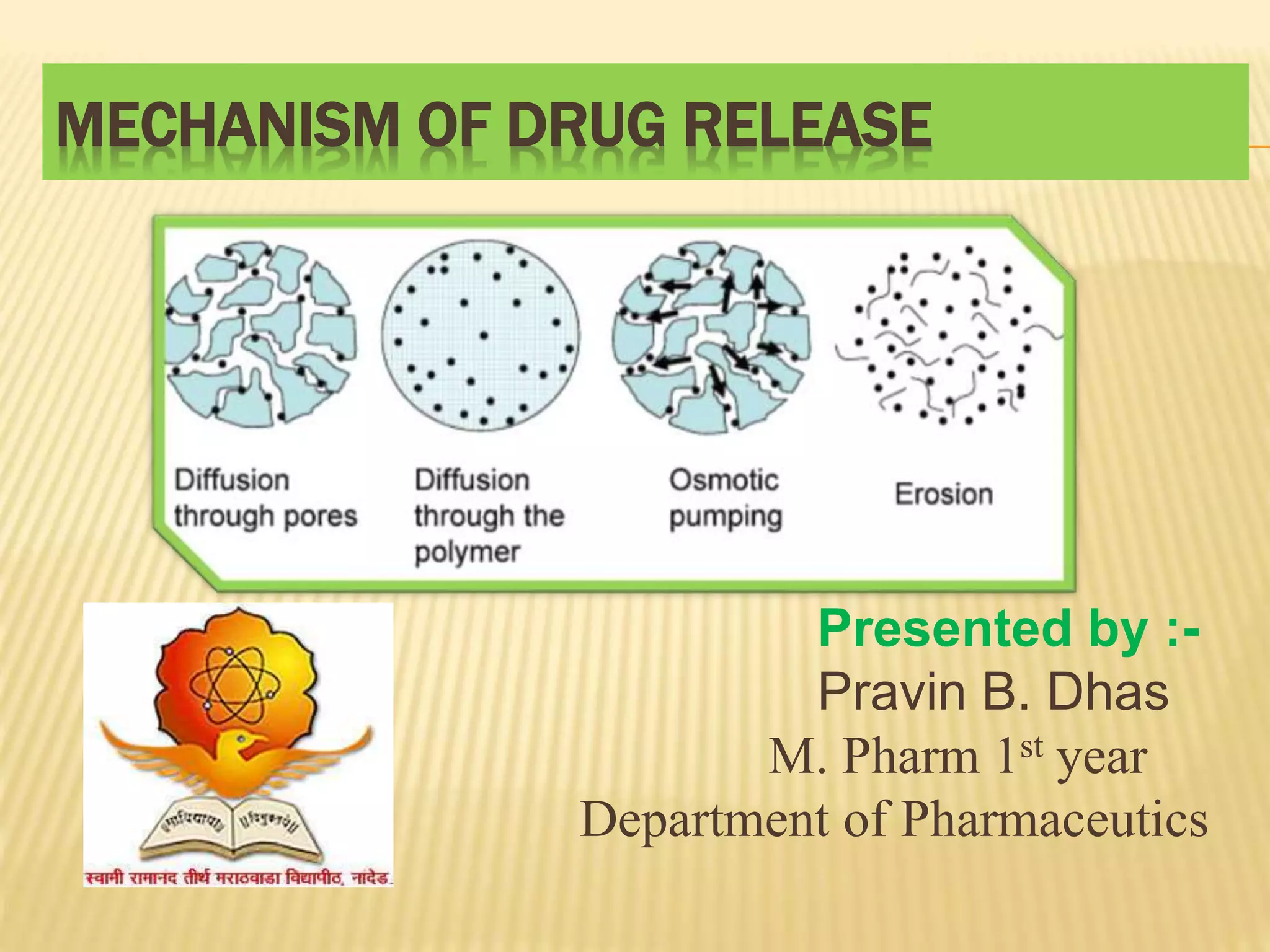
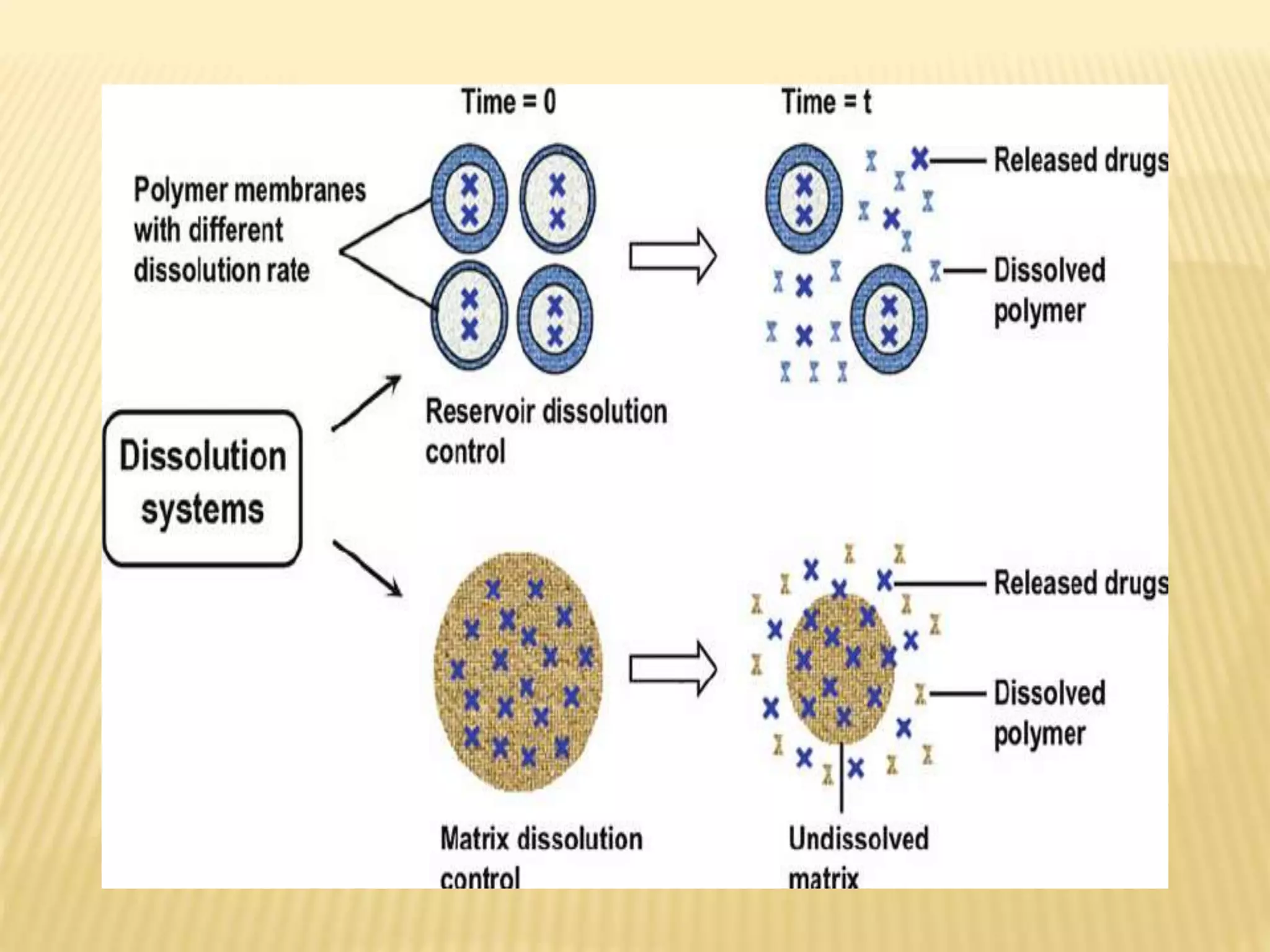
This document summarizes different mechanisms of drug release from delivery systems. There are three main types of mechanisms: dissolution controlled, diffusion controlled, and dissolution/diffusion controlled. Dissolution controlled systems release drug through the dissolution of a coating or matrix that encapsulates or embeds the drug. Diffusion controlled systems release drug through diffusion out of an inert membrane barrier. Dissolution/diffusion controlled systems combine aspects of both mechanisms, as the drug core is encased in a partially soluble membrane through which aqueous medium can enter to dissolve the drug and pores in the membrane allow dissolved drug to diffuse out over time. These controlled release mechanisms aim to improve drug delivery to the body.