Embed presentation
Downloaded 53 times













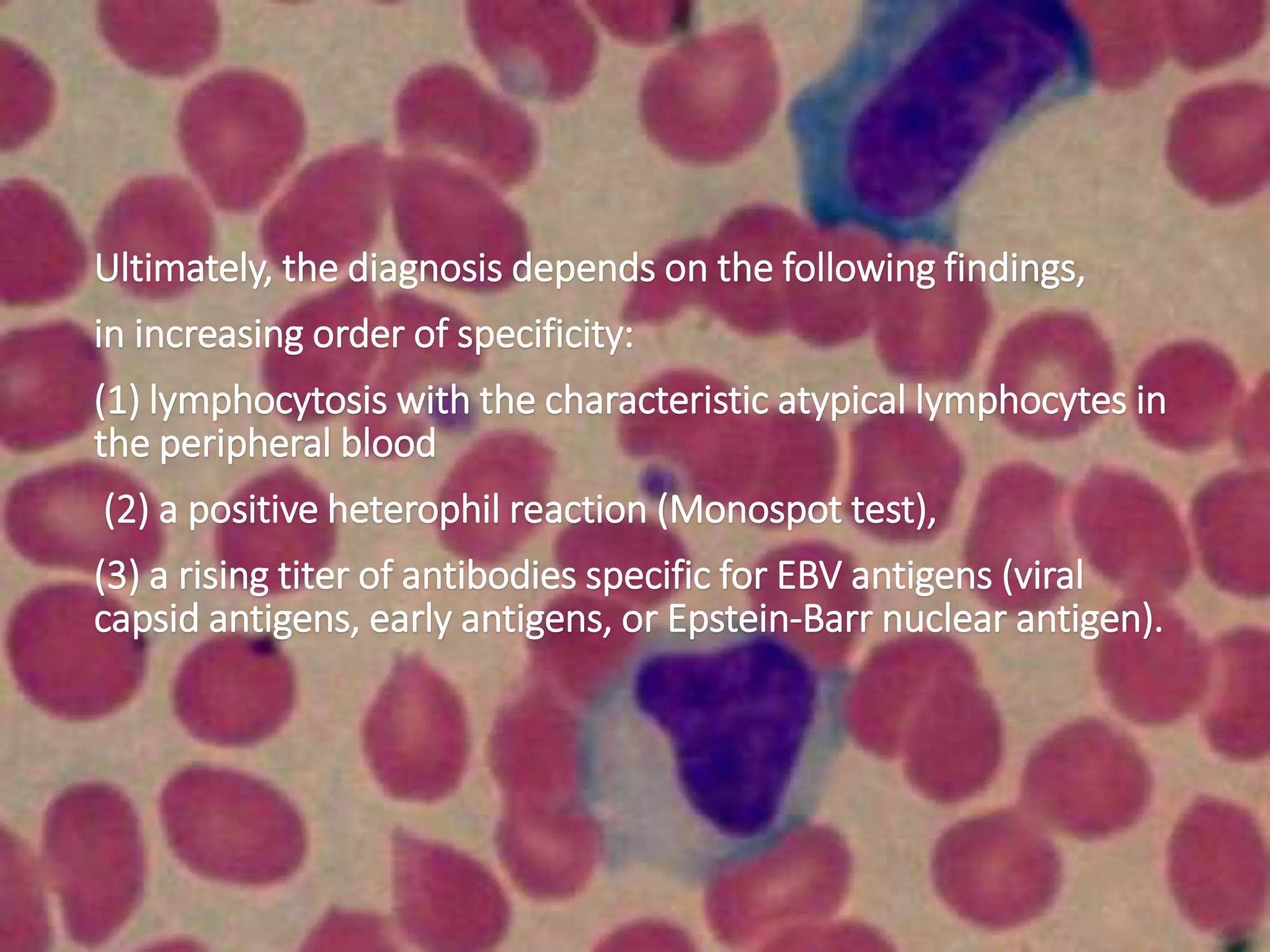



Infectious mononucleosis is caused by the Epstein-Barr virus and causes an acute self-limited disease typically in adolescents and young adults. It is characterized by lymphocytosis showing atypical lymphocytes in blood smears, lymphadenopathy, and sometimes splenomegaly. The diagnosis involves detecting atypical lymphocytes in blood, a positive Monospot test, or a rising titer of antibodies to EBV antigens.















