hormone. - Produced by C (parafollicular) cells. • Sometimes high calcitonin levels can point to a rare type of medullary thyroid cancer. • This cancer, which starts in the C-cells, can be connected to multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2b and multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2a. • However, the calcitonin levels do not cause the cancer.
- 9. 9 The pituitary and Hypothalamus • The pituitary gland is often called the master gland because it controls several other hormone glands in your body. ♦ Hormones produced by the pituitary gland: • The two sections of the pituitary gland produce a number of different hormones which act on different target glands or cells. ♣ Anterior pituitary • Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH) • Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) • Luteinising hormone (LH) • Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) • Prolactin (PRL) • Growth hormone (GH) • Melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH) ♣ Posterior pituitary • Anti-diuretic hormone (ADH) • Oxytocin
- 10. 10 • The secretion of hormones from the anterior pituitary is controlled by the production of hormones by the hypothalamus. • Although there are a number of different hormones they can be split into two main types: • hormones that tell the pituitary to switch on production of a hormone (a releasing hormone) • hormones that tell the pituitary to switch off production of a hormone (an inhibiting hormone). • The hormones secreted by the posterior pituitary are produced in the hypothalamus and then passed down a tube between the hypothalamus and the pituitary (the pituitary stalk) when they are then secreted into the blood.
- 11. 11 Diseases and Disorders of the Pituitary Gland • Pituitary tumors are the most common pituitary disorder, and many adults have them. • There are two types of pituitary tumors—secretory and non-secretory. - Secretory tumors secrete too much of a hormone. - Non-secretory tumors don’t secrete excess hormone. Symptoms related to specific conditions ♣ Diabetes Insipidus (DI) • Due to a lack of the hormone vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone),this can be due to damage to the hypothalamus or pituitary gland or genetics. • Passing excessive urine much more than usual during the day and frequently through the night • Urine is very pale, possibly clear and doesn’t concentrate • Extreme thirst, which cannot be quenched • Preference of icy cold drinks • Headaches (which may be due to dehydration) • Exhaustion • Shivering • Nausea • Dehydration symptoms: parched mouth, cracked lips, coated tongue, dry eyes and dry skin • Most foods intolerable with a preference to drink fluids • Weight loss
- 12. 12 ♣ Cushing's disease • Cushing's disease is a cause of Cushing's syndrome characterised by increased secretion of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) from the anterior pituitary • Weight gain to trunk of body, plus rounding of face • Fatty hump at top of spine/back • Flushed appearance and roundness of face • Low mood, can feel depressed • Loss of bone density (if left untreated over time) due to excess cortisol • Extreme mood swings • Weakness, possible muscle wasting • Darkening of skin pigmentation • Dark purple striae (similar to stretch marks on abdomen and tops of thighs) • Hirsutism (extreme hairiness) ♣ Prolactinoma • A prolactinoma is a benign tumor (adenoma) of the pituitary gland that produces a hormone called prolactin. • Loss of periods (female) • Infertility • Low or lack of libido • Weight gain bloated stomach • Lethargy/exhaustion, falling asleep during day • Headaches • Milk/fluid excreting from nipples when not pregnant (males can have this too) ♣ Hypopituitarism • Hypopituitarism is the decreased secretion of one or more of the eight hormones normally produced by the pituitary gland at the base of the brain • (can include cortisol, growth hormone and thyroid deficiencies) • Flu type feelings low or no cortisol in body, regular colds and/or infections 'hung over’ type feeling without having drunk alcohol • No body temperature control either feeling too hot, or too cold • Nausea • Mood swings feelings of depression, apathy or low mood • Joint aches and pains, and/or poor muscle tone • Exhaustion • Constipation • Difficulty finding words • Poor sleep patterns • Low blood pressure feeling light-headed • Pale pallor
