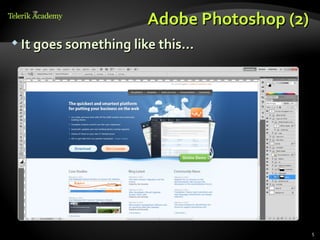
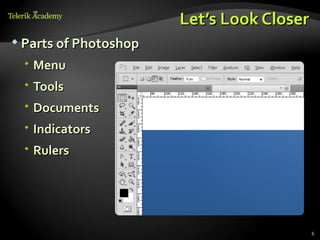
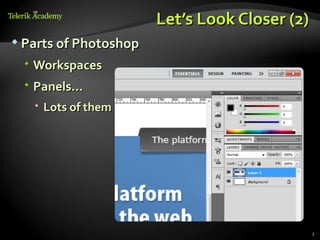
This document discusses processing and exporting images in Adobe Photoshop. It covers Photoshop toolboxes including tools, layers and groups, history, and type. It also discusses must-know concepts for slicing images like backgrounds, tiles, formats, and feathering. The document provides examples for slicing buttons and creating shadows and menus from image assets. It emphasizes using layers, groups, and the save for web option for exporting optimized images.



































![Exercises
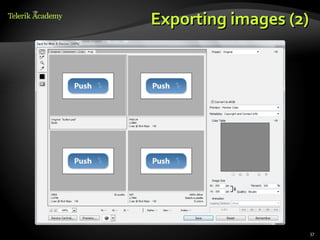
( Given the file button.psd create a Web page (HTML
+ CSS + images) that displays two buttons and a
hyperlink:
[OK]
[Cancel]
View More Information
The buttons and the hyperlink should look like in the
Photoshop file.
47](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9-photoshop-120524085328-phpapp02/85/Adobe-Photoshop-47-320.jpg)
