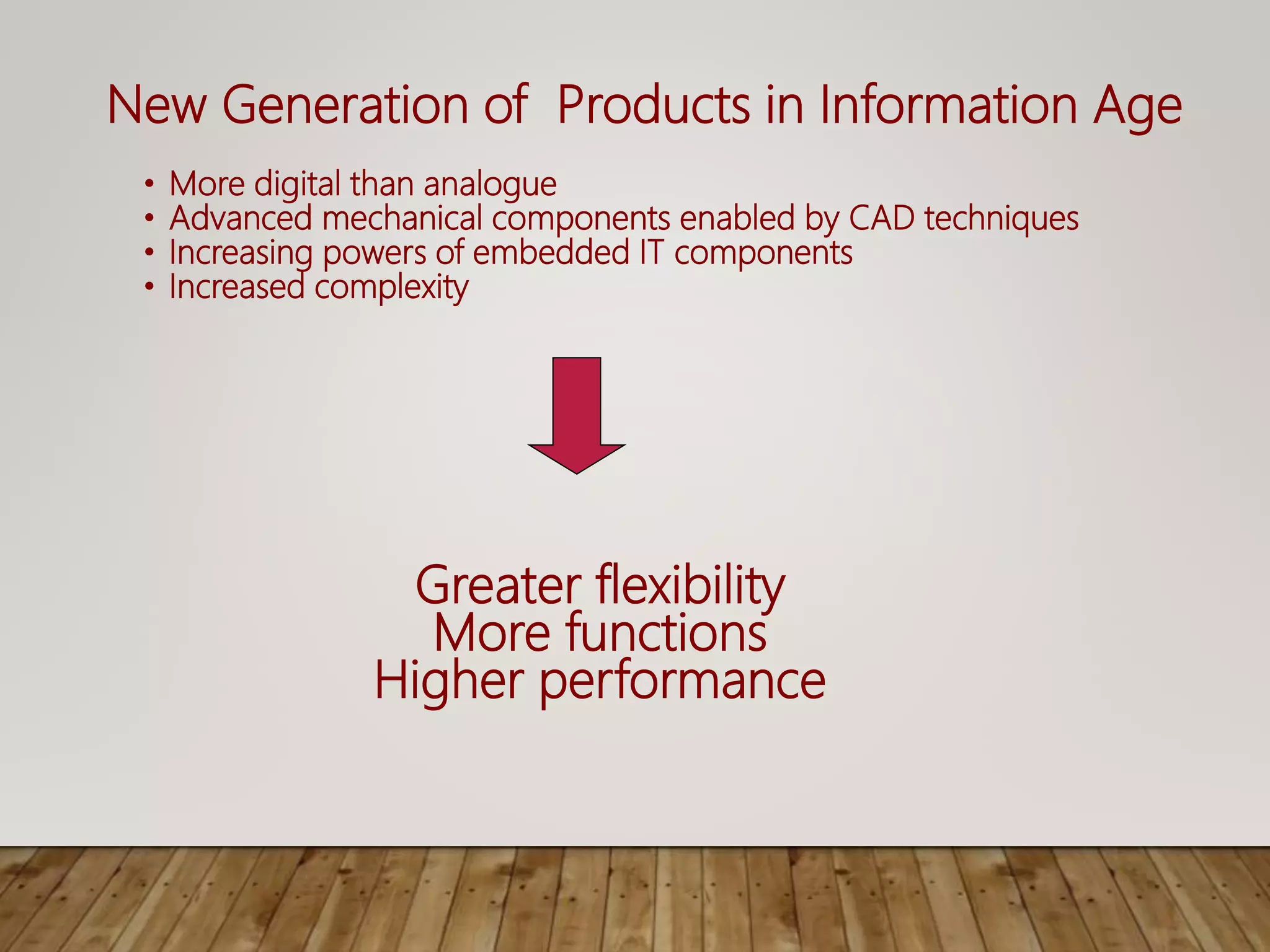
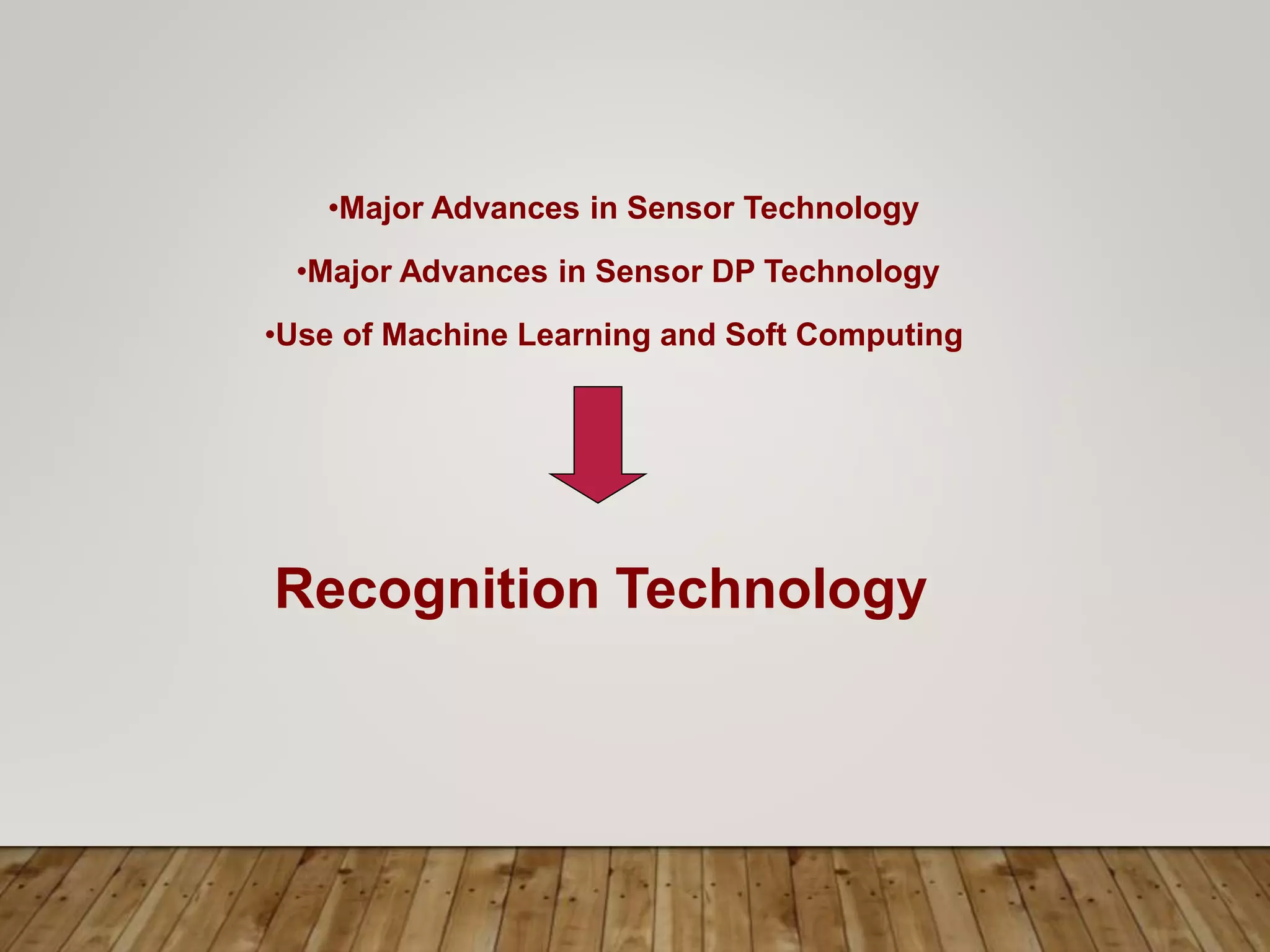
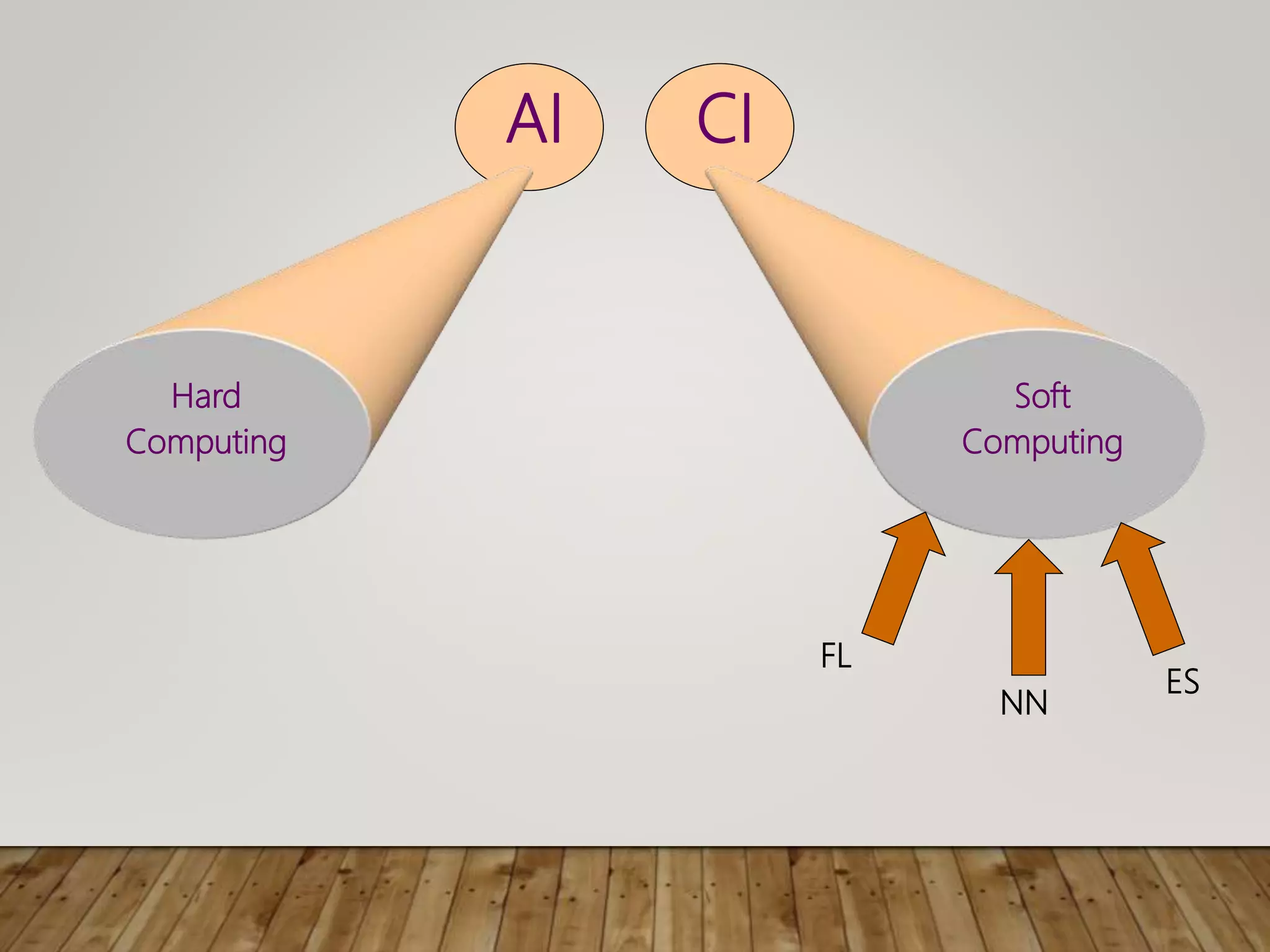
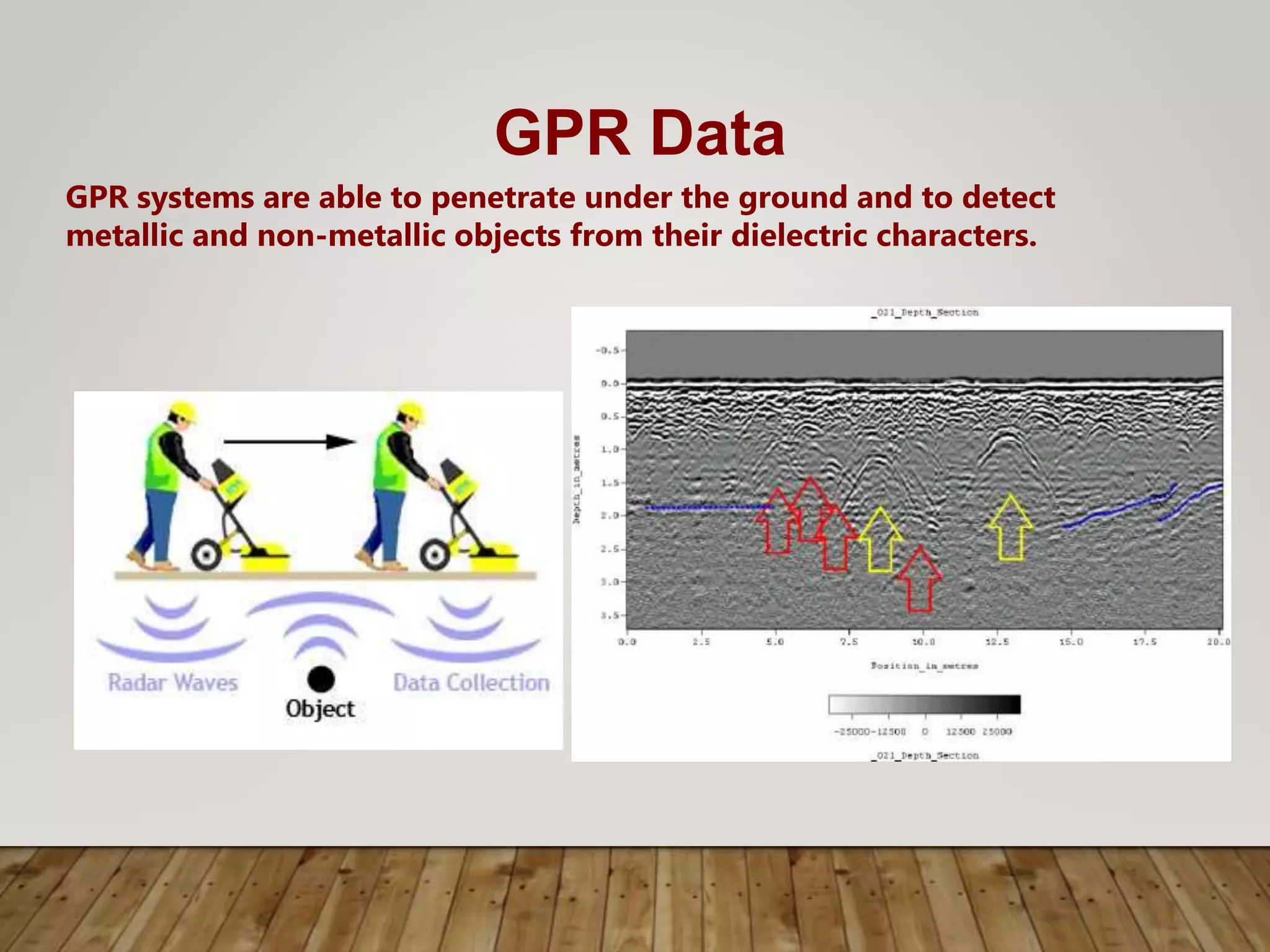
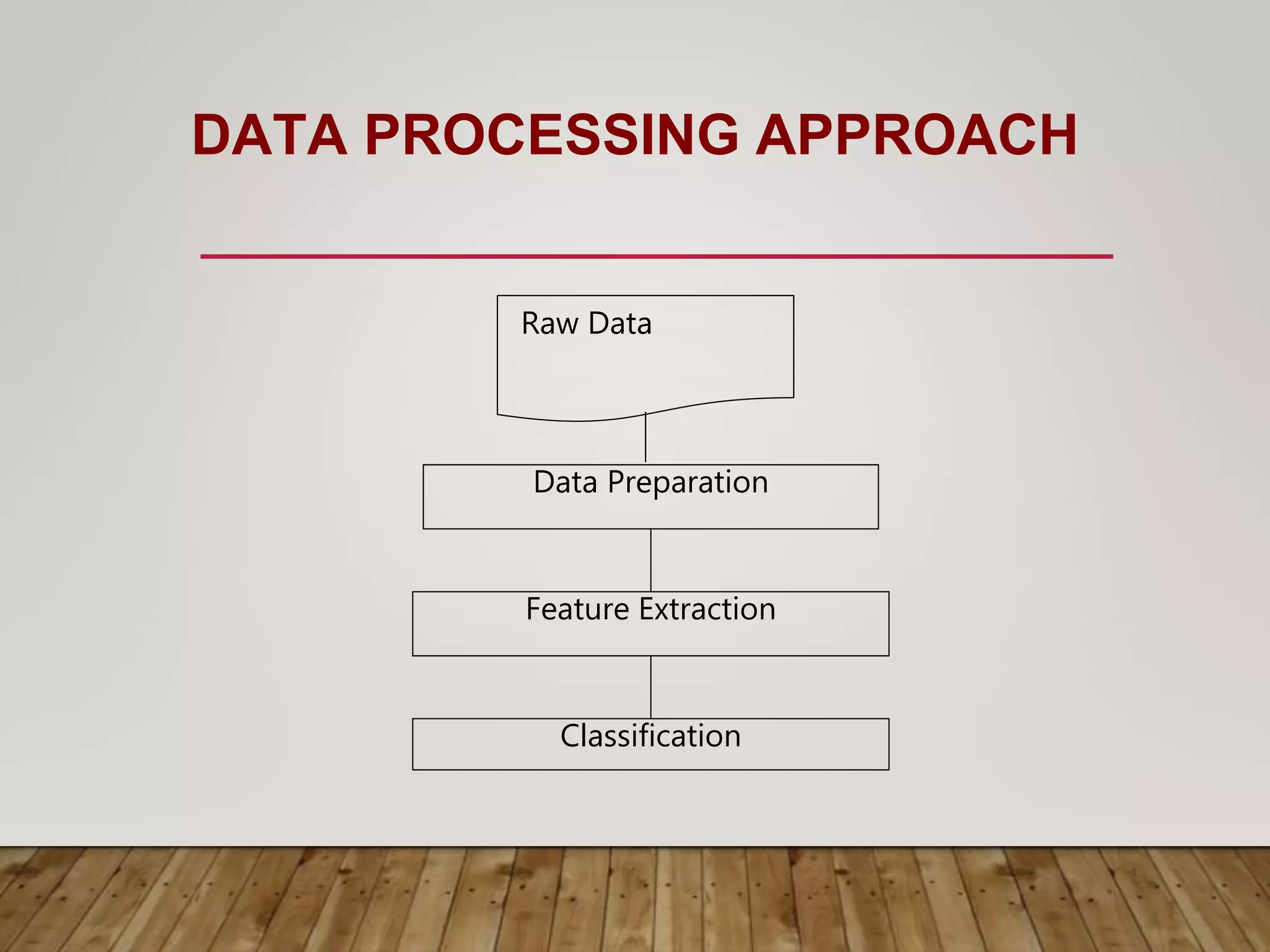
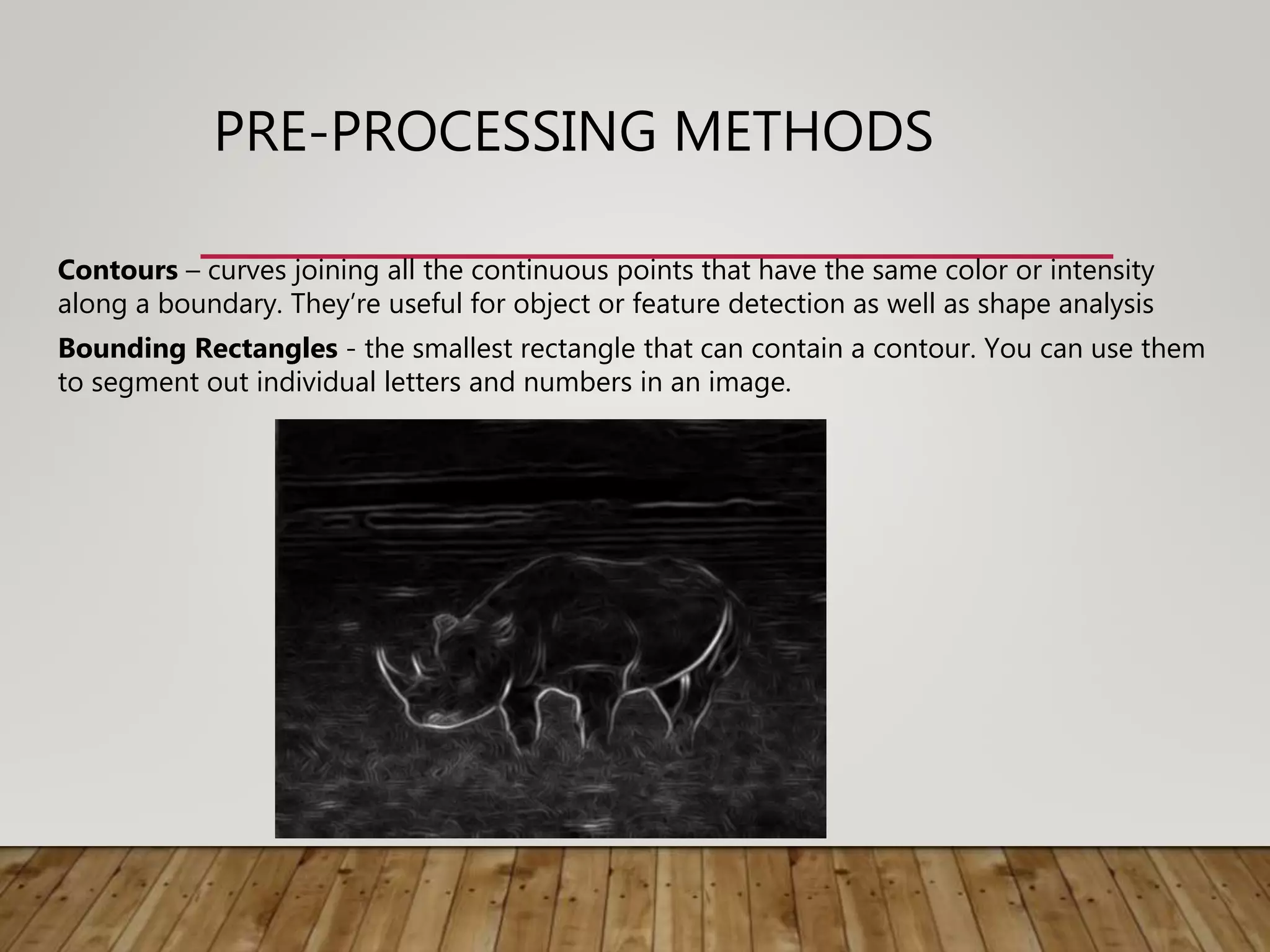
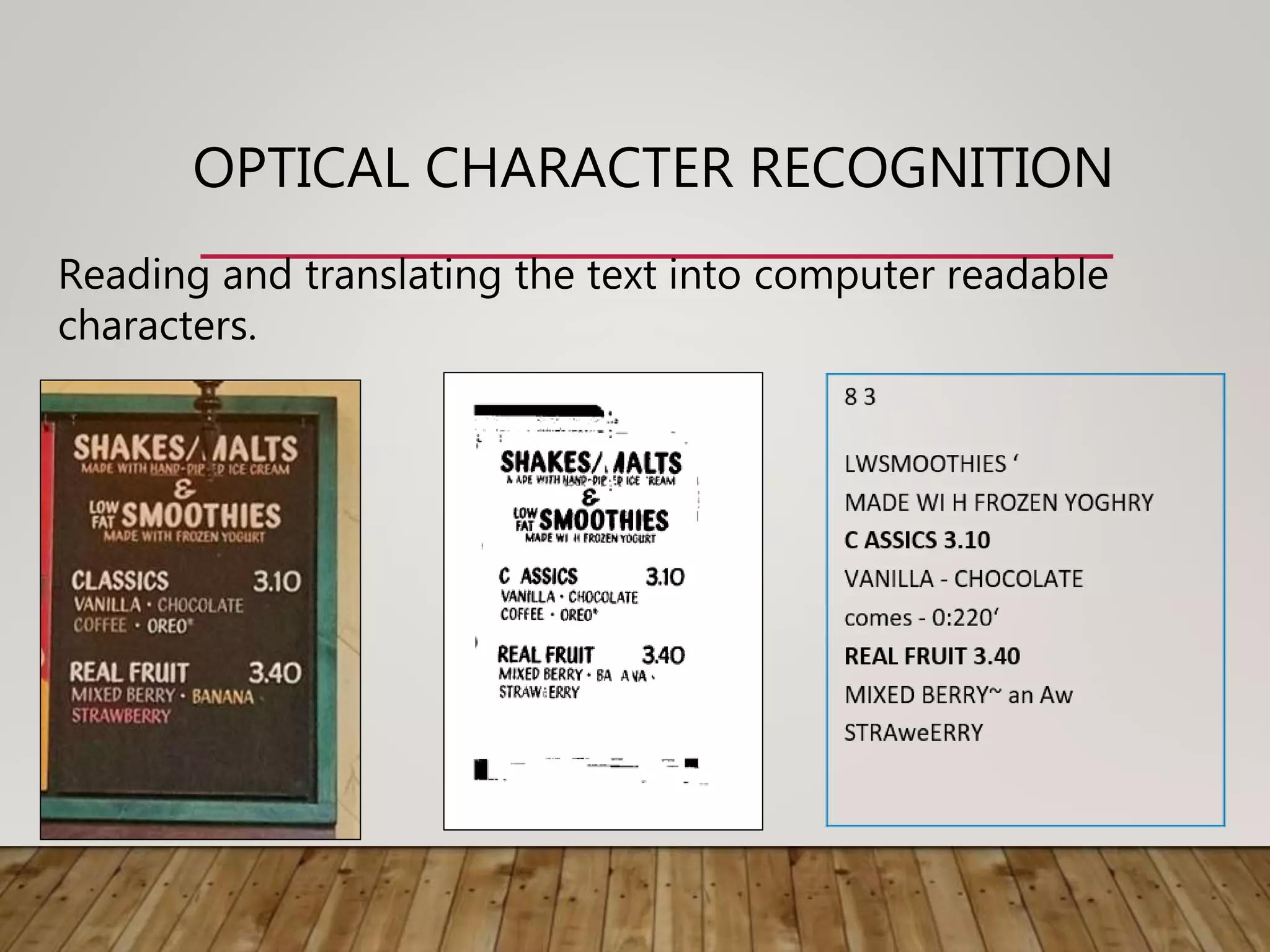
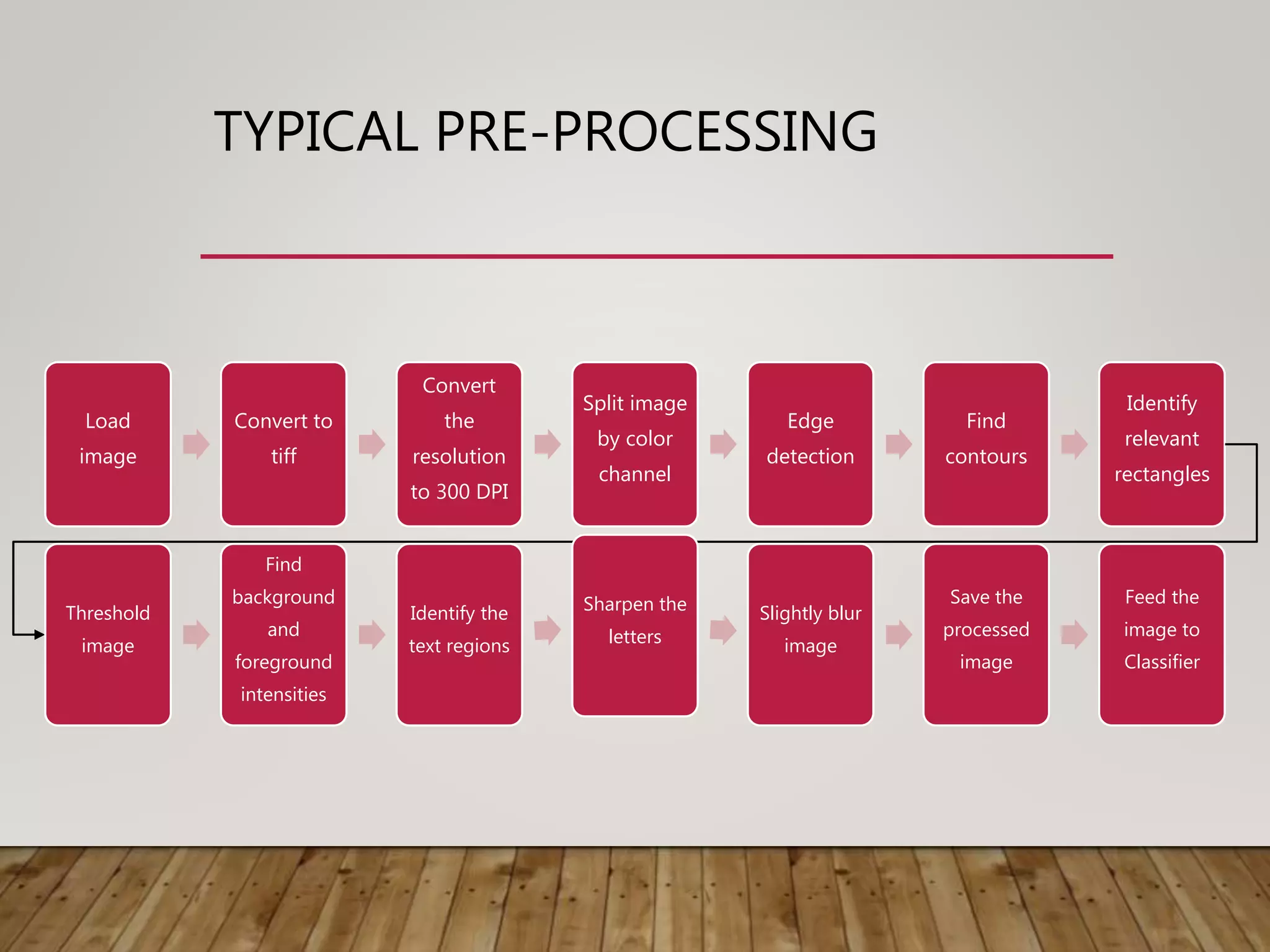
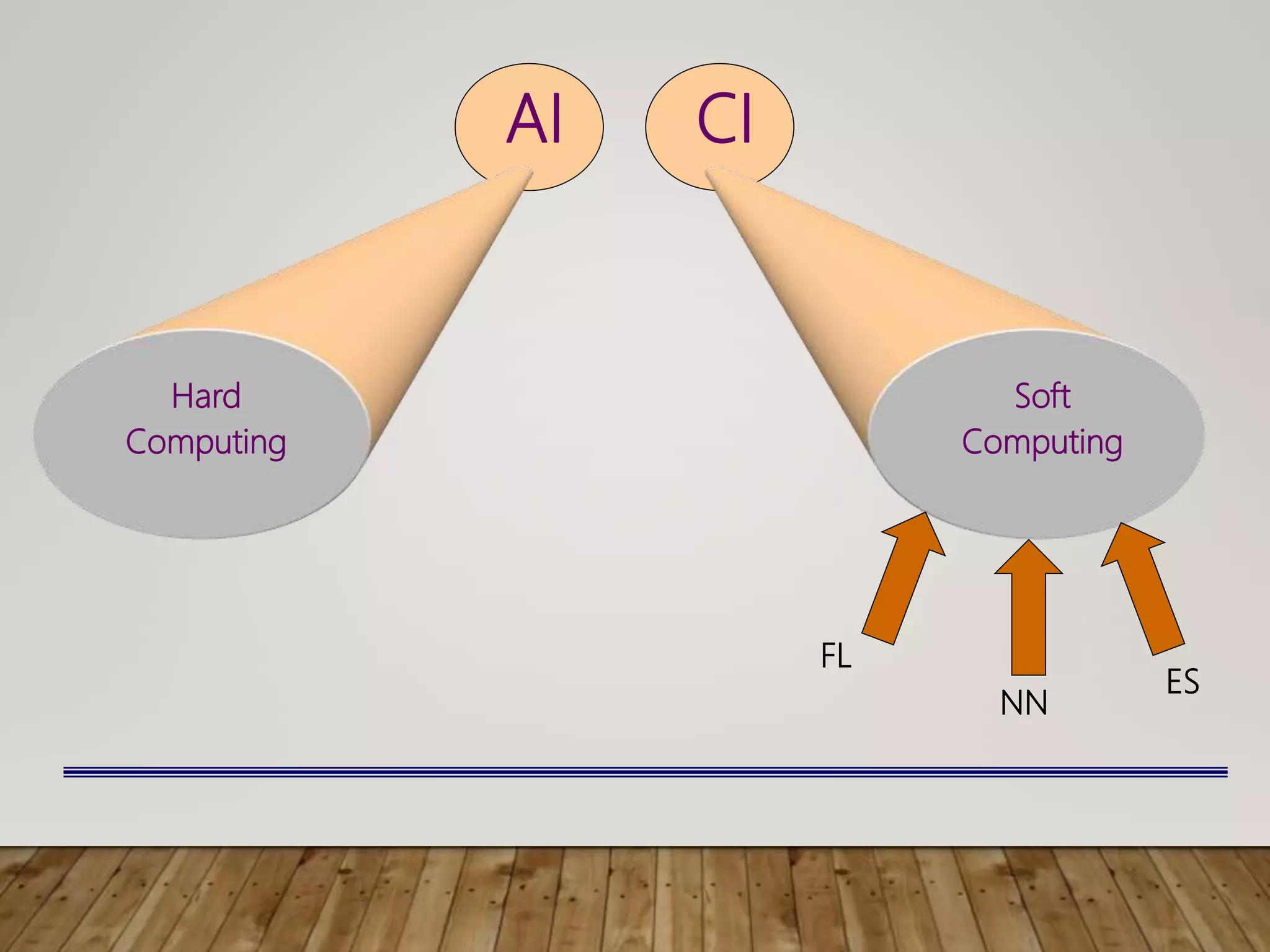
This document discusses image processing and big data initiatives. It describes how data can be used to create either useful applications or dangerous weapons. It also discusses the erosion of boundaries between different fields due to information technologies. New products are increasingly digital and complex due to advances in areas like sensors, machine learning, and computer technologies. Intelligent recognition technologies can now identify people from iris scans or detect diseases from molecular breath analysis. Both artificial intelligence and computational intelligence are discussed in the context of using data and algorithms to enable adaptive and intelligent systems. Various methods for preprocessing and classifying data are also outlined.