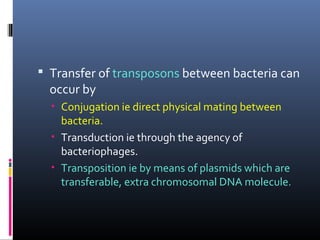
This document discusses sensitivity testing, which determines the effectiveness of antimicrobial drugs against bacterial strains. Sensitivity testing helps select the most effective drug and identify pathogens. It is done using diffusion or dilution techniques to measure zones of inhibition or minimum inhibitory concentrations. However, sensitivity testing only measures drug effectiveness in laboratory conditions and does not account for patient factors. Antimicrobial resistance can develop through genetic mutations or exchange between bacteria, allowing resistance to spread to multiple drugs. Sensitivity testing guides optimal treatment while addressing the rise of antimicrobial resistance.