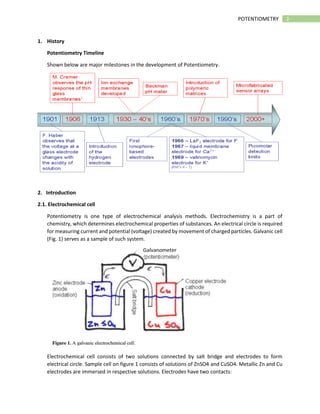
Potentiometry is an electroanalytical technique that measures the electric potential of electrochemical cells under zero-current conditions. It involves measuring the potential difference between a reference electrode with a known potential and an indicator electrode whose potential varies with the concentration of the analyte ion. The potential difference is used to determine analyte concentration based on the Nernst equation. Common applications of potentiometry include clinical analysis of electrolytes, environmental analysis of ions in water, and titration measurements.