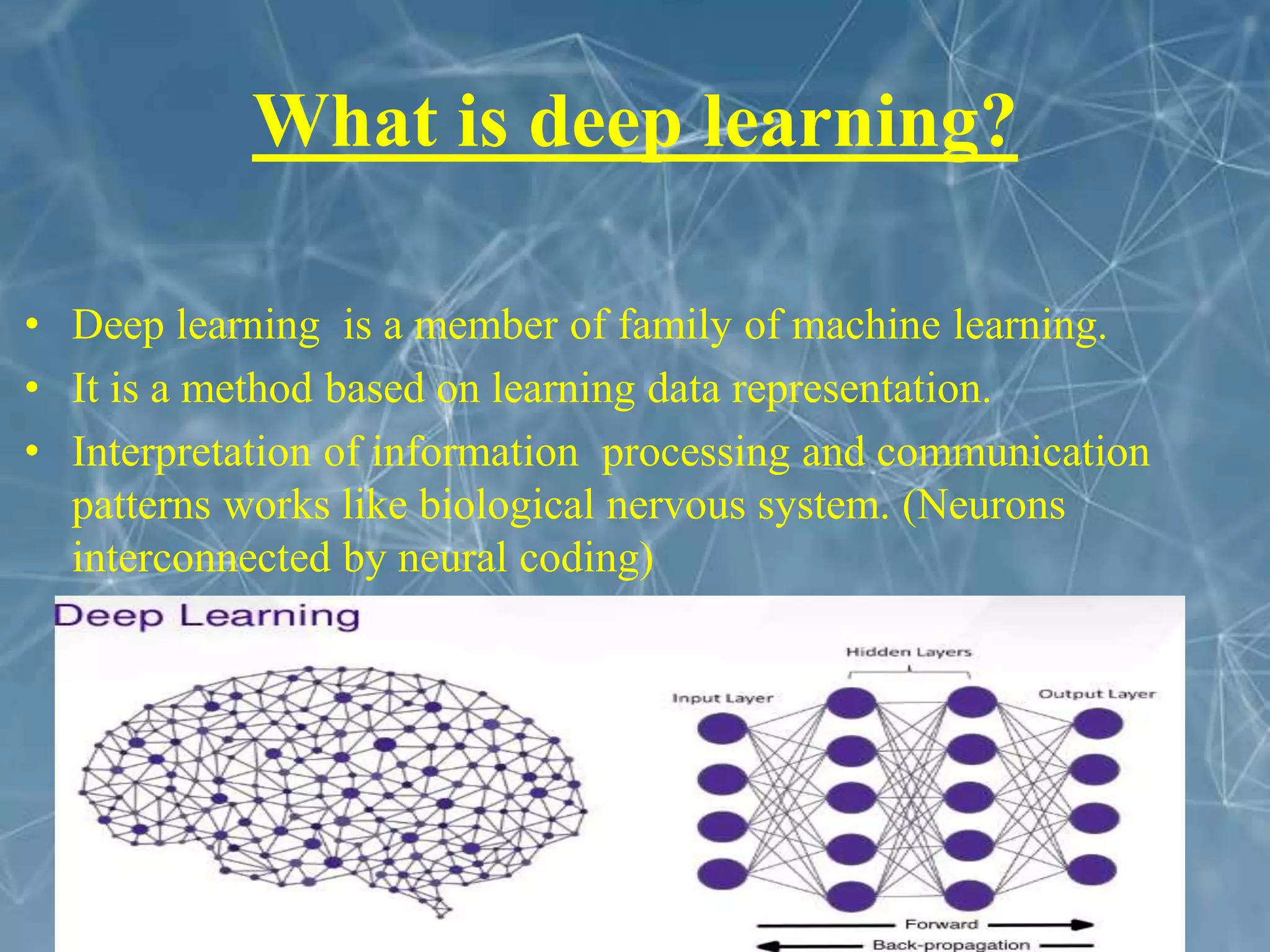
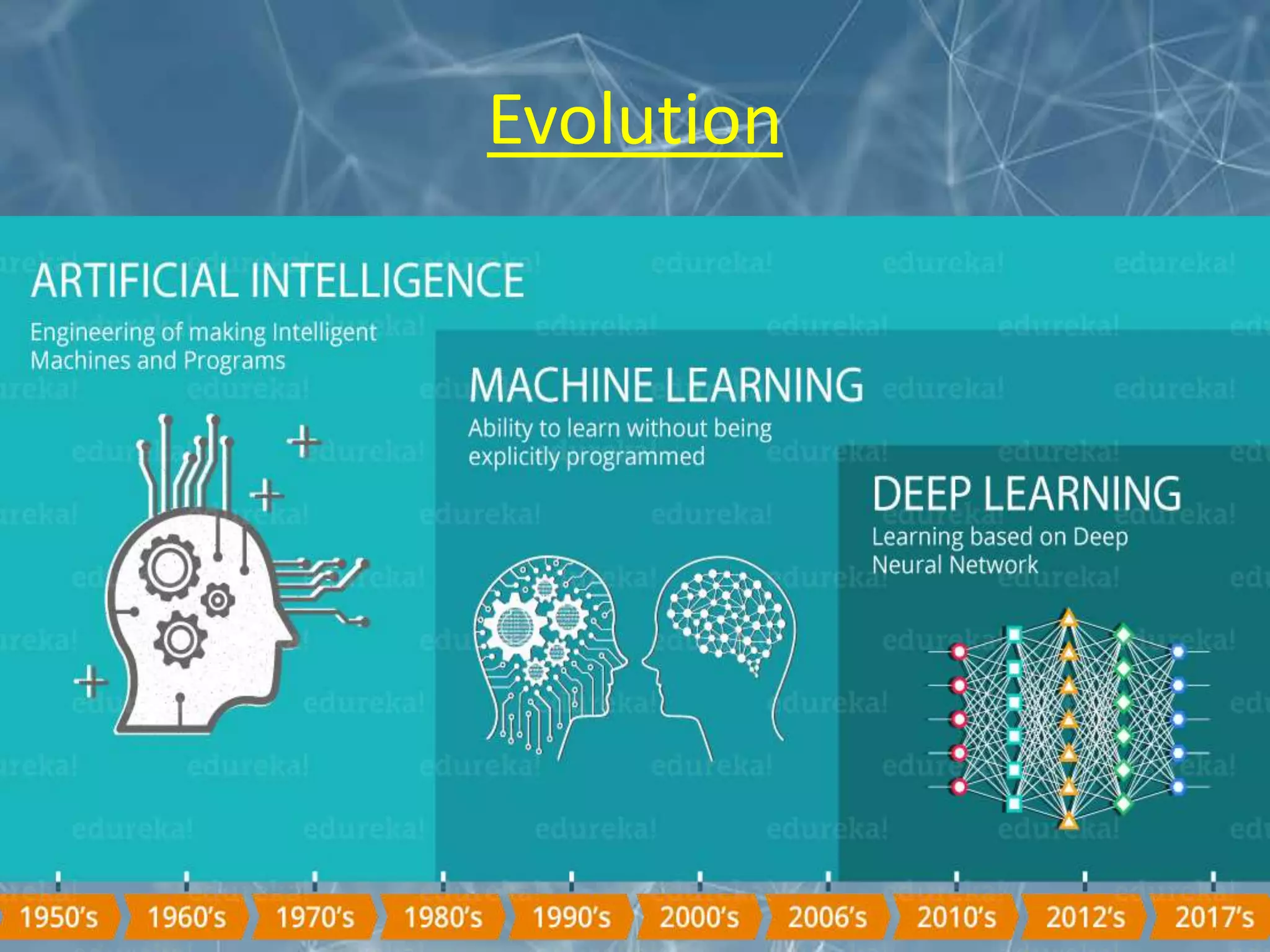
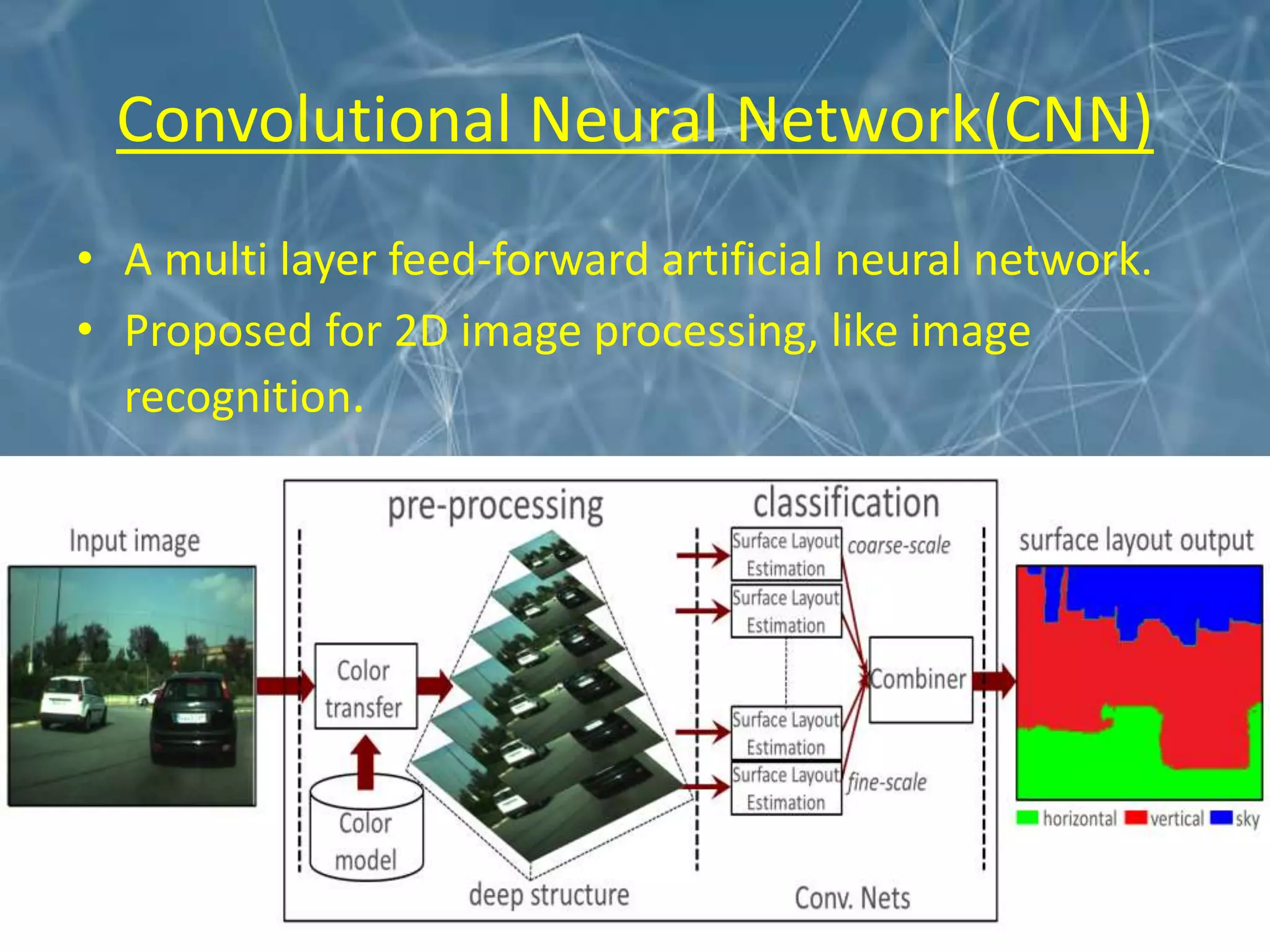
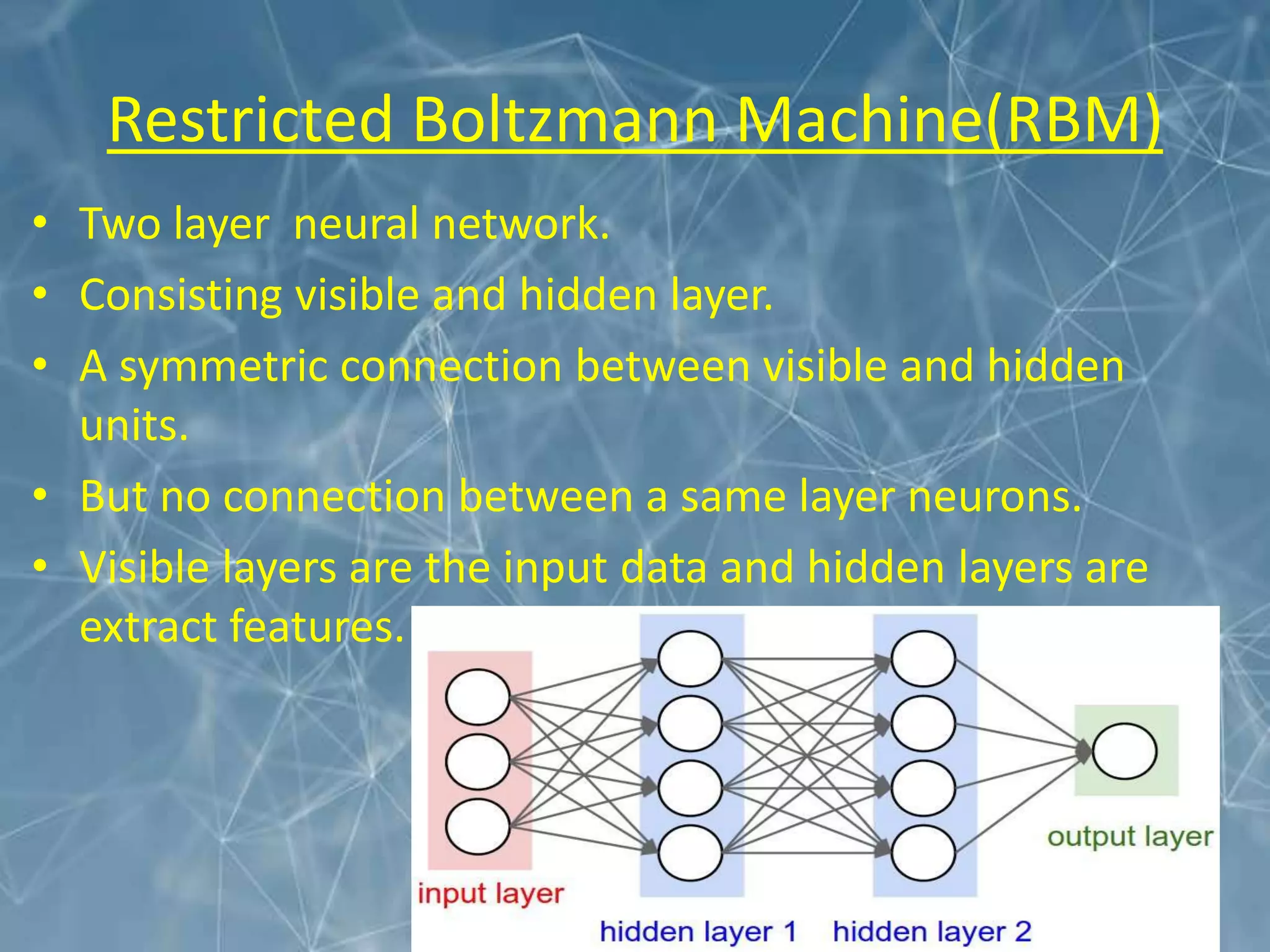
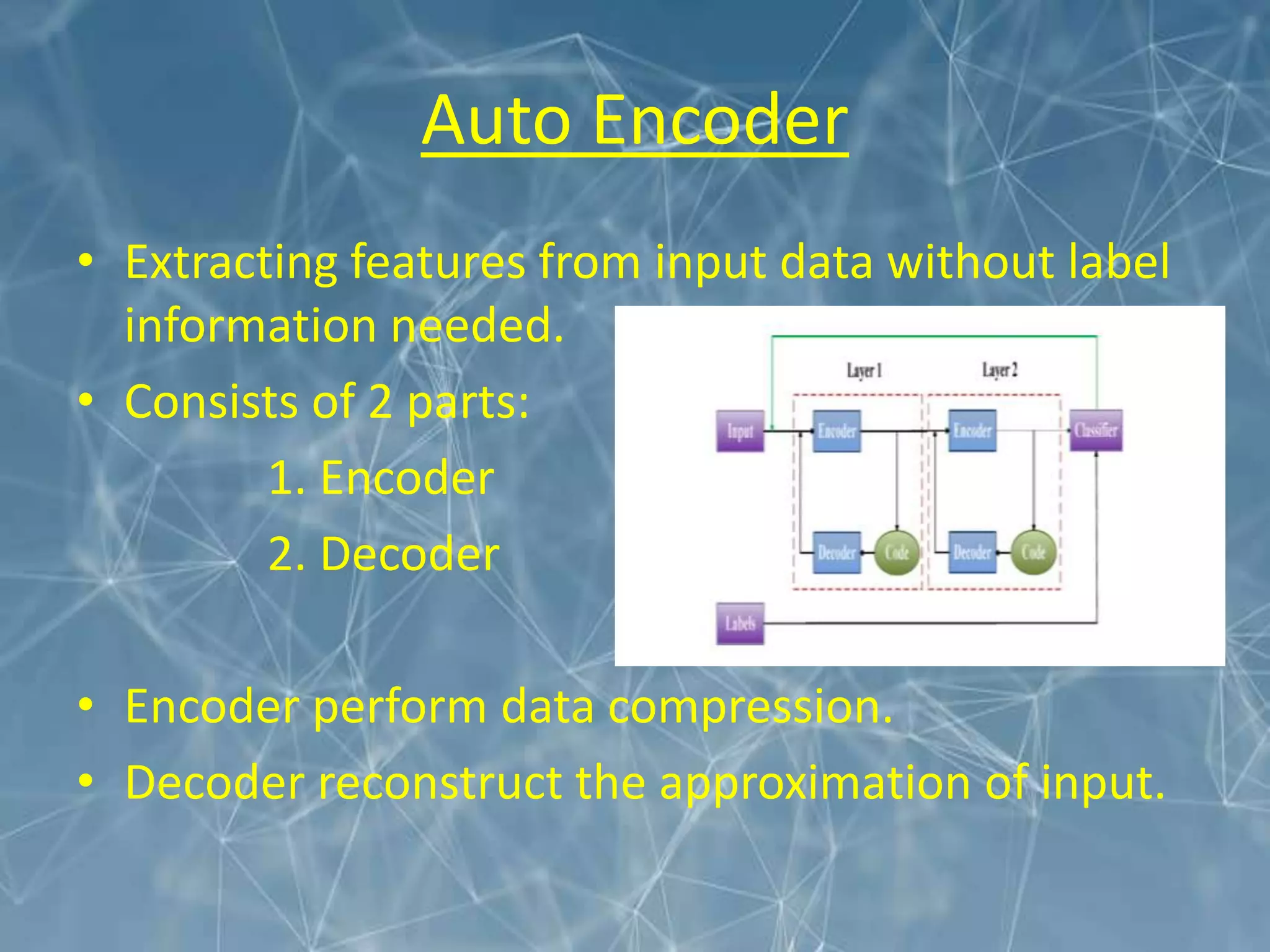
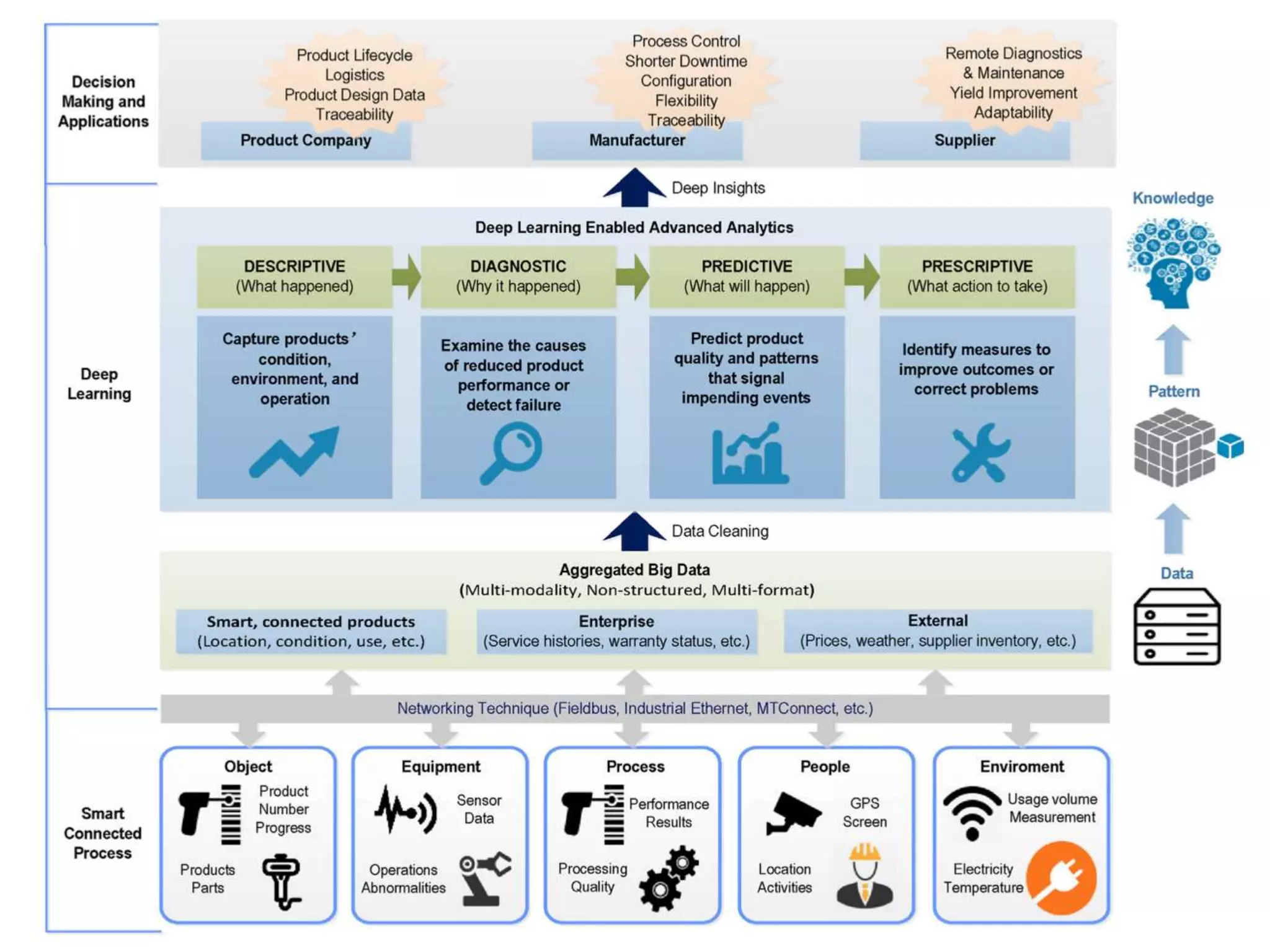
This document discusses the application of deep learning techniques for smart manufacturing. It begins with an overview that outlines key areas like introduction, evolution, neural network architecture, artificial neural networks, applications in smart manufacturing, advantages, and disadvantages. It then defines smart manufacturing as employing computer control and high adaptability during the manufacturing process. Deep learning is described as a machine learning method based on learning data representations through neural network-inspired architectures. Various deep learning architectures are discussed for smart manufacturing applications, including convolutional neural networks, recurrent neural networks, autoencoders, and restricted Boltzmann machines. Specific applications of deep learning discussed include product quality inspection using computer vision, fault diagnosis, design and performance optimization, material handling, and forecasting. The document













![References
[1] Deep learning for smart manufacturing: Methods and
applications Jinjiang Wanga,Yulin Maa, Laibin Zhanga, Robert X.
Gao b, Dazhong Wu.
[2] Hu T, Li P, Zhang C, Liu R. Design and application of a real-time
industrial Ethernet protocol under Linux using RTAI. Int J Comput
Integr Manuf 2013;26(5):429–39.
[3] Ye Y, Hu T, Zhang C, Luo W. Design and development of a CNC
machining process knowledge base using cloud technology.
Int J Adv Manuf Technol 2016:1–13.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deeplearningforsmartmanufacturing-180508042233/75/Deep-learning-for-smart-manufacturing-22-2048.jpg)

