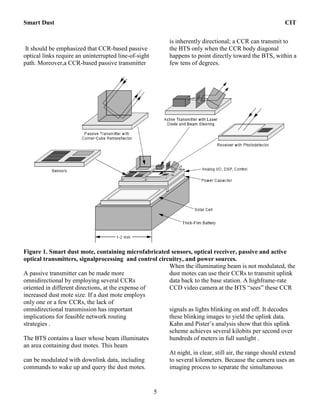
Smart dust is a network of tiny wireless sensor nodes called motes that are the size of dust particles. Each mote contains sensors, communication capabilities, computation power, and a power supply. Key challenges for smart dust include developing networking and applications for large numbers of mobile nodes that consume extremely low power and communicate at low bit rates. Optical communication using techniques like passive transmission with corner-cube retroreflectors shows promise for meeting smart dust's challenging power and size constraints, allowing for self-powered wireless sensing and communication in a cubic millimeter volume.
![Smart Dust CIT
1
CHANNABASAVESHWARA
INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
KNEW - 2009
A PAPER
ON
NEXT CENTUARY CHALLENGE:
MOBILE NETWORKING “SMART DUST”
PRESENTED BY
UTPHALA P AND SANITHA G
[7TH SEM CSE]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e06b4ffd-b1c1-43ad-9d2e-79a6d80c37ae-160902193340/85/Smart-Dust-1-320.jpg)