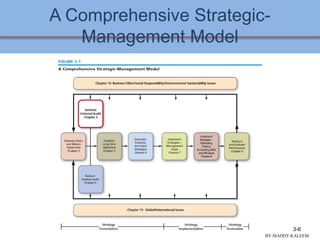
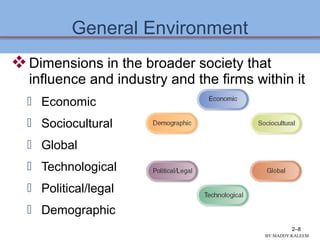
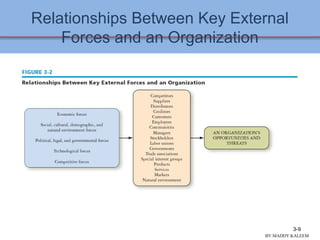
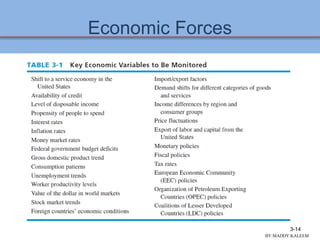
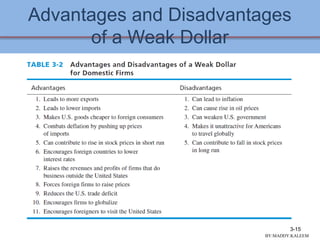
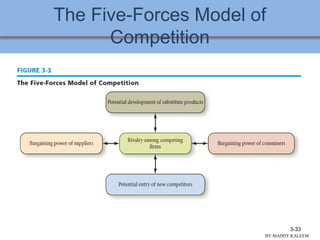
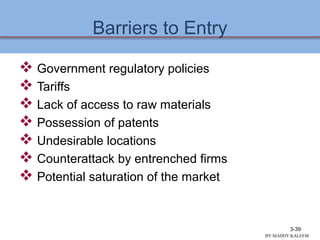
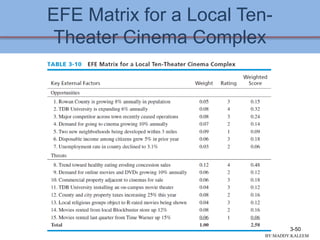
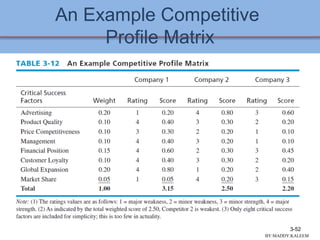
This document discusses conducting an external audit to analyze external factors affecting an organization. It covers 10 major external forces including economic, social, technological and competitive factors. The key steps in an external audit are to gather information on these forces from sources like the internet, evaluate the factors, identify important opportunities and threats, and communicate the findings. Tools like the EFE matrix and competitive profile matrix are used to analyze external industry factors and competitors. Monitoring external trends and developing competitive intelligence are important parts of the external audit process.