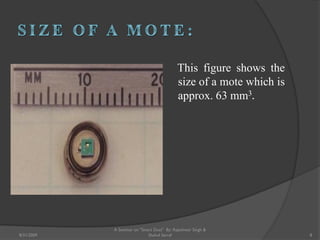
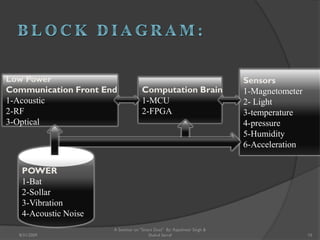
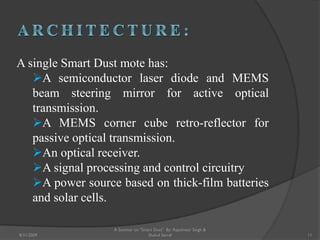
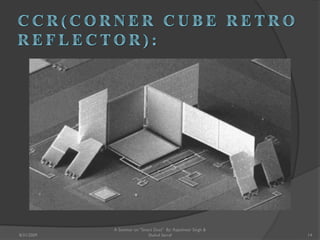
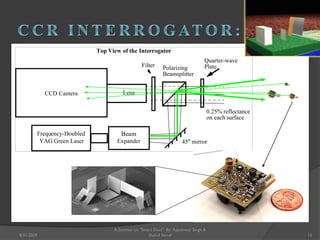
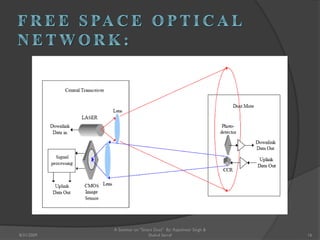
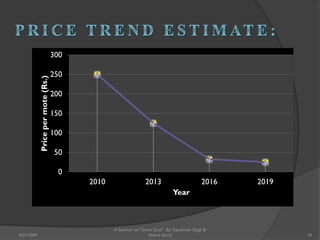
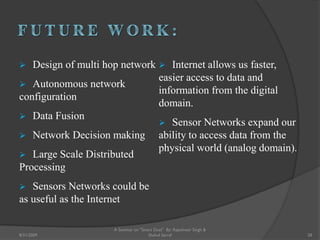
The document presents a seminar on smart dust by Rajeshwar Singh and Shahul Sarraf. Smart dust are tiny wireless sensing devices that are as small as dust particles and can monitor environmental conditions. They have sensing, computing and wireless communication abilities and can operate autonomously using an onboard power source. The seminar describes the internal structure of smart dust motes, optical and radio frequency communication technologies, applications in military, commercial and environmental monitoring, and challenges in developing smart dust networks.