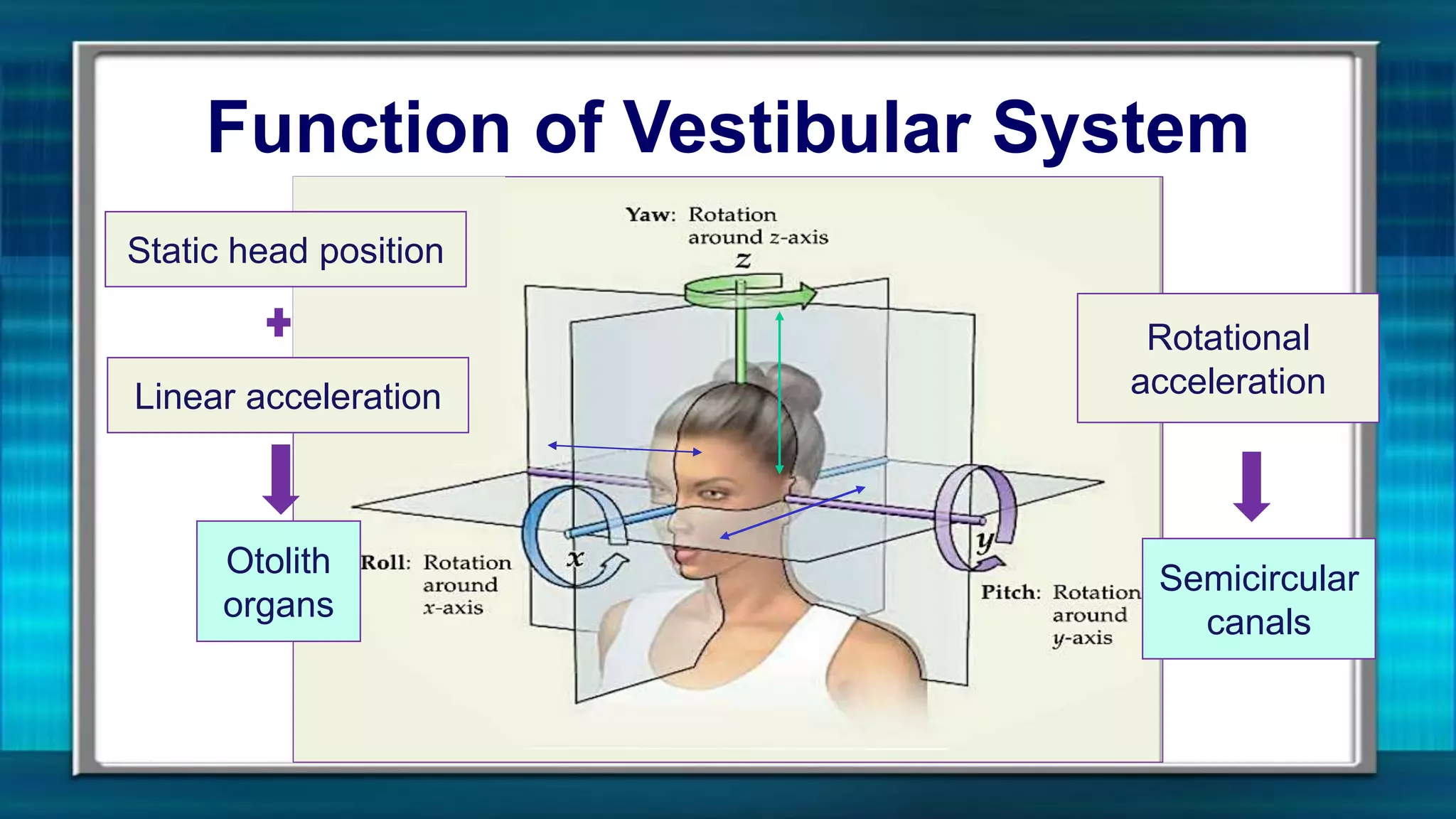
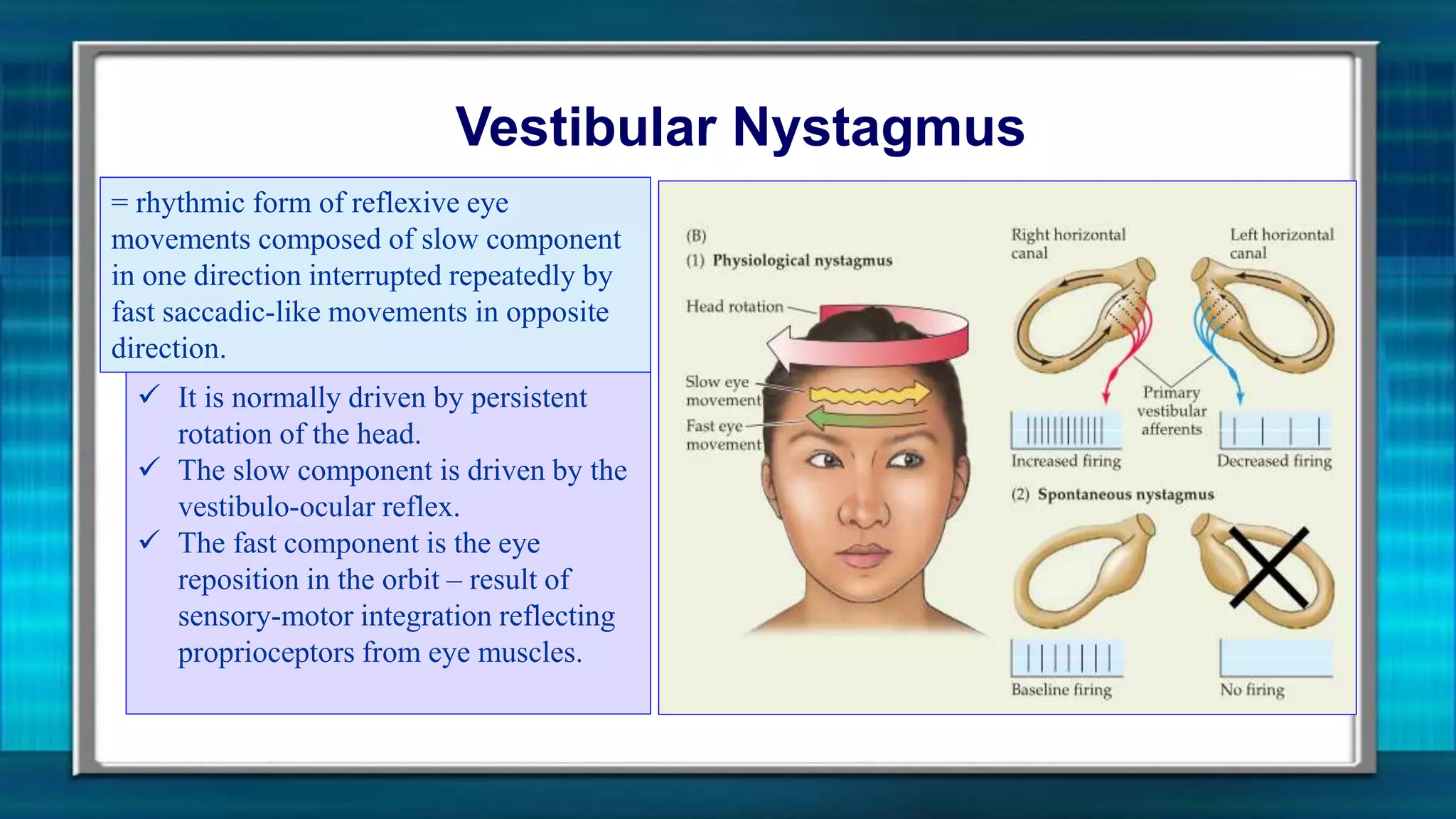
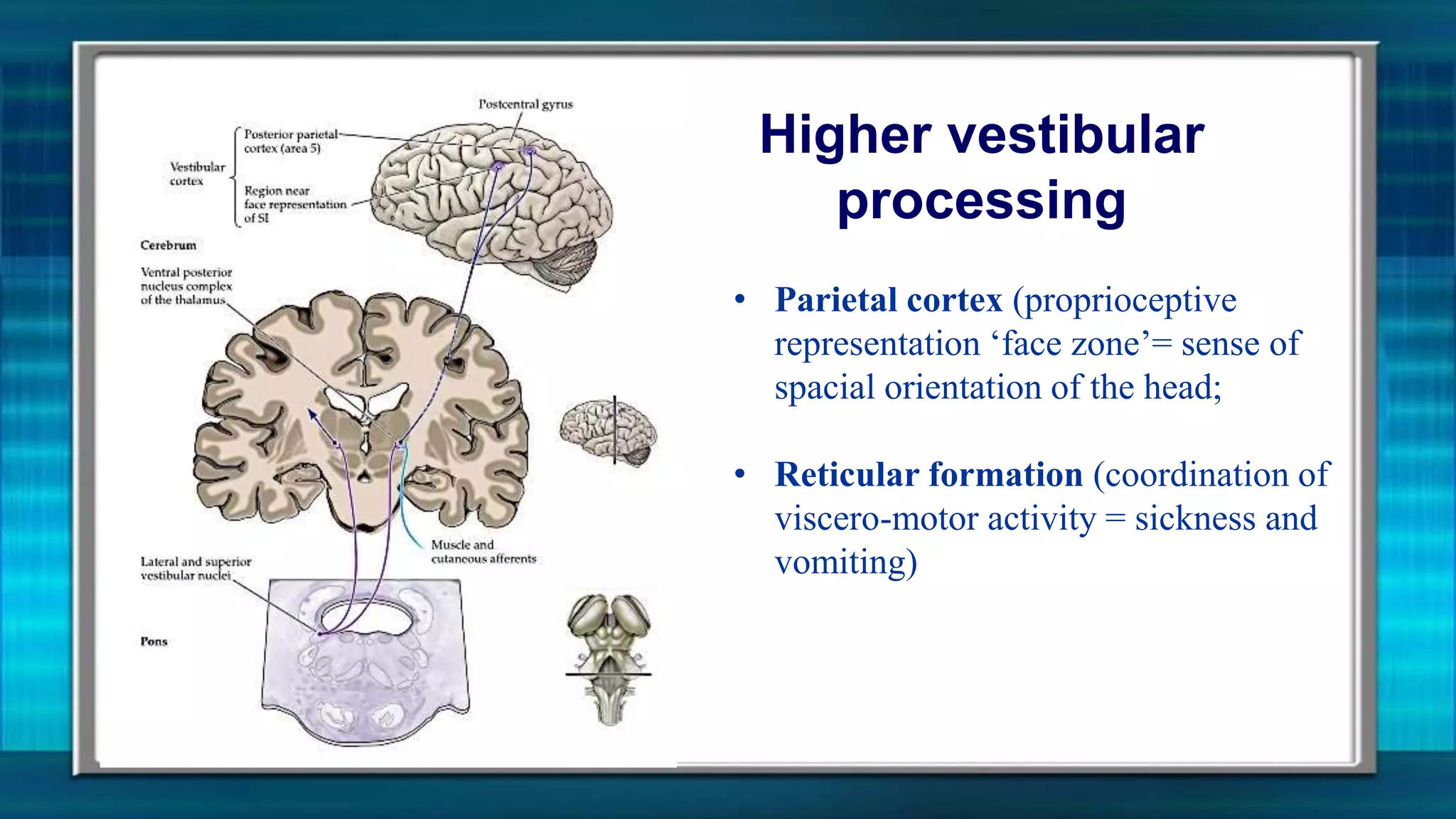
The vestibular system senses motion and orientation of the head. It contains two classes of sensory structures: the otolith organs (utricle and saccule) which detect linear acceleration and the semicircular canals which detect rotational acceleration. Sensory hair cells in these structures transduce motion signals into neural impulses. The vestibular nuclei integrate this information and send signals to control eye movements via the vestibulo-ocular reflex and posture/balance via vestibulospinal pathways. Damage to the vestibular system can cause vertigo, nystagmus and loss of balance/orientation.