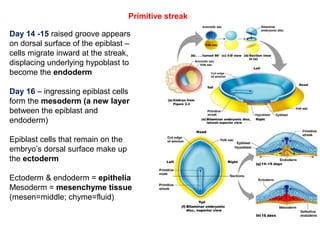
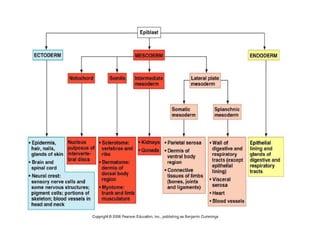
1. Gastrulation begins around day 14-15 with the formation of the primitive streak on the dorsal surface of the embryo, through which epiblast cells migrate inward to form the mesoderm and endoderm.
2. Cells invaginating the primitive pit move forward to form the notochordal process, which later forms the definitive notochord, a solid cord of cells.
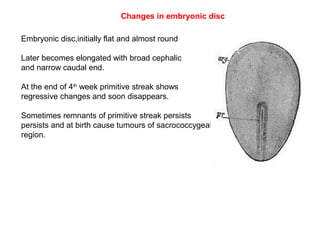
3. By the end of the 4th week, the primitive streak begins to regress and disappear, and the embryonic disc becomes elongated with broad and narrow ends.