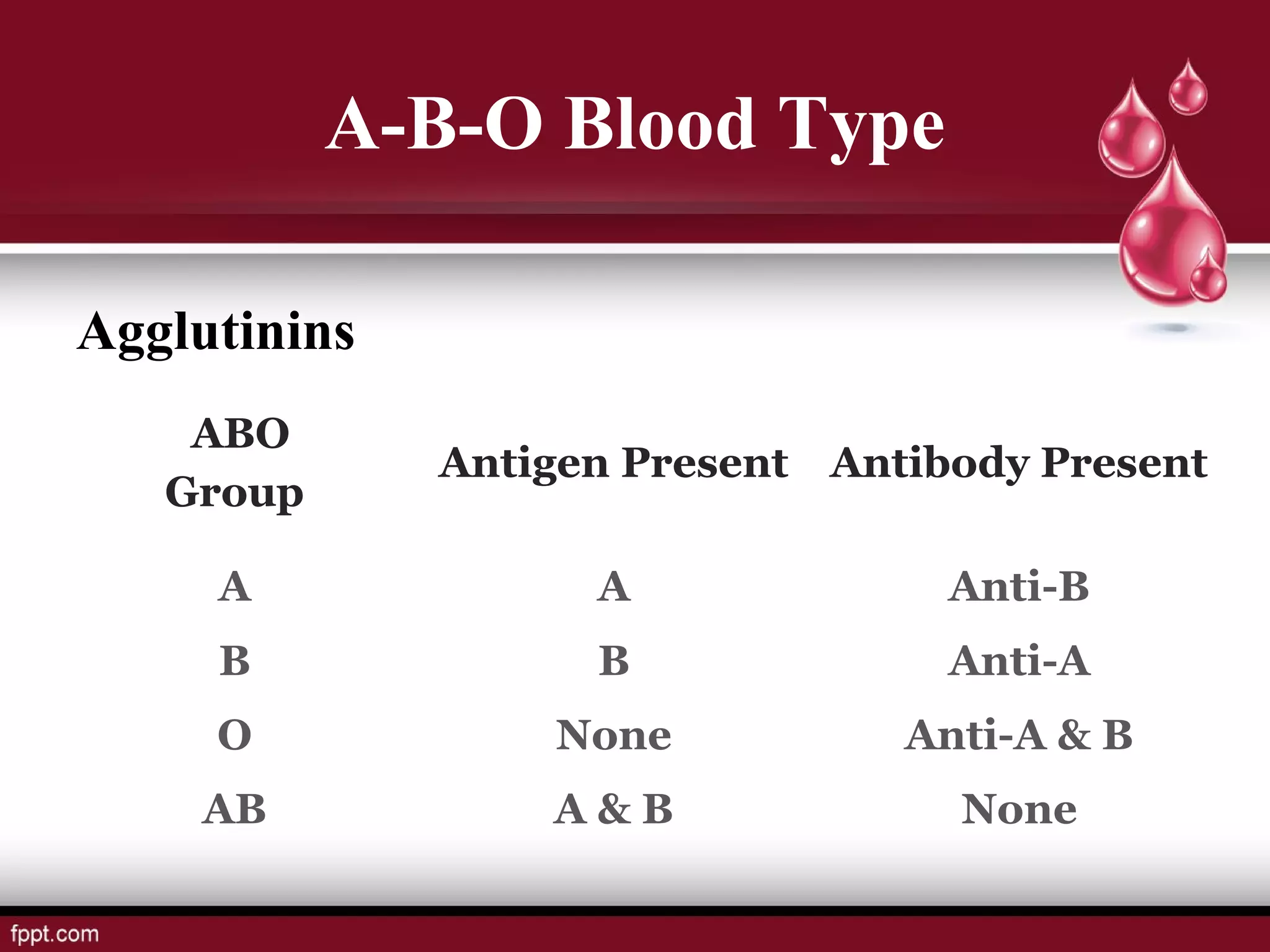
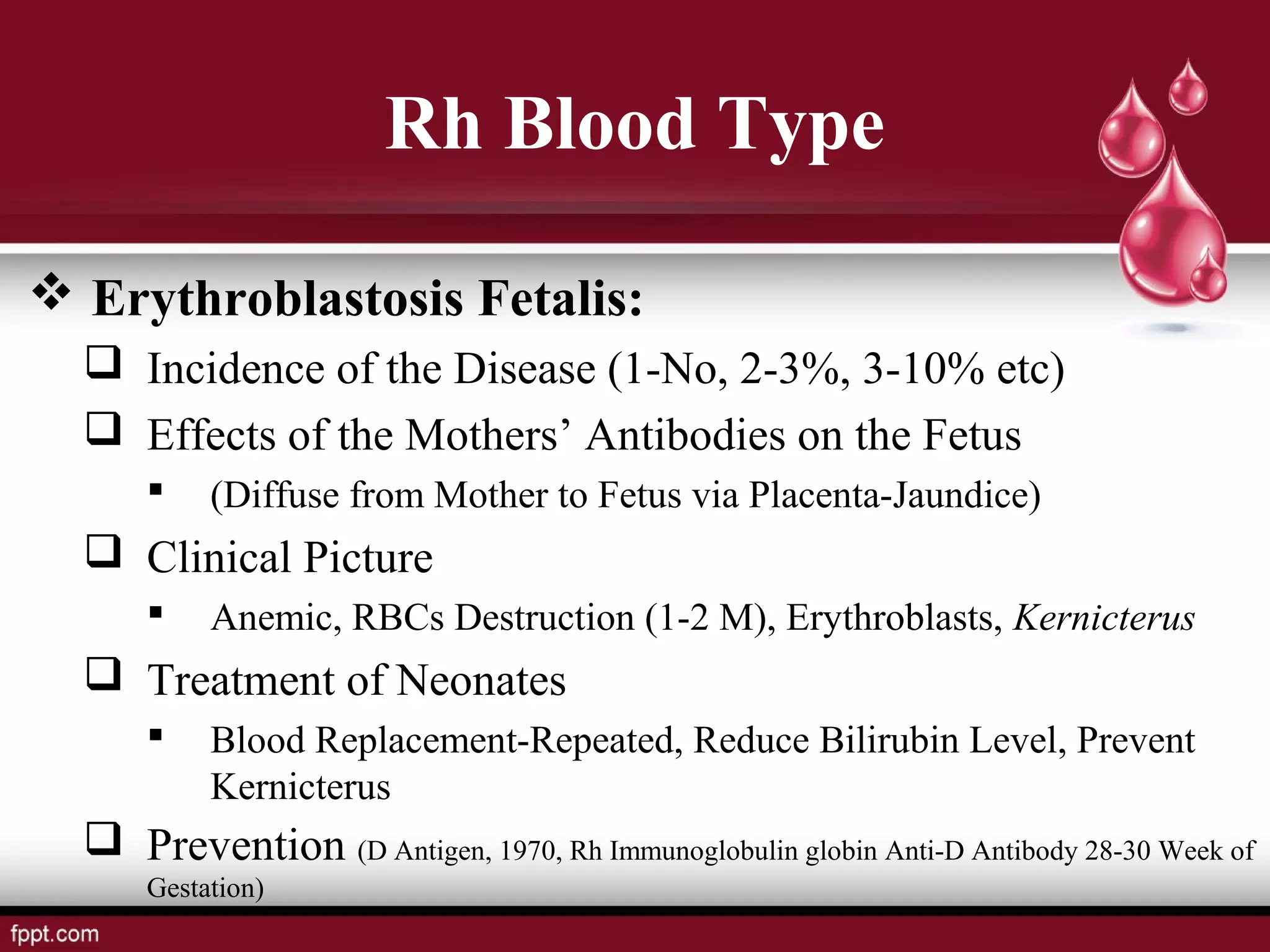
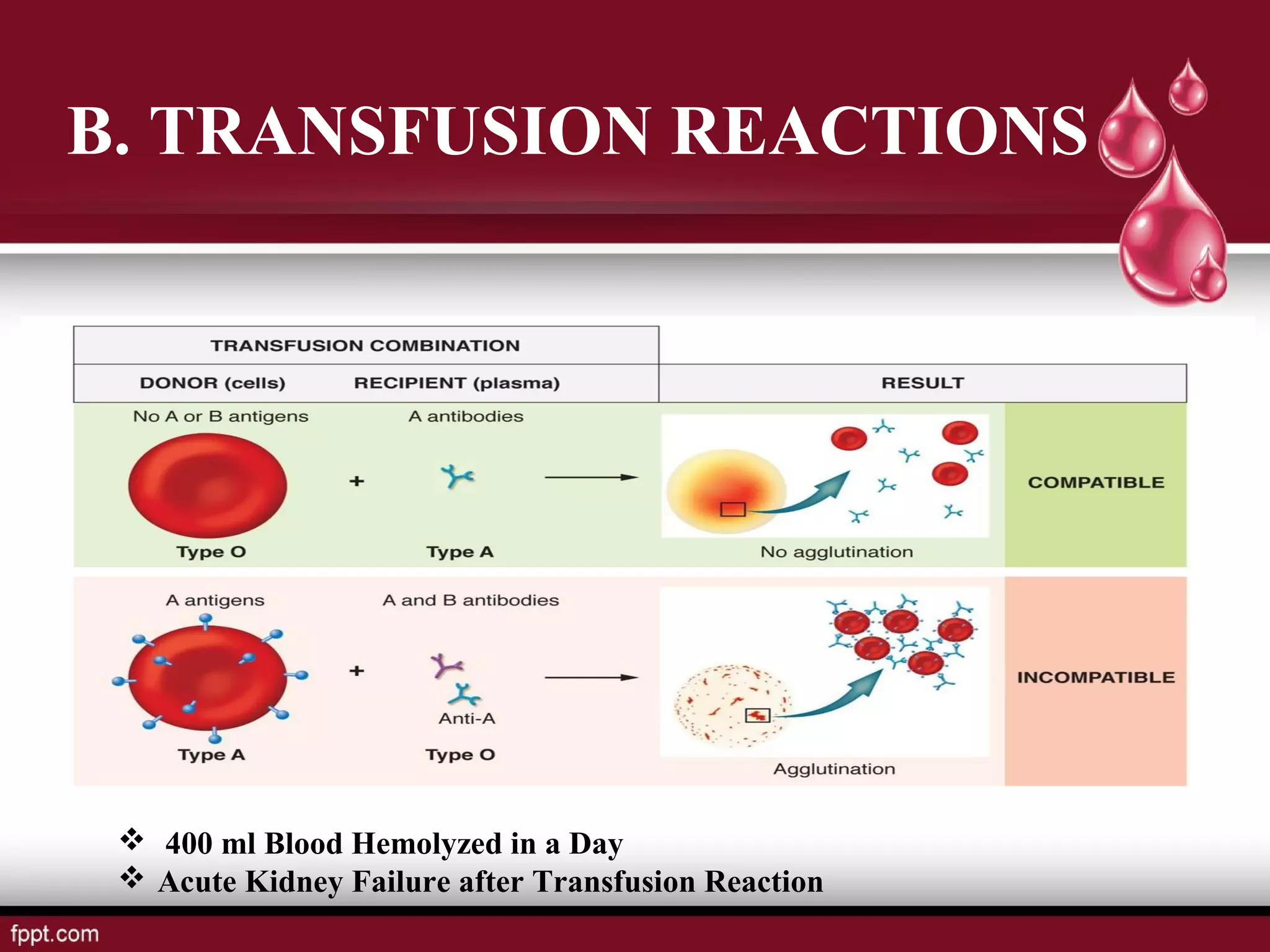
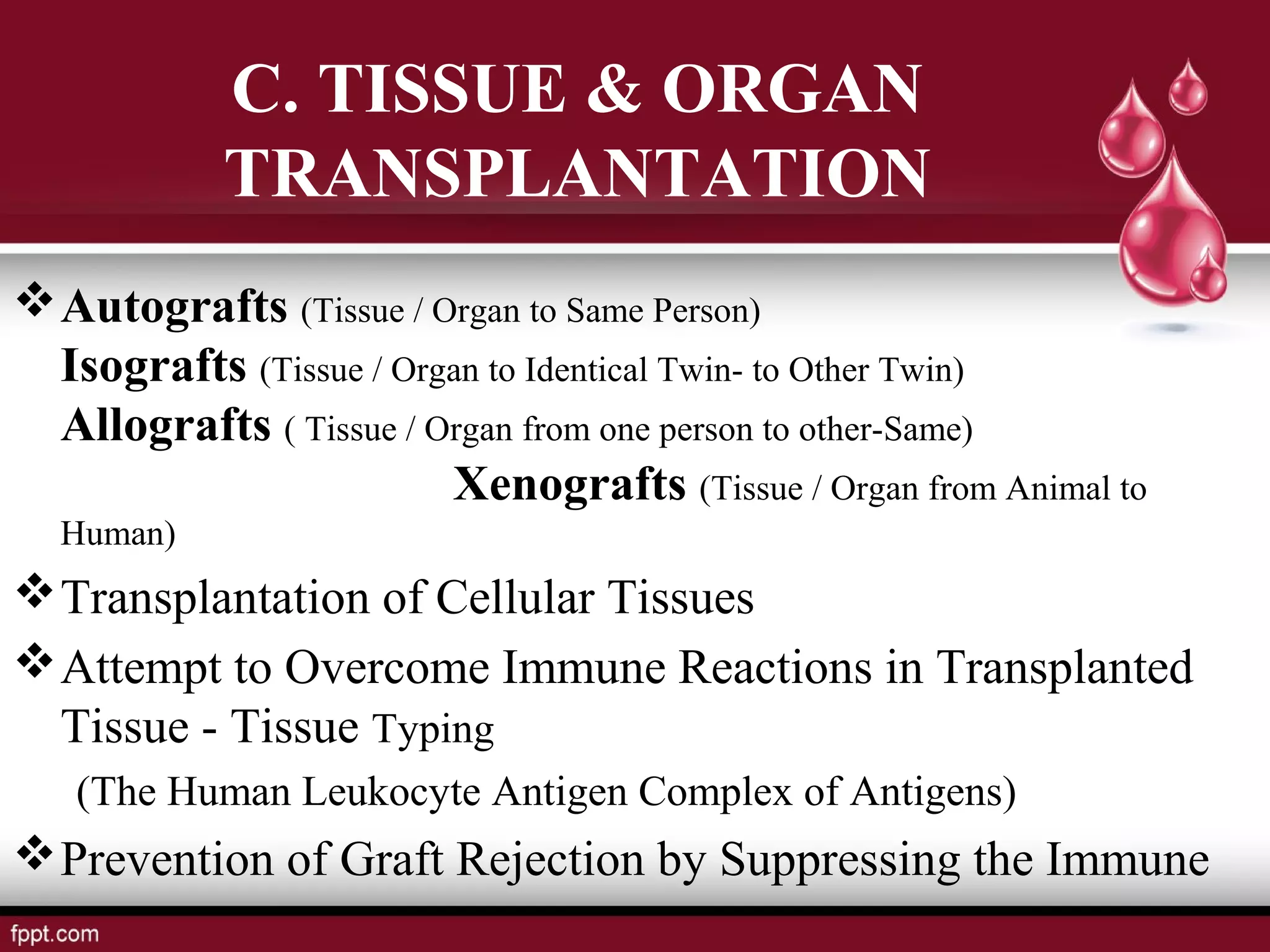
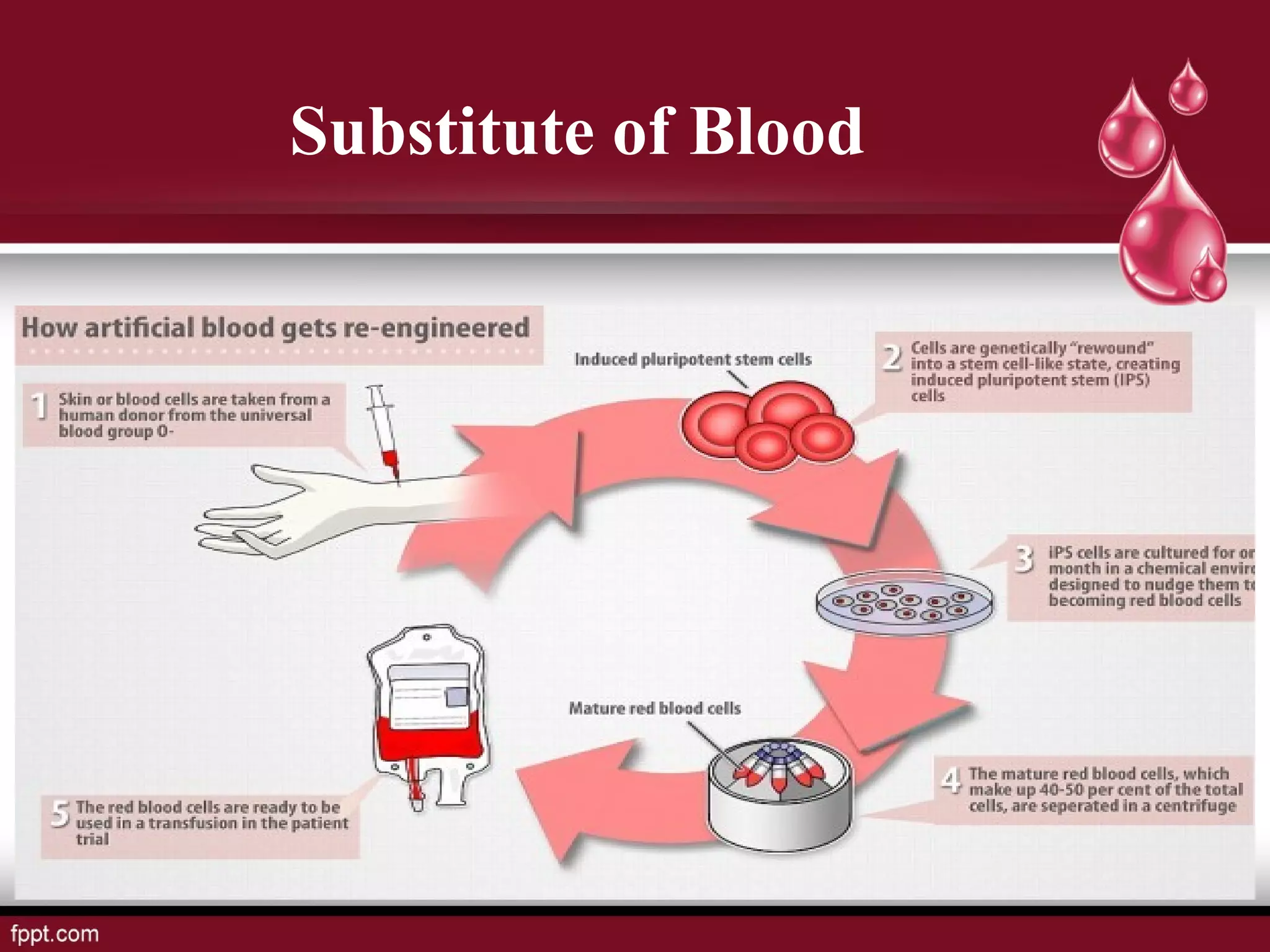
Blood types and tissue/organ transplantation were discussed. There are four main blood types - A, B, AB, and O - determined by the presence or absence of antigens on red blood cells. Transfusing incompatible blood can cause agglutination and hemolysis. The Rh system involves D antigens that can sensitize mothers, risking hemolytic disease in subsequent Rh-positive babies. Tissue and organ transplantation requires matching donors and recipients to reduce immune rejection. Immunosuppressants are used but autografts and isografts have least risk of rejection compared to allografts and xenografts.