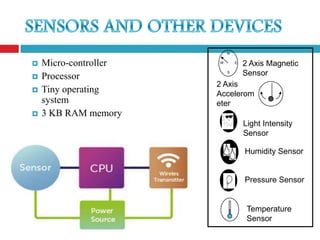
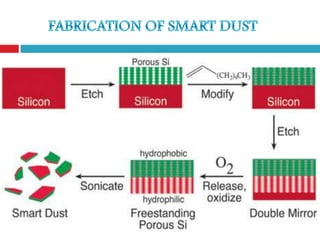
Smart dust is a network of tiny sensor-equipped motes that can monitor environmental conditions. Each mote contains sensors, memory, a processor, and a means of communication. They are self-contained and can communicate with each other or a base station depending on the application. While smart dust provides benefits like environmental monitoring and safety applications, challenges remain in minimizing their size and power needs while ensuring privacy and security of the data.