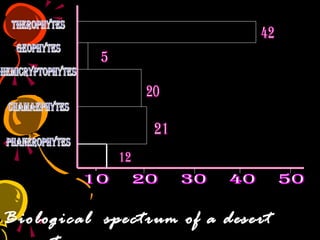
Community ecology is the study of the interactions between species within a biological community. A community is defined as an assemblage of plant and animal species that occur together in a specific habitat. Characteristics of a community include species diversity, dominance by one or a few species, trophic structure consisting of producers, consumers, and decomposers, and successional changes over time. Communities can be classified and analyzed based on quantitative characteristics like frequency, density, and cover, and qualitative characteristics like physiognomy, phenology, and stratification. Ecotones form transitional zones between two adjacent communities, and the biological spectrum indicates the distribution of life forms in a community.