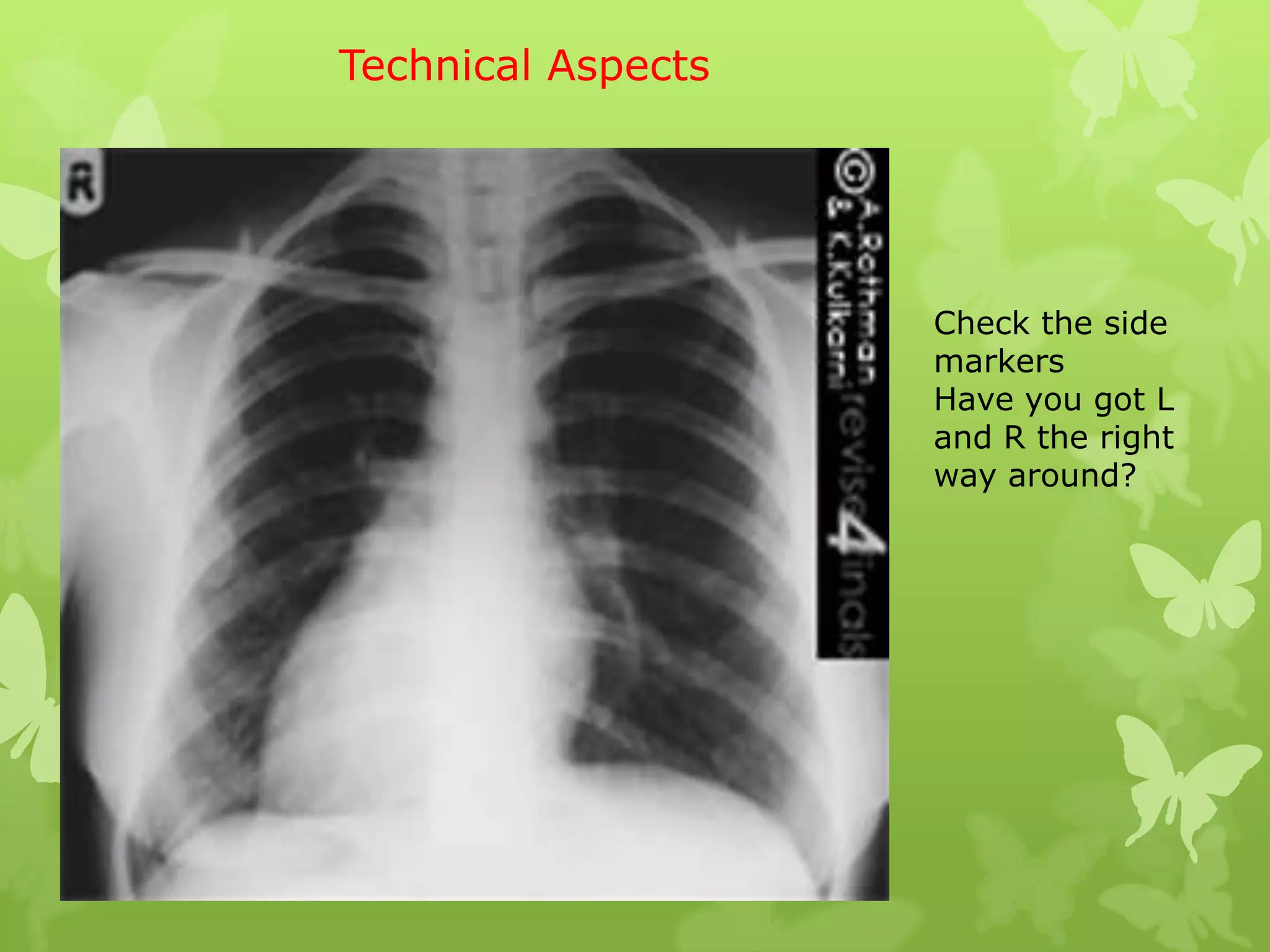
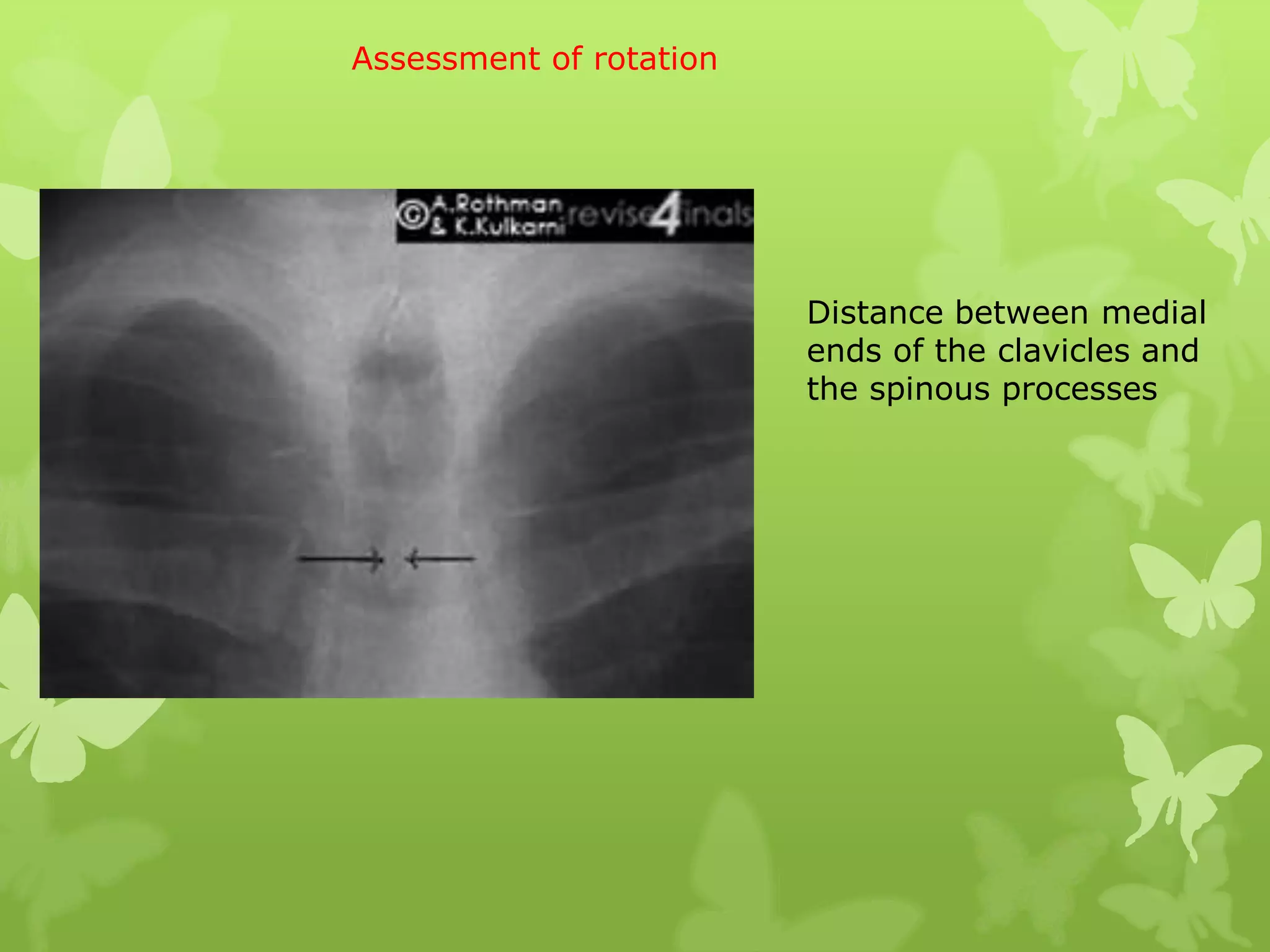
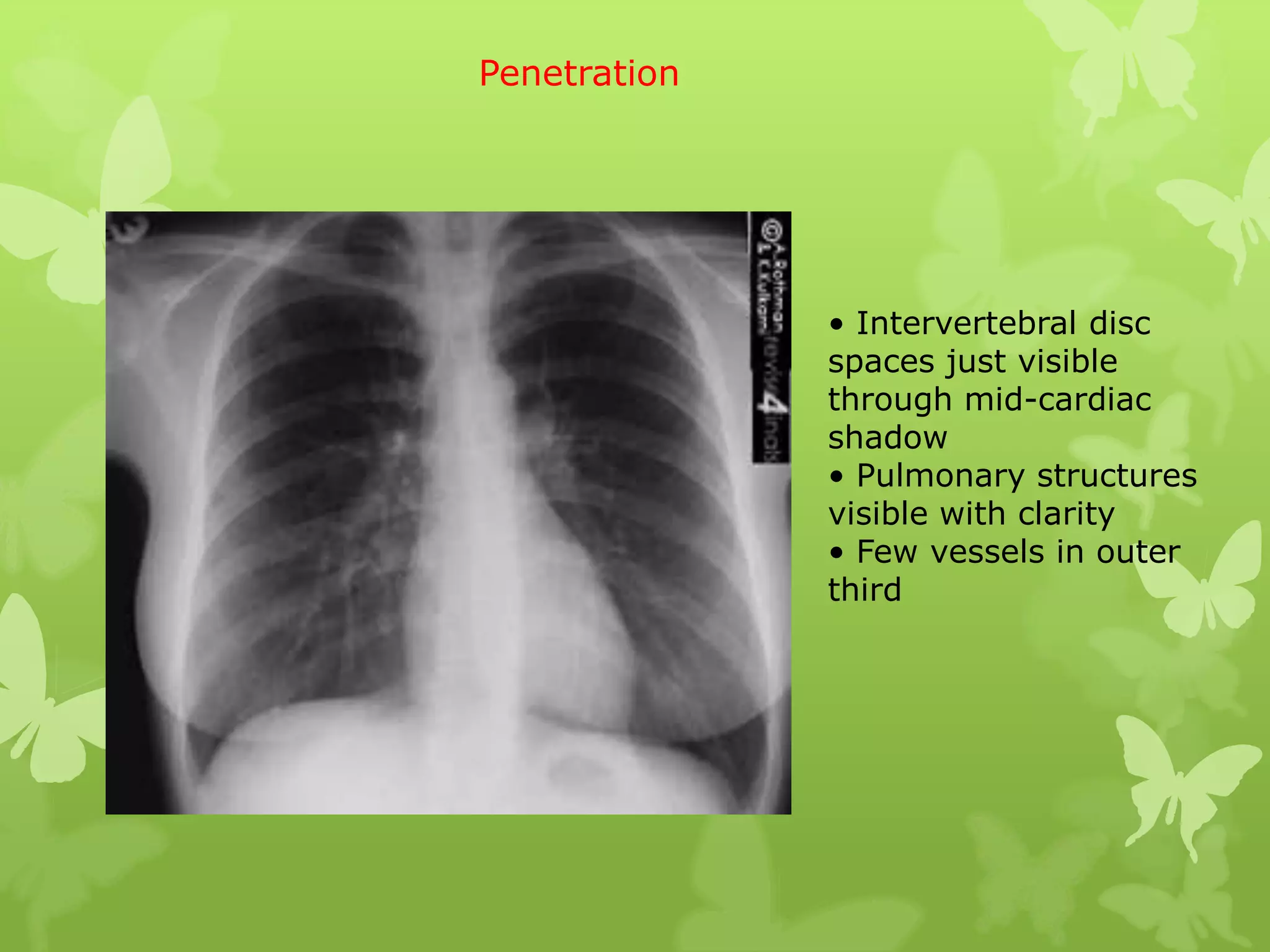
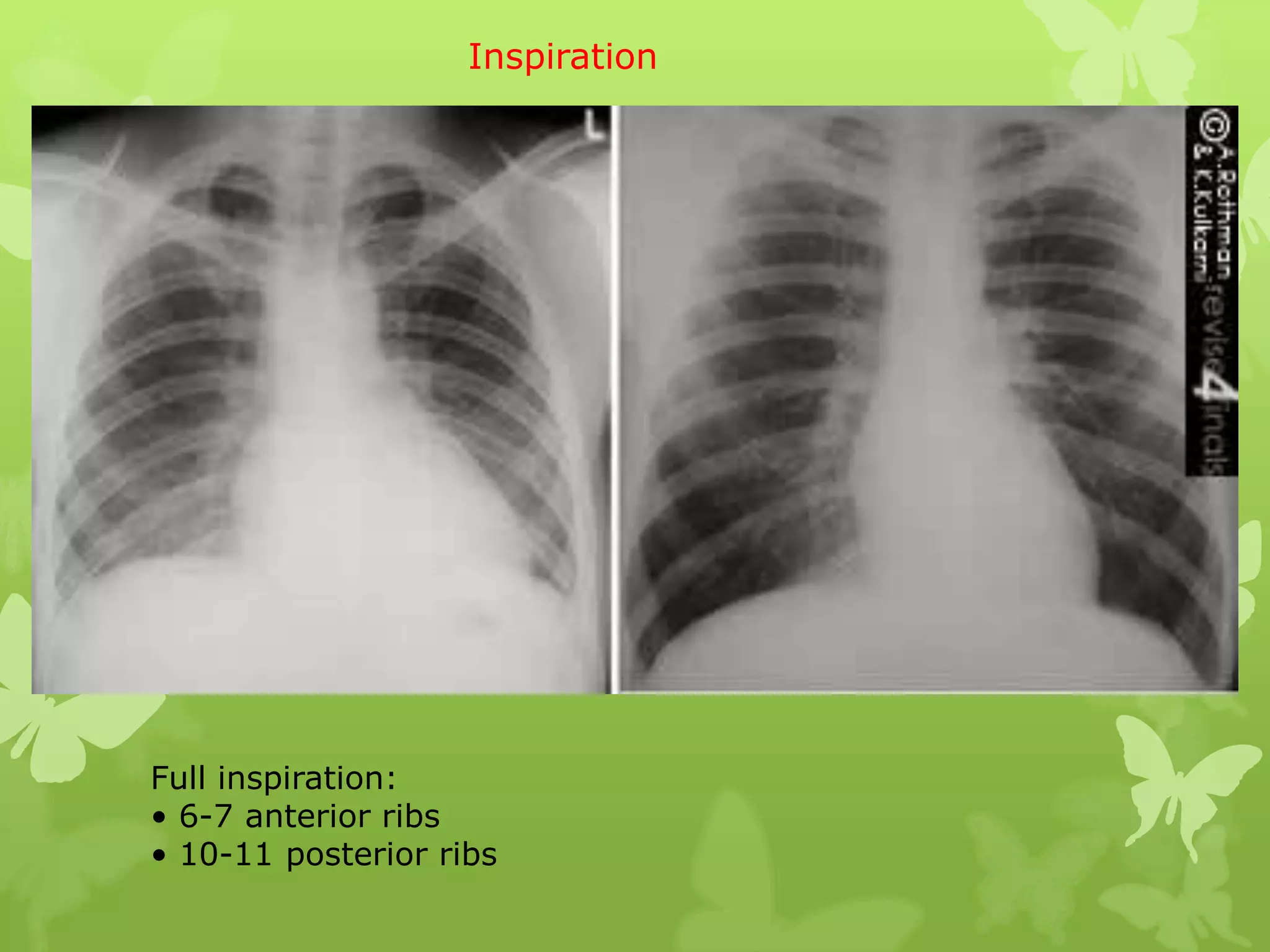
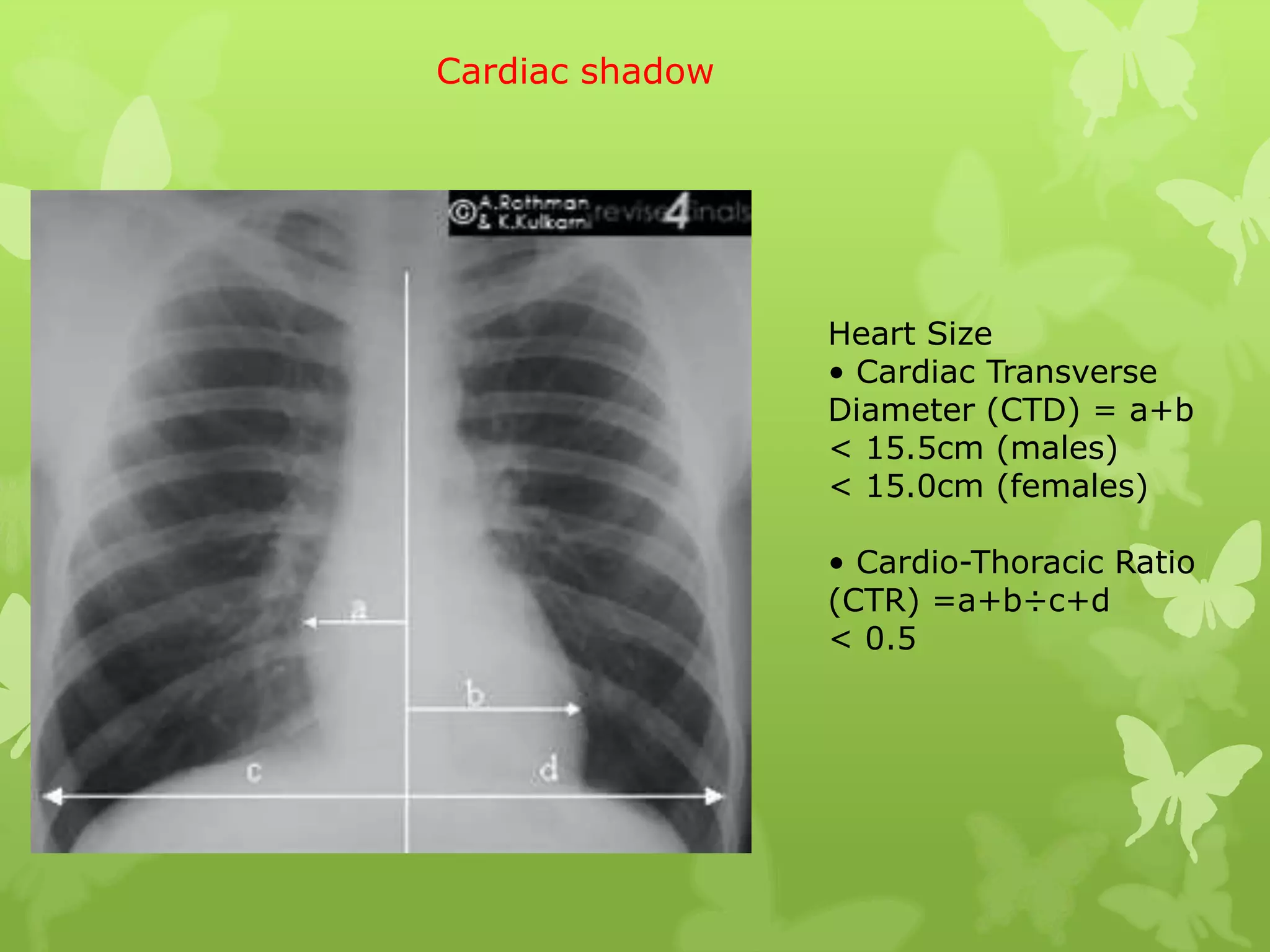
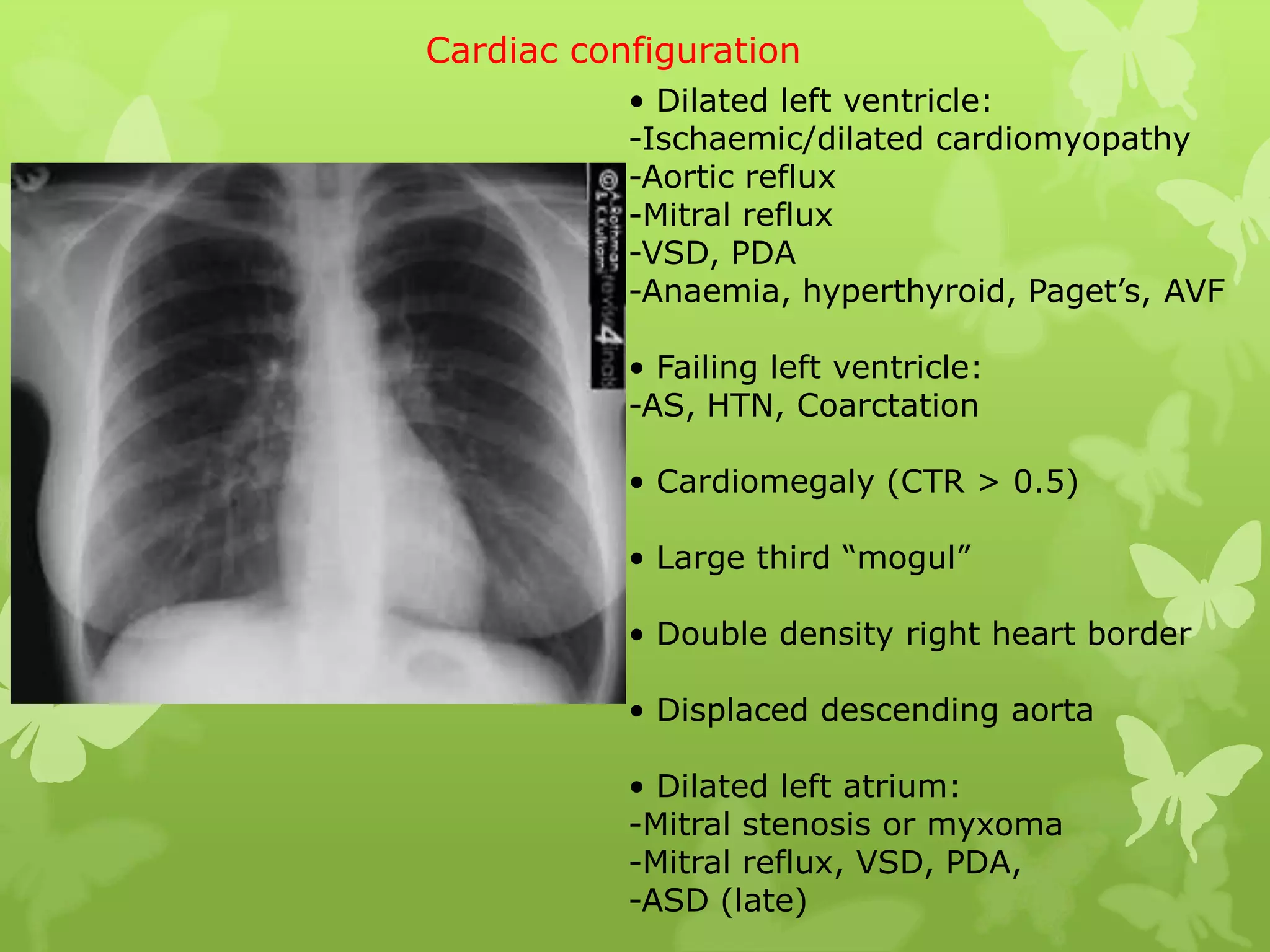
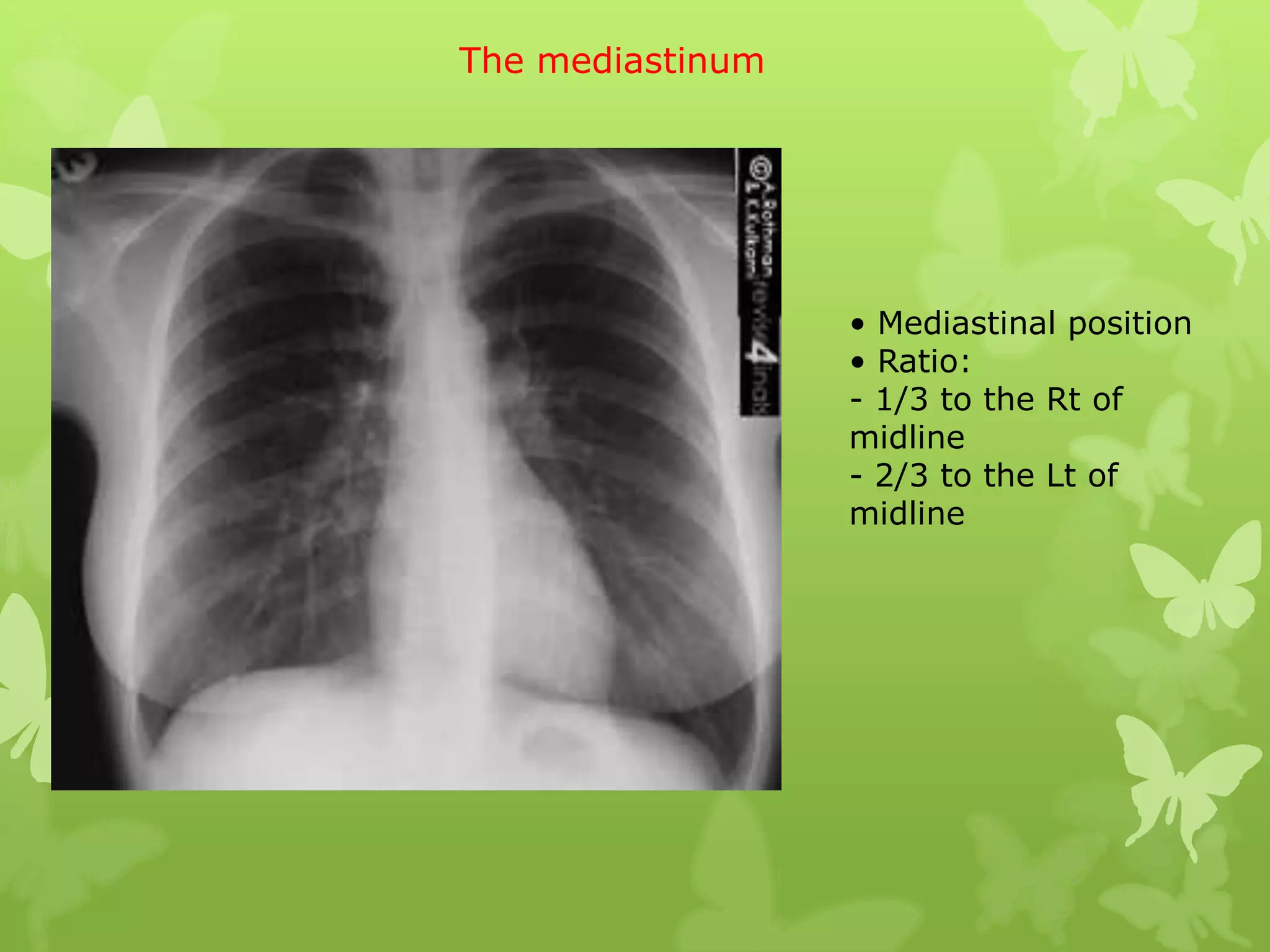
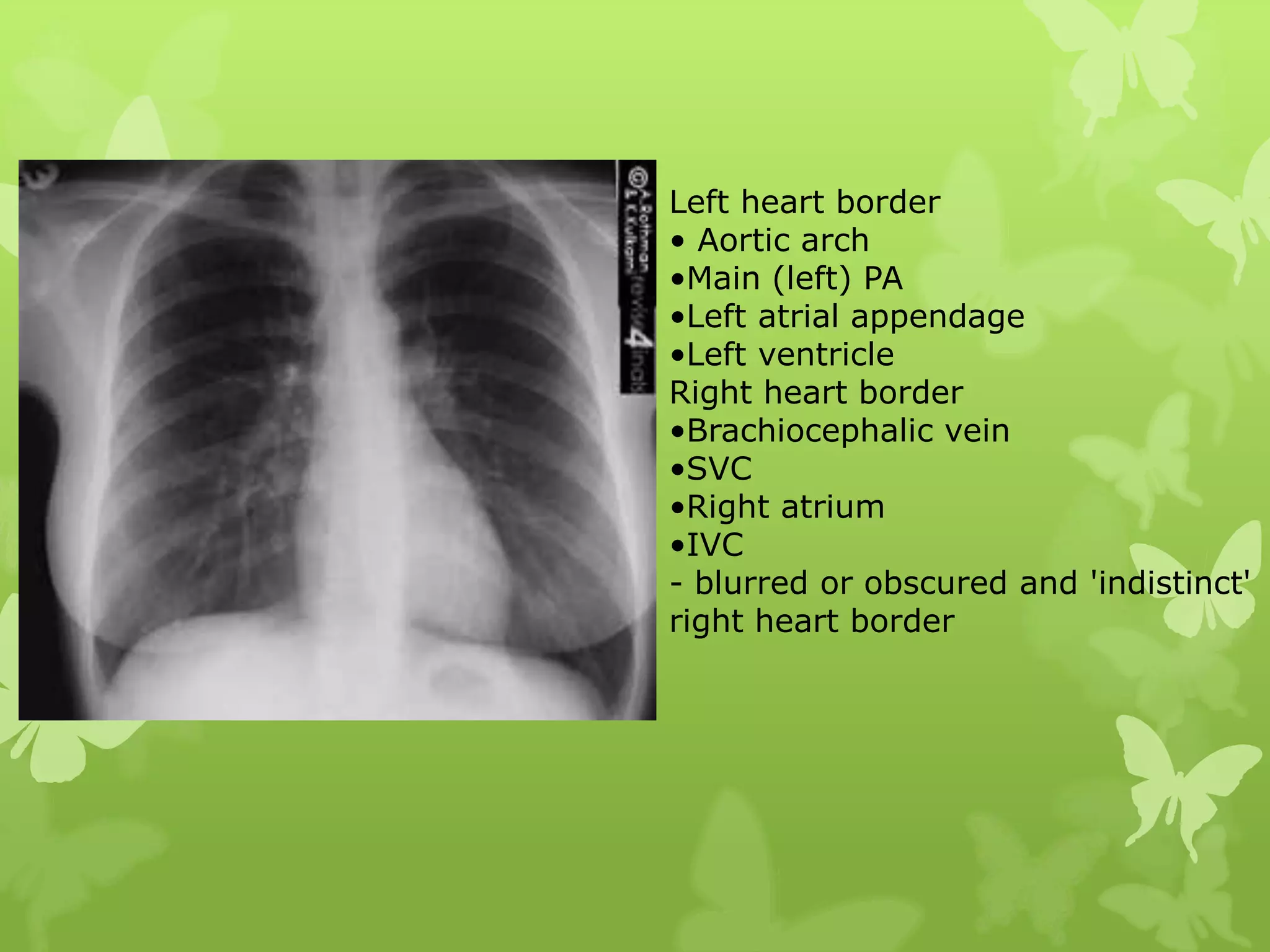
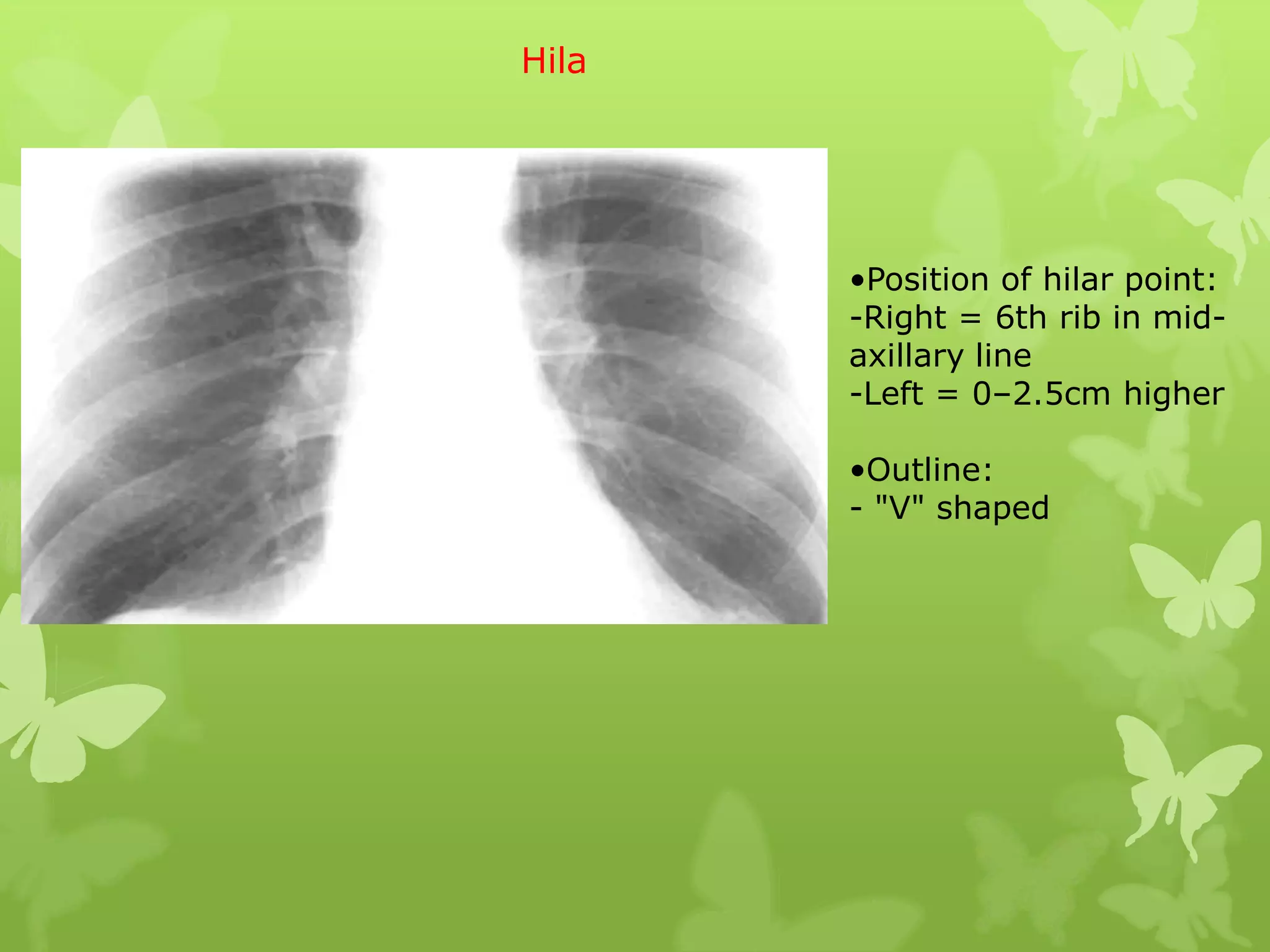
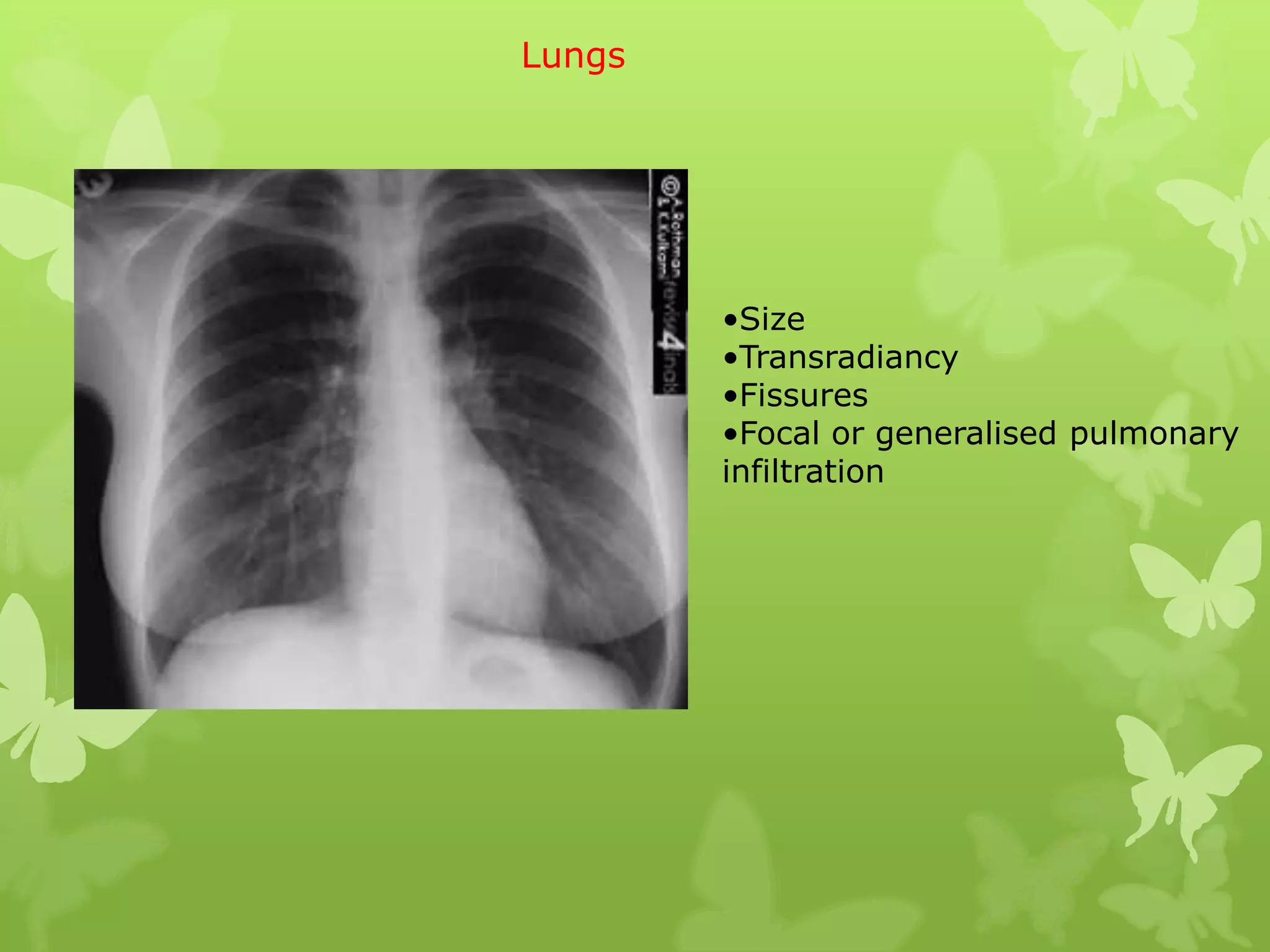
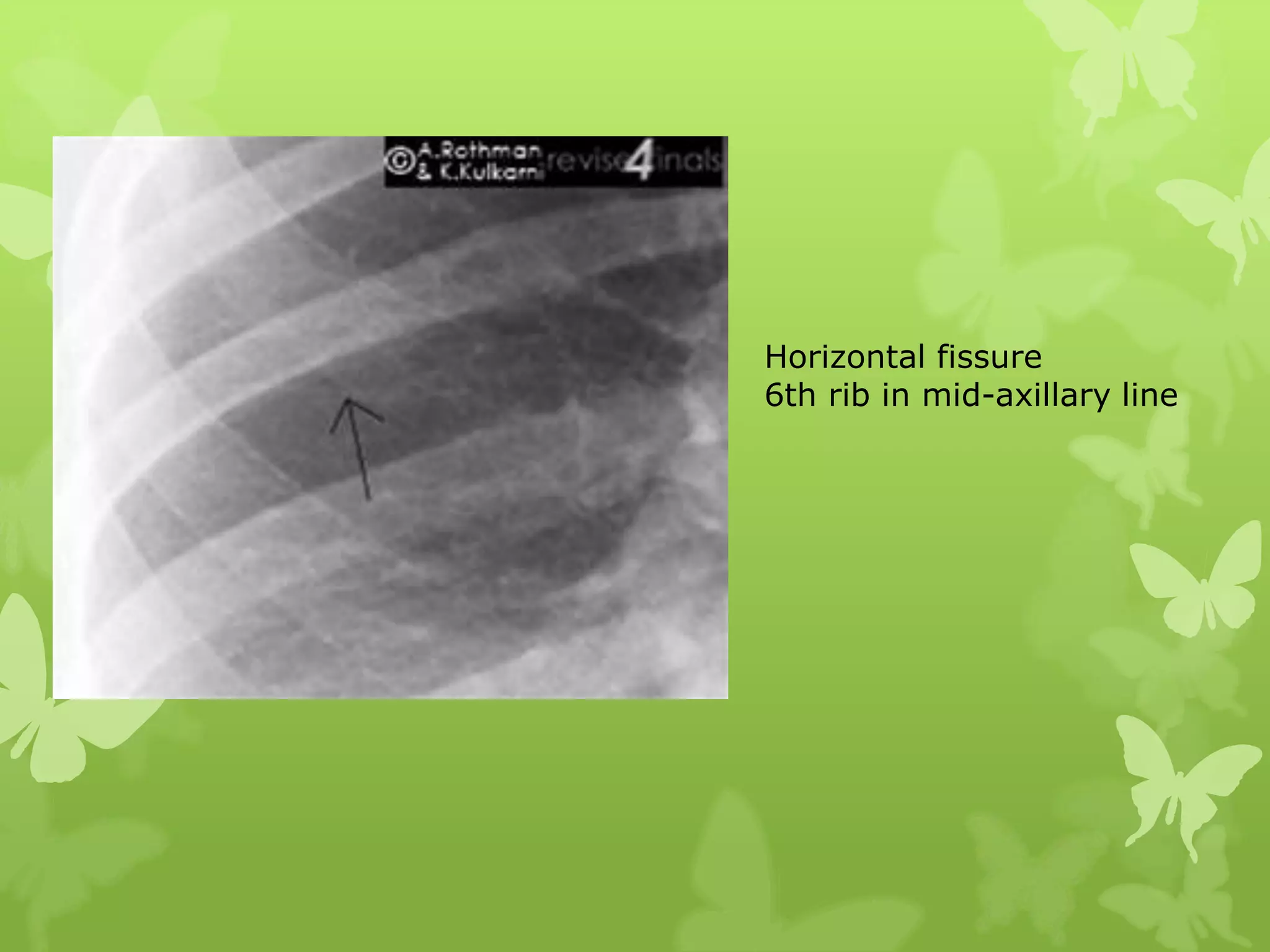
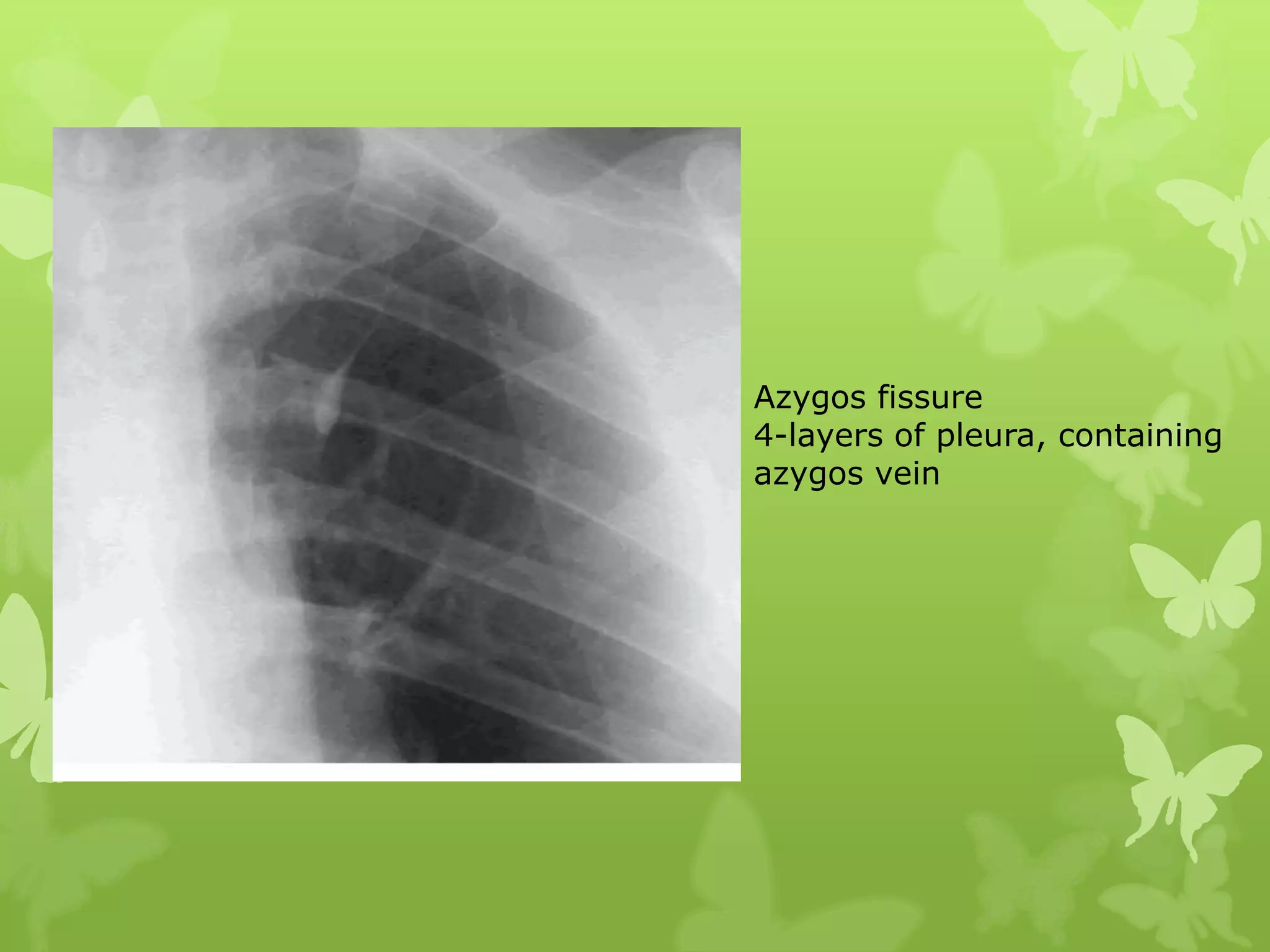
This document provides guidance on interpreting a chest X-ray by reviewing the key anatomical structures and abnormalities to examine, including the cardiac shadow, mediastinum, hila, lungs, pleural spaces, bones, and soft tissues. The technical aspects of the image such as patient information, projection, inspiration, and penetration should first be checked. Common findings for each area are then described.