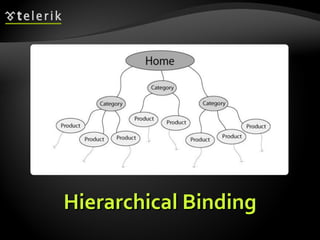
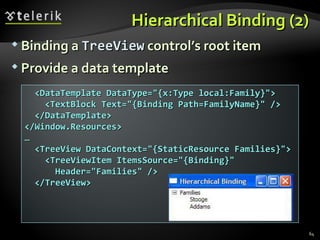
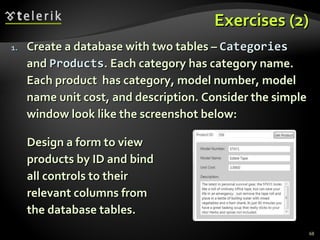
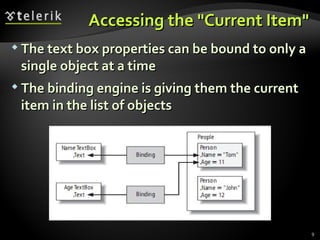
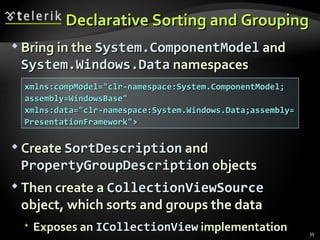
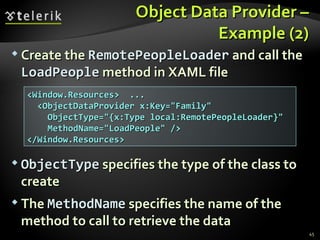
The document provides an overview of complex data binding in WPF, including binding to collections, accessing selected items, lookup bindings, data templates, sorting, filtering, grouping, object data providers, relational data binding, and XML data binding. Key points covered include binding list controls, using display and value member paths, collection views for navigation and filtering, and declarative and programmatic approaches to sorting and grouping data.




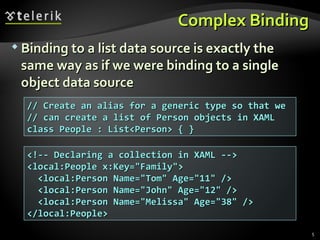













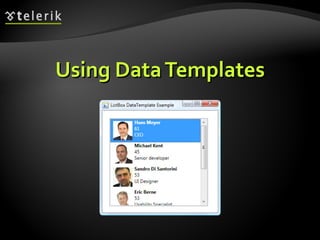




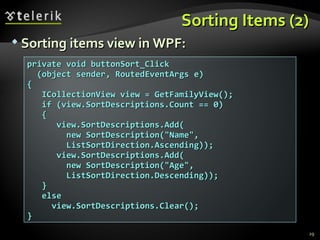


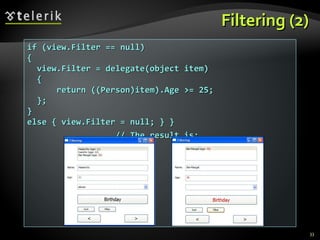

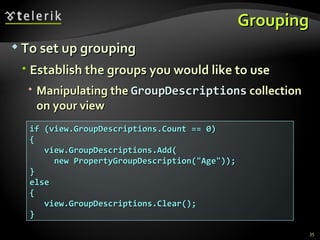
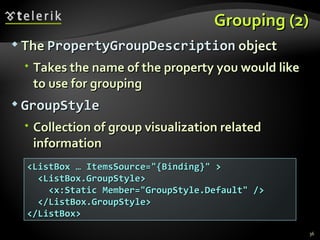










![XML Data Source Provider (4) person.SetAttribute("Age", (int.Parse( person.Attributes["Age"].Value) + 1).ToString( )); MessageBox.Show( string.Format("Happy Birthday, {0}, age {1}!", person.Attributes["Name"].Value, person.Attributes["Age"].Value), "Birthday"); } … void groupButton_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) { ICollectionView view = GetFamilyView( ); if( view.GroupDescriptions.Count == 0 ) { view.GroupDescriptions.Add(new PropertyGroupDescription("@Age")); } else { view.GroupDescriptions.Clear(); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7-binding-lists-120225044116-phpapp01/85/Complex-Data-Binding-53-320.jpg)