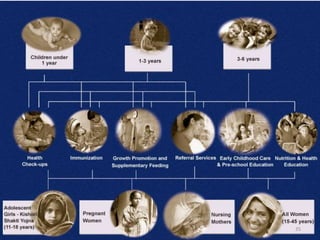
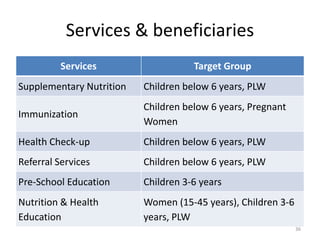
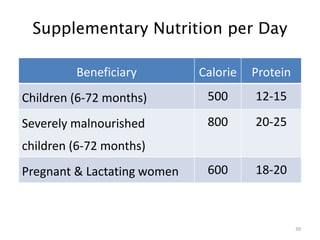
This document provides an overview of various community nutrition programmes (CNP) in India, including their objectives, target groups, and provisions. It discusses programmes such as vitamin A prophylaxis, control of nutritional anemia, control of iodine deficiency disorders, special nutrition programmes, balwadi nutrition programmes, Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS), mid-day meal programmes, and mid-day meal schemes. ICDS is described as one of the world's largest programmes for early childhood development, aiming to improve nutrition, health and development of children under 6 years old. It provides several services including supplementary nutrition, immunization, health checkups, and pre-school education. Challenges in implementing CNP such as