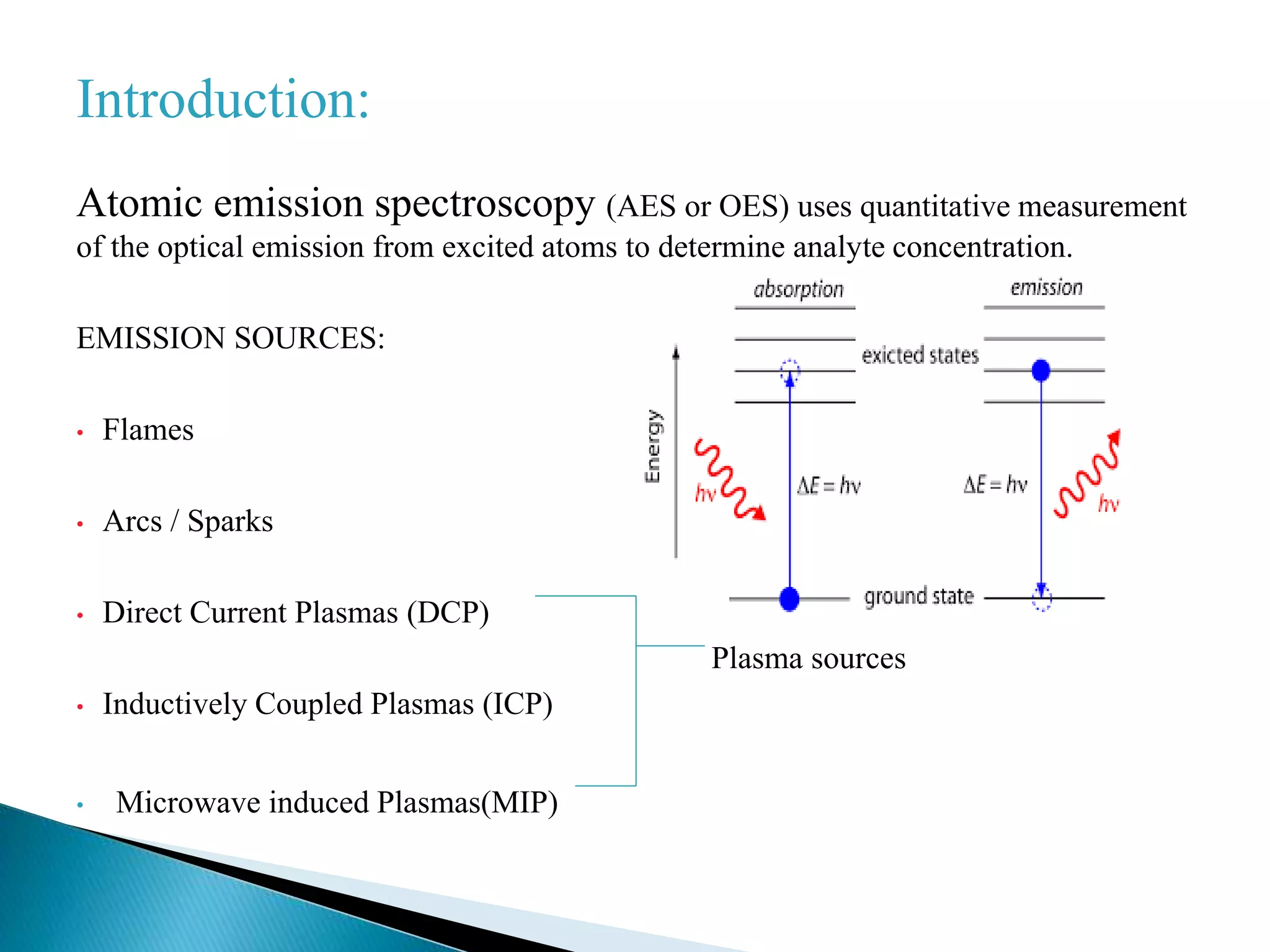
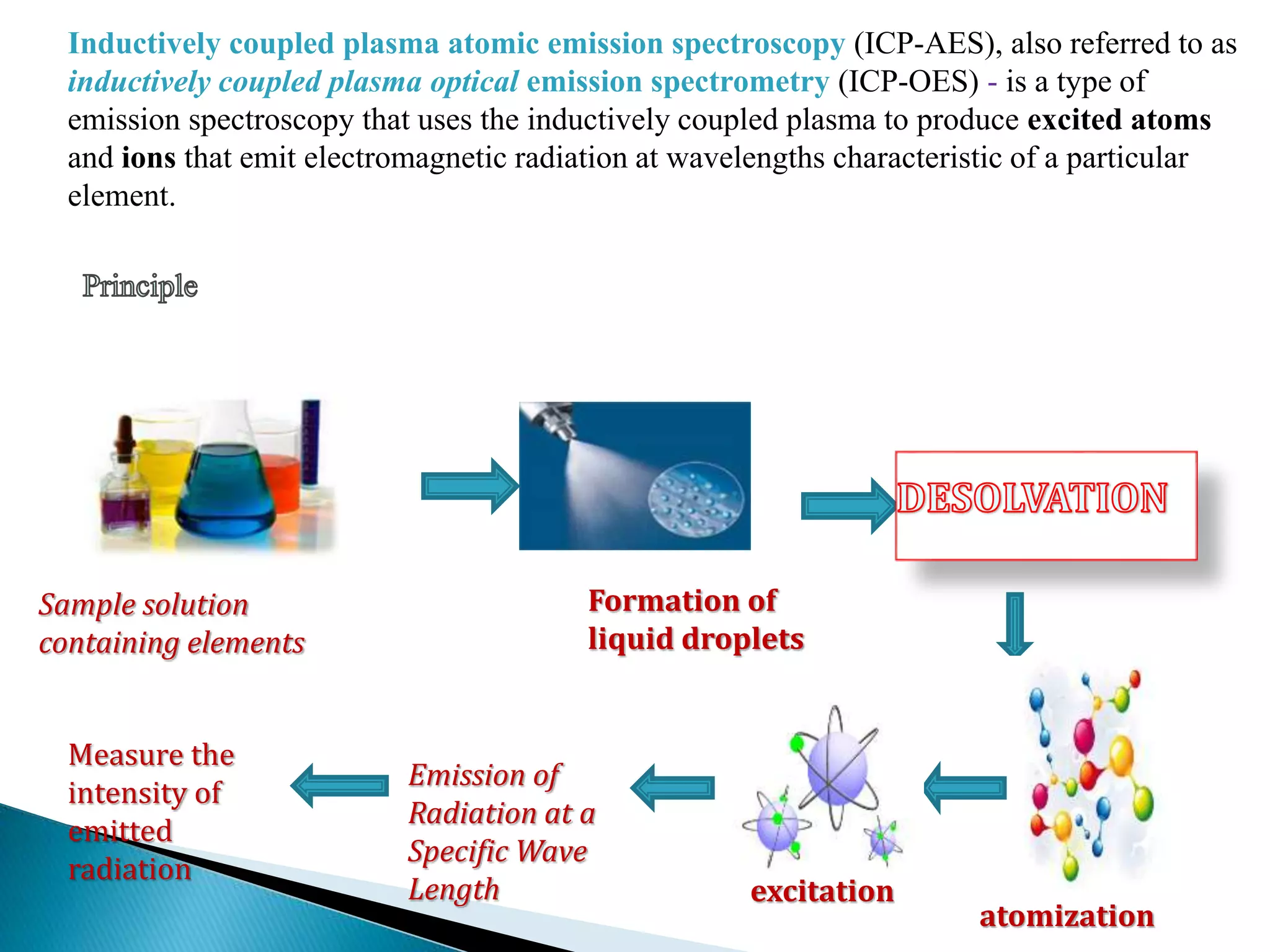
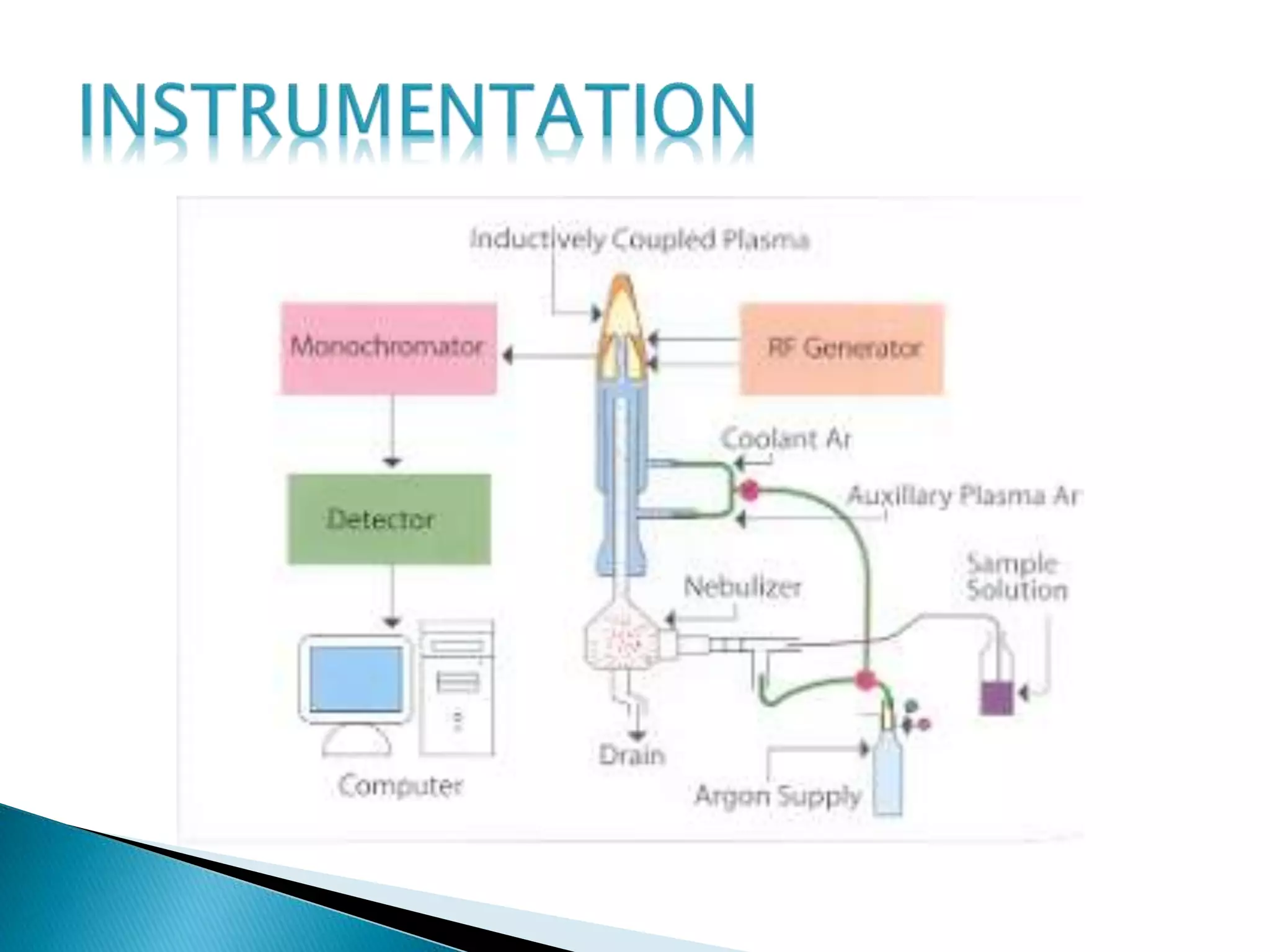
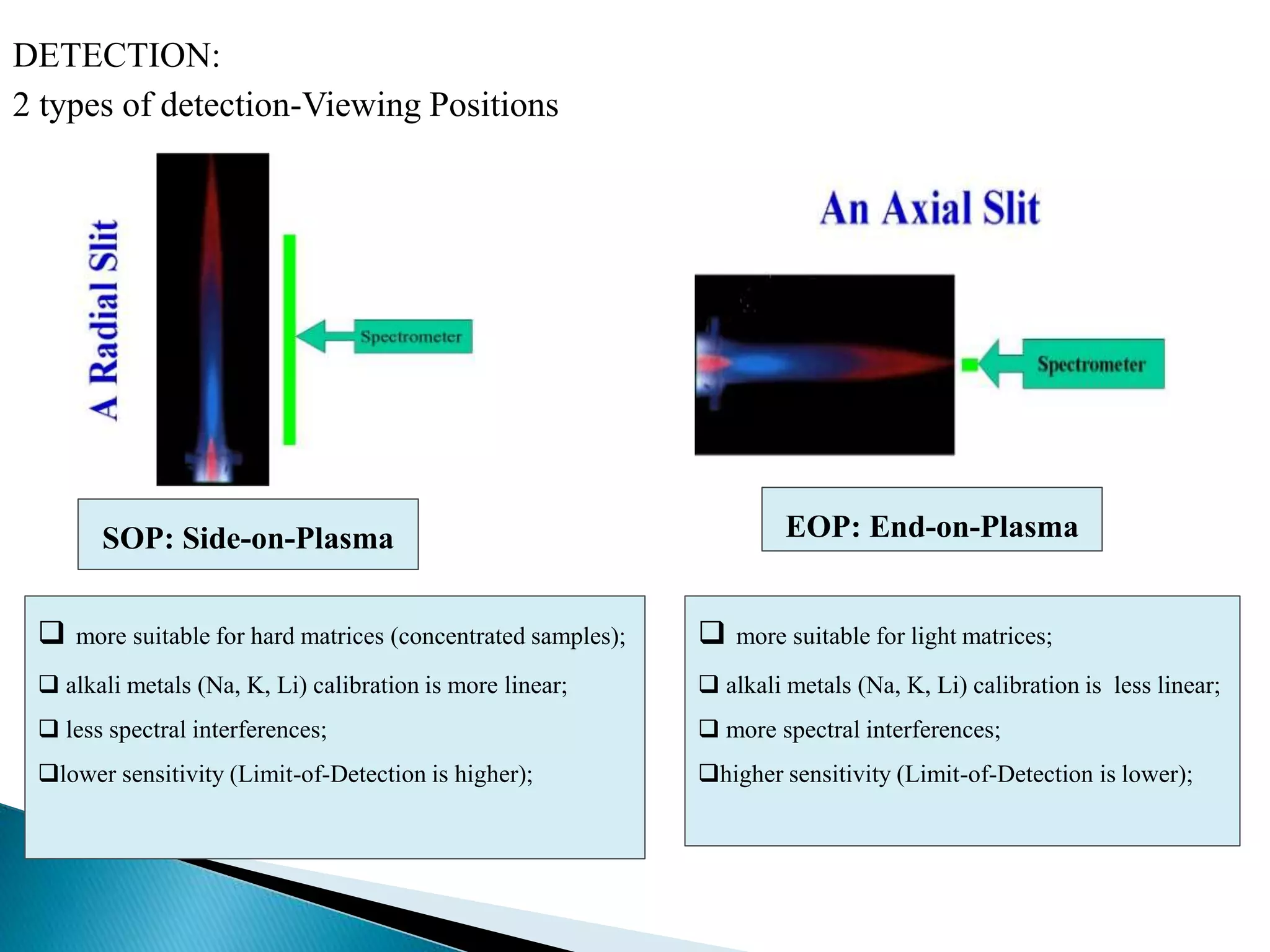
Inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES) uses a plasma to produce excited atoms and ions that emit electromagnetic radiation at wavelengths specific to elements. The document discusses how ICP-AES works, including that a sample is nebulized and transported to the plasma where it is atomized and excited, emitting radiation measured by a spectrometer. Common applications are clinical, environmental, pharmaceutical and industrial analysis to determine trace metal concentrations.