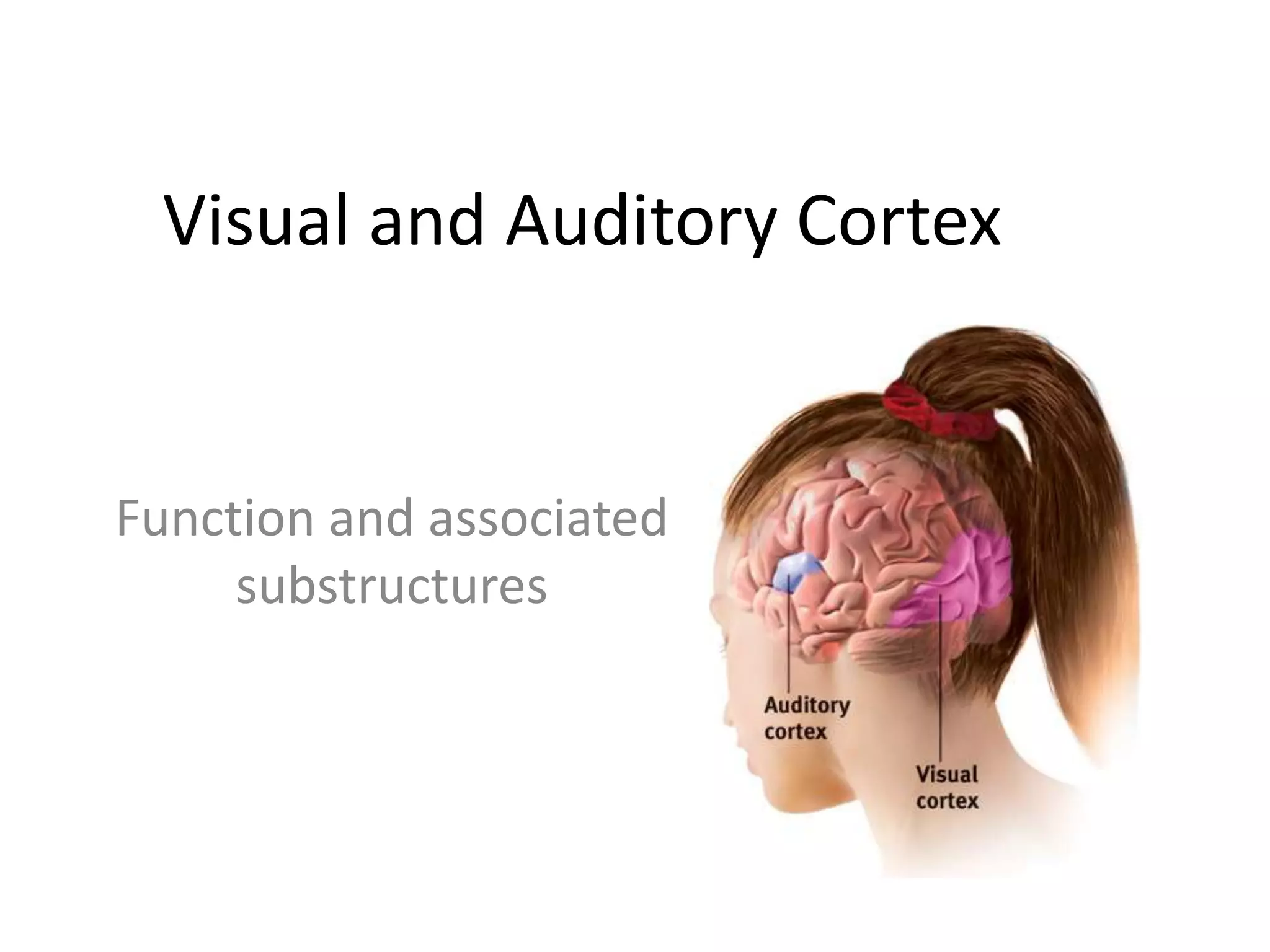
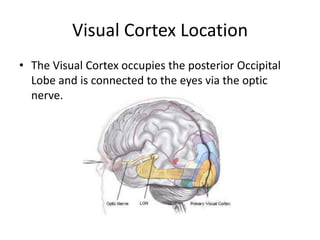
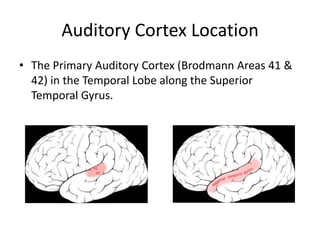
The visual cortex is located in the occipital lobe and processes visual information from the eyes via the optic nerve. It contains specialized regions for color, spatial awareness, depth, texture, and motion. The primary auditory cortex is located in the temporal lobe and processes pitch and volume. Higher-level auditory areas integrate these basics into perceptions of speech, music, and sounds. The fusiform gyrus is located near tertiary auditory areas and visual area V3, and is involved in face recognition based on its location in the brain.