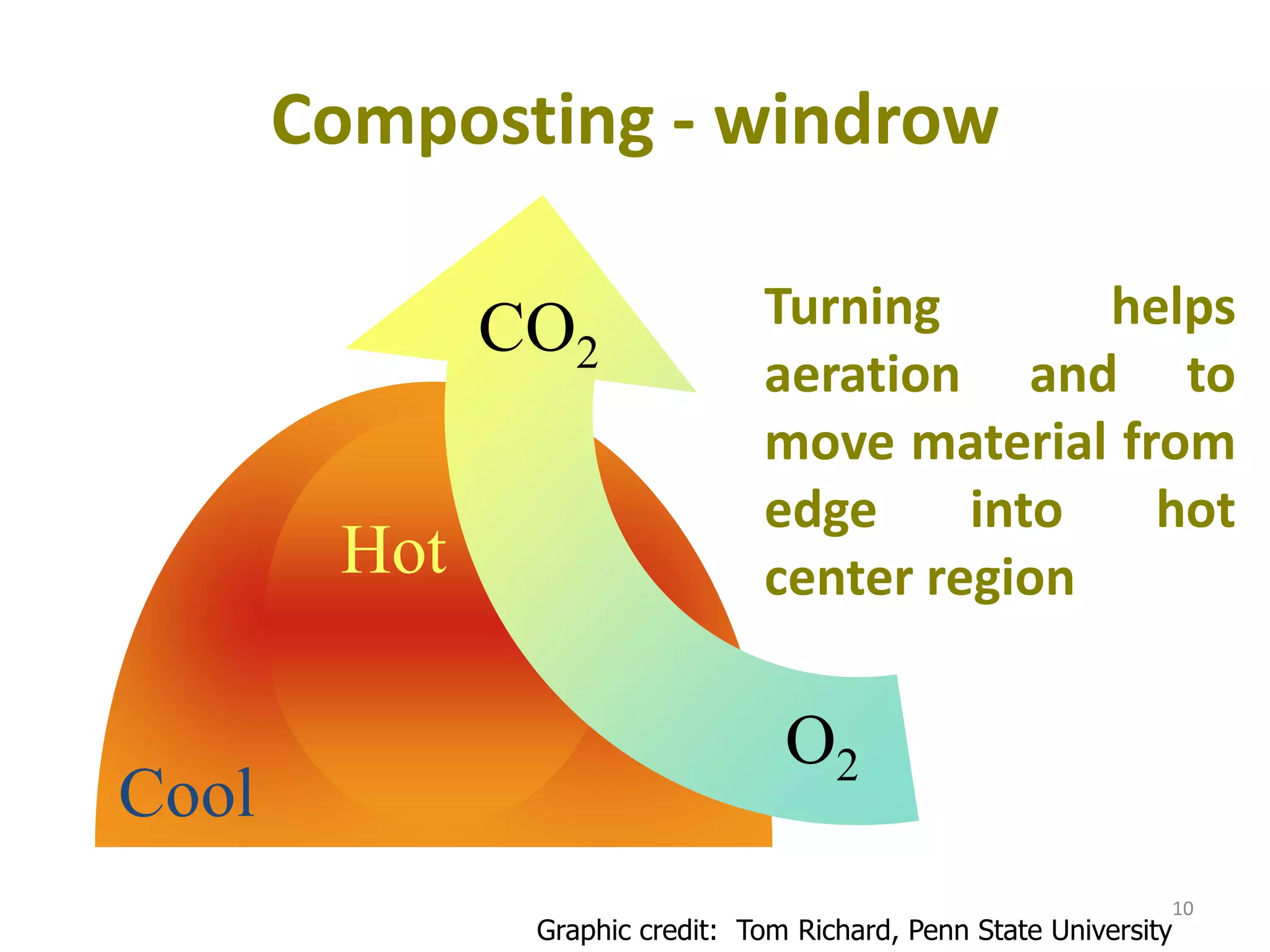
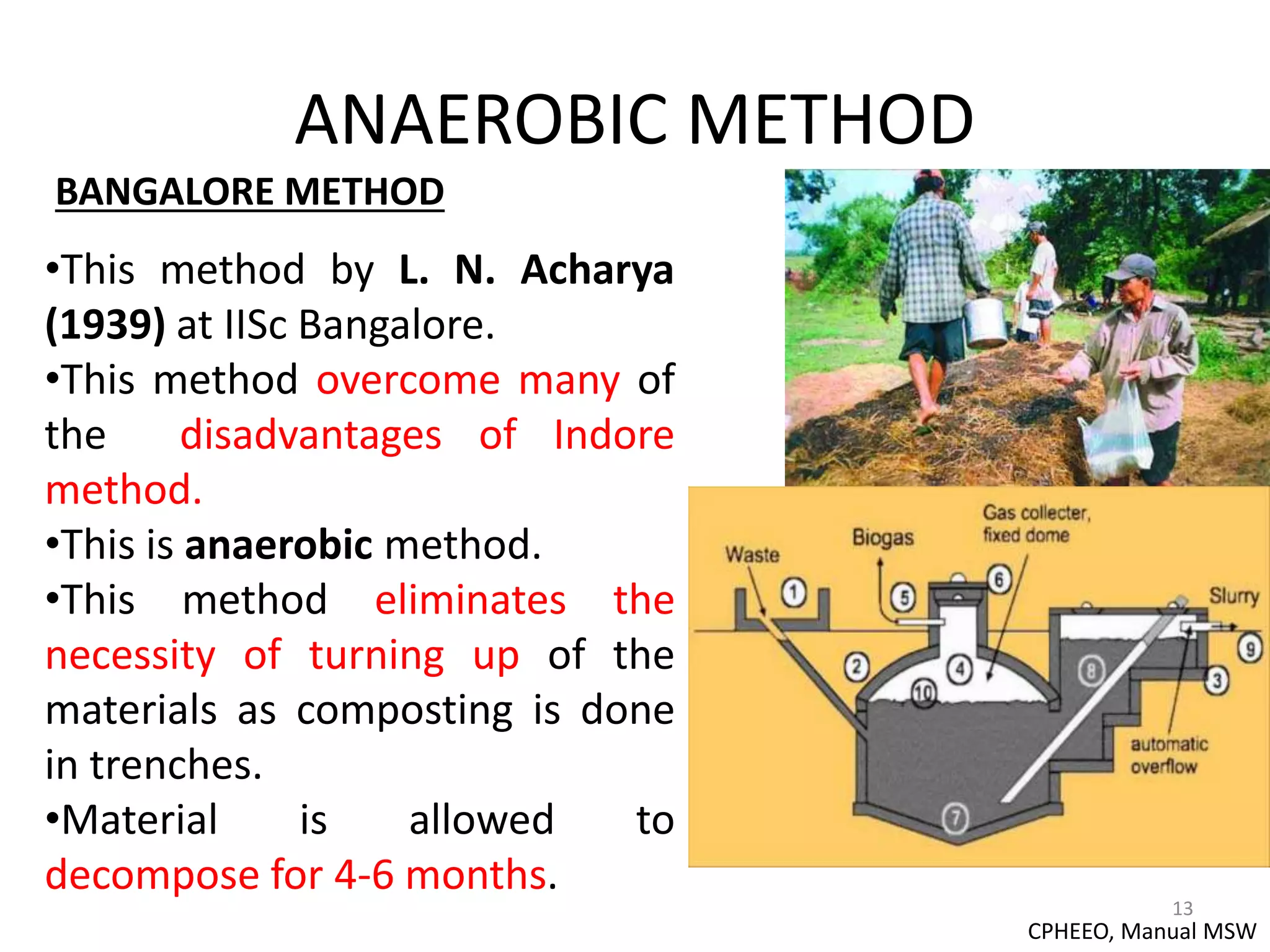
This document discusses composting as a solution for managing municipal solid waste in India. It provides information on the sources and composition of organic waste that can be composted. Various composting methods are described, including windrow composting, Indore and Bangalore methods, aerobic and anaerobic processes. Key factors that affect composting like carbon-nitrogen ratio, moisture level, temperature and aeration are outlined. The document also provides statistics on composting in India, like the capacity for compost production and treatment of municipal solid waste.