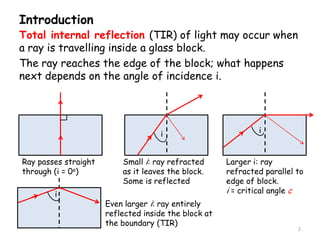
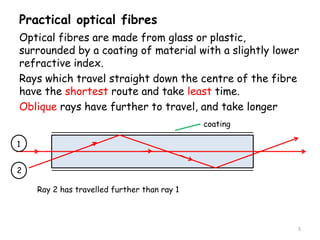
Total internal reflection occurs when a light ray traveling through a higher refractive index material reaches the boundary with a lower refractive index material at an angle greater than or equal to the critical angle. At this critical angle, the refracted ray travels parallel to the surface. Total internal reflection is used in optical fibers to transmit light along the fiber by repeated reflections off the inner fiber surface. Optical fibers have advantages over metal cables for data transmission as they can carry vastly more data and the signals are less susceptible to noise and tapping.