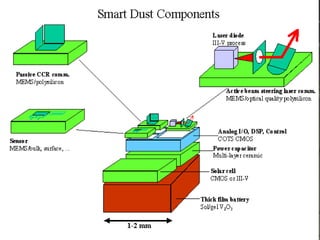
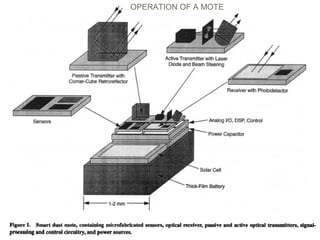
The document discusses 'smart dust', which consists of tiny electronic devices called motes that use MEMS technology to capture environmental data while floating on air. These motes communicate wirelessly via radio frequency and optical transmission techniques, and have diverse applications in civil and military fields. Challenges include low power consumption and efficient energy use to maximize operational life.