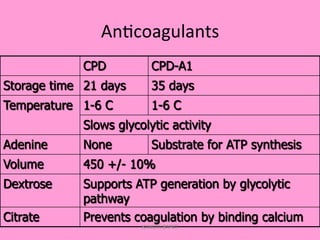
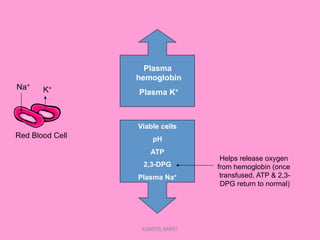
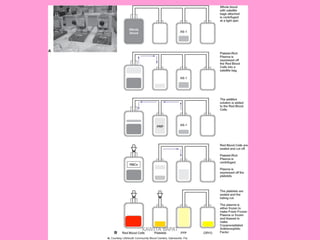
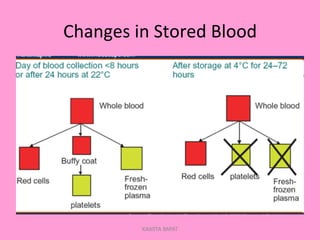
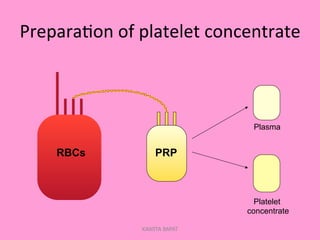
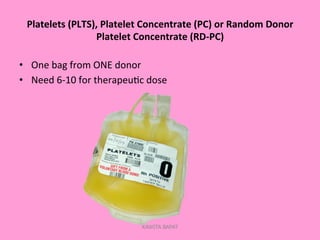
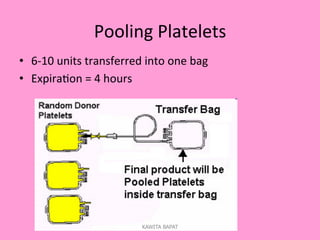
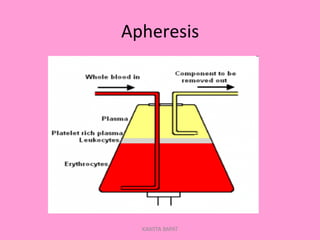
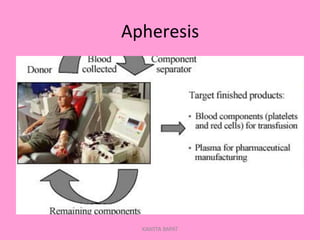
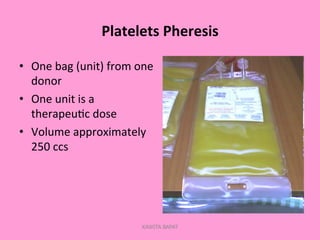
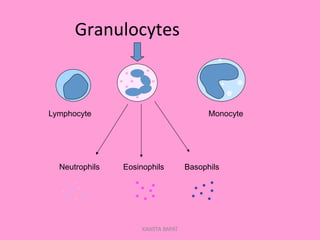
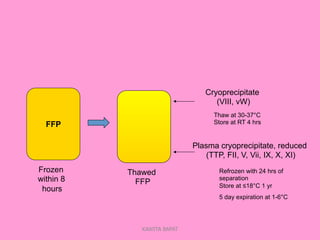
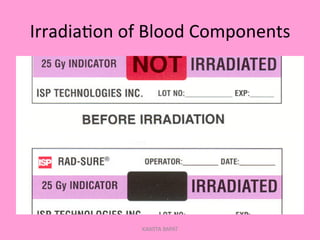
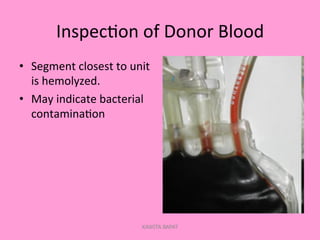
One unit of whole blood can be separated into various blood components through centrifugation and other processing steps. This allows each component to be stored optimally and transfused only as needed by patients. Red blood cells can be stored for 21 days in CPD or 42 days when added to ADSOL. Platelets are stored at room temperature while plasma products like FFP and cryoprecipitate must be frozen and thawed as needed. Whole blood is rarely used today due to non-functional platelets and labile coagulation factors after collection.