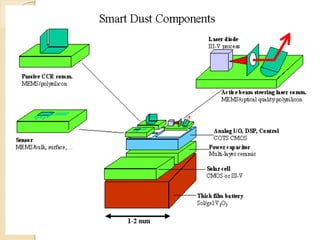
This document discusses smart dust, which are tiny devices that combine sensing, computing, wireless communication and power within a volume of a few millimeters. Smart dust motes can remain suspended in the air like dust particles and are used to monitor environments without disruption. Each mote contains MEMS sensors, beam steering mirrors for optical transmission, receivers and control circuitry powered by batteries and solar cells. Applications include environmental monitoring, habitat monitoring, military monitoring and health monitoring. Challenges include maintaining low power consumption while incorporating diverse functions within a small volume.