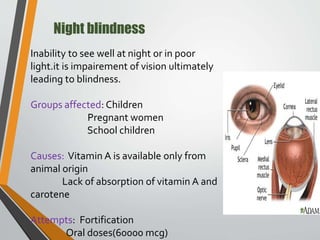
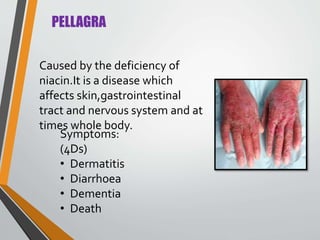
This document summarizes several common nutritional disorders caused by deficiencies of proteins, minerals, vitamins, and other nutrients. It discusses protein-energy malnutrition (PEM) disorders like kwashiorkor and marasmus caused by inadequate protein and energy intake. Mineral deficiencies covered include anemia from iron deficiency and iodine deficiency disorders (IDD) like goiter. Vitamin deficiencies discussed are night blindness from vitamin A deficiency, rickets from vitamin D deficiency, scurvy from vitamin C deficiency, and several B-complex deficiencies like beriberi, photophobia, and pellagra. The document provides details on symptoms, affected groups, causes, and prevention strategies for each nutritional disorder.