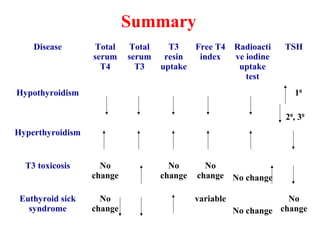
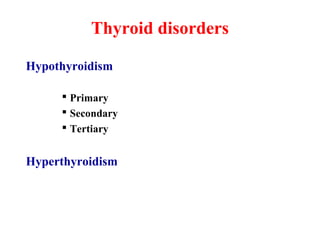
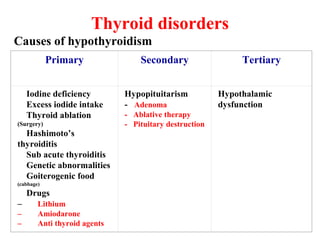
This document summarizes thyroid function tests. It describes the thyroid hormones T4 and T3, their binding proteins, and differences between the hormones. Thyroid disorders like hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism are discussed along with their symptoms and causes. Various thyroid tests are outlined that measure thyroid hormone levels, evaluate the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis, assess thyroid gland function, and detect antibodies. Reference ranges are provided for tests like free T4, total T4, T3 resin uptake, free T4 index, total T3, TSH, and radioactive iodine uptake. The summary provides expected results for these tests in conditions like hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism,








![Thyroid tests
Total serum T4:
Reference range: 4 - 12 microgram/dl
Measures both bound and free T4
Increased total serum T4 – hyperthyroidism/
increase concentration of thyroid binding proteins
Decreased total serum T4 –
hypothyroidism/decrease concentration of thyroid
binding proteins/ non thyroid illness [DM, liver disease,
renal failure, prolonged infection and CV diseases]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thyroidfunctiontests-140319142003-phpapp01/85/Thyroid-function-tests-12-320.jpg)