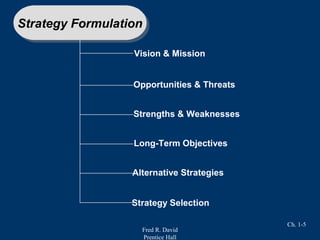
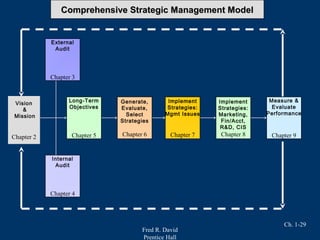
Strategic management involves three main stages: strategy formulation, strategy implementation, and strategy evaluation. It integrates management, marketing, finance, operations, R&D, and information systems to achieve organizational success. A key part of strategic management is analyzing internal strengths and weaknesses as well as external opportunities and threats to determine how to best position an organization for long-term success. Benefits of strategic management include improved financial and organizational performance as well as enhanced ability to adapt to changes in the business environment.