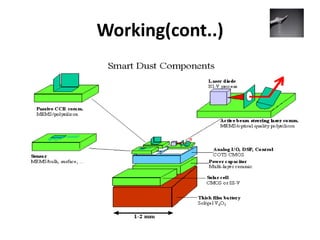
Smart dust is a network of tiny sensor motes that can detect environmental conditions like light and vibrations. Each mote contains sensors and computational ability to communicate wirelessly with other motes or a base station. Though constrained by their small size, the motes conserve power by powering on intermittently to perform tasks then powering off. Potential applications include environmental monitoring and situations where wired sensors are impractical. While smart dust enables connectivity and low costs, privacy concerns and challenges around power management and self-maintenance exist. However, companies are investing in the technology to integrate it into future systems and networks.