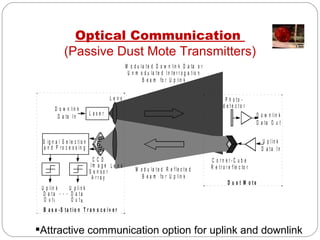
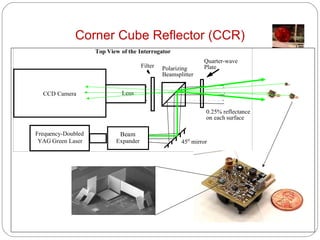
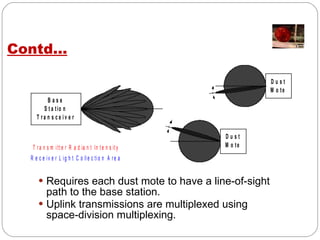
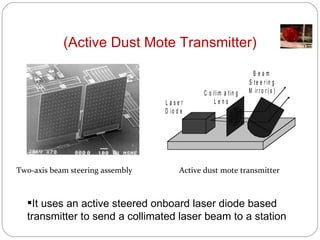
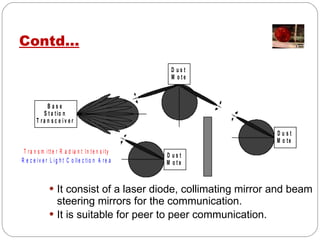
Smart dust consists of tiny autonomous sensing devices called motes that are less than 1.5mm3 in volume and 5mg in mass. Motes can collect sensor data and transmit it wirelessly over distances of 15-50m to a base station using radio frequency, passive optical reflectors, or active laser transmitters. They incorporate sensors, microprocessors, memory, transmitters and receivers, and thick film batteries or solar cells to operate independently for long periods with very low power usage. Potential applications include environmental monitoring, infrastructure inspection, health monitoring, and more.