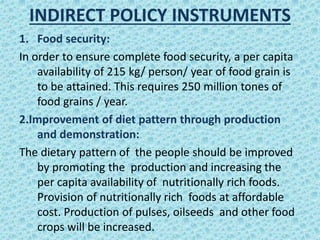
The National Nutritional Policy adopted in 1993 aims to achieve optimal nutrition for all sections of Indian society, with priority given to vulnerable groups like women, children, and mothers. The policy recognizes malnutrition as a multisectoral issue requiring action across areas like food production, health, agriculture, and education. It sets goals like reducing child malnutrition, low birth weight, and micronutrient deficiencies. The policy pursues these goals through direct interventions like expanding safety nets and nutrition programs, as well as indirect strategies like ensuring food security, improving diets, and increasing health and nutrition awareness.