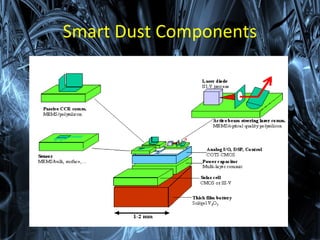
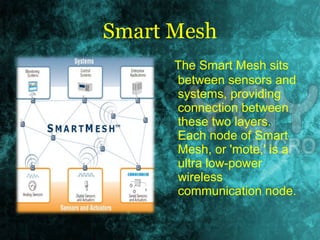
This document discusses smart dust, which are tiny wireless sensing devices that can measure light, temperature, vibration and other environmental factors. Smart dust was invented in 2001 and funded by DARPA for military surveillance applications. Individual smart dust motes are only a few millimeters in size and contain sensors, microprocessors, radio transmitters and batteries. They are designed to operate autonomously for weeks to years while wirelessly communicating sensor readings to other devices. Potential uses include distributed environmental monitoring, military surveillance networks and future planetary exploration.